Abstract
Some numerical models of various degrees of complexity for studying river atmosphere heat exchange are discussed. Also described are issues related to obtaining the basic meteorological and the required hydrological data. As meteorological and hydrological parameters vary strongly within one year and from year to year, a large amount of information has to be collected and analysed for obtaining a representative picture.
The necessary effort depends clearly on the application. It is much larger, when the absolute temperature and the transient response have to be calculated, than when only the average temperature increase due to anthropogenic heat discharges is of interest.
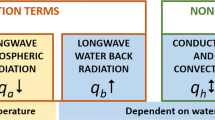
Results for the exchange of radiative, latent and sensible heat between atmosphere and water surface including the overall exchange coefficient are given for 21 years, in detail for Basel and summarised for 8 locations along the Rhein. Yearly averages vary little, monthly averages show the expected seasonal variation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abwärmekommission, 1983: ‘Abwärmekommission, Auswirkungen, Verminderung, Nutzung’. Zusammenfassender Bericht űber die Arbeit der Abwärmekommission 1974–1982. Erich Schmidt Verlag, Berlin 1983.
Becker, A. 1965: ‘Die Belastbarkeit der Binnengewässer und die bei Durchflusskűhlung eintretende Nutzungsverluste’. Besondere Mitteilungen zum Gewässeerkundlichen Jahrbuch der DDR, Nr. 2.
Gilbert, A., Gras, H. and Roult, D. 1986: ‘Numerical Computation of Natural River Temperature’. International Conference on Water Quality Modelling in the Inland Natural Environment, Bournemouth, England 10–13 June 1986.
Hollard, J.-M. 1986: ‘Simulation du comportement thermique des cours d'eau. Application du bassin du Rhin’. Eidg. Institut fűr Reaktorforschung, Wűrenlingen, Switzerland.
Klein, P. and Momal, D. 1979: ‘Méthode d'estimation du rayonnement solaire, sa mise en oeuvre numérique'. Electricité de France’, Division Echauffement et pollution des eaux, Ecologie, Chatou, France.
Kuhn, W. 1978: ‘Aus Wärmehaushault und Klimadaten berechnete Verdunstung des Zűrichsees’. Vierteljahresschrift der Naturforschenden Gesellschaft in Zűrich, Jahrgang 123, Heft 4, 261–283.
Poulin, M. 1980: ‘Modèlisation du comportement thermique des cours d'eau, application au Rhin’. Thèse de Diplôme, Paris, France.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Joss, J., Resele, G. Mathematical modelling of the heat exchange between a river and the atmosphere. Boundary-Layer Meteorol 41, 27–40 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00120429
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00120429