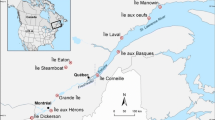
The potential use of retinoids and β-carotene as biomarkers in the eggs of the Great Blue Heron was investigated. In the spring of 1991, 65 eggs were collected from nine heronries (seven along the St Lawrence River and two reference sites). A method was specifically developed for the extraction and analysis of β-carotene and the retinoids in heron egg yolks by reversed-phase HPLC. When results were expressed either as the molar ratio of retinol: retinyl palmitate or as retinyl palmitate concentration, significant differences were found between colonies; however, retinyl palmitate concentration was deemed the better biomarker because it was not significantly influenced by embryonic stage of development. Retinyl palmitate concentrations in freshwater colonies were negatively related to PCB congeners Nos 105 and 118 as well as their TCDD-EQ values (p < 0.02, r 2=0.78). Egg tetrachloro-mono-ortho biphenyl concentrations were also negatively related to retinyl palmitate (p < 0.005, r 2=0.90). With the exception of the two mono-ortho co-planar congeners detected in the present study, the contamination levels found in heron eggs were well below those found for other bird species in the Great Lakes area and, so far, no detrimental effects have been reported in Great Blue Heron populations in Quebec. These results suggest that retinyl palmitate may be useful as a sensitive and non-invasive biomarker for monitoring organochlorine contaminant effects in the Great Blue Heron in freshwater sites.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ankley, G.T., Niemi, G.J., Lodge, K.B., Harris, H.J., Beaver, D.L., Tillitt, D.E., Schwartz, T.R., Giesy, J.P., Jones, P.D. and Hagley, C. (1993) Uptake of planar polychlorinated biphenyls and 2,3,7,8-substituted polychlorinated dibenzofurans and dibenzo-p-dioxins by birds nesting in the lower Fox River and Green Bay, Wisconsin, USA. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 24, 332–44.
Bélanger, L. and Tremblay, S. (1989) Québec: Ministère du Loisir, de la Chasse et de la Pêche, Direction générale de la Faune, Distribution et caractéristiques forestières des héronnières du Québec. 51 pages.
Bellward, G.D., Norstrom, R.J., Whitehead, P.E., Elliott, J.E., Bandiera, S.M., Dworschak, C., Chang, T., Forbes, S., Cadario, B., Hart, L.E. and Chen, K.M. (1990) Comparison of polychlorinated dibenzodioxin levels with hepatic mixed-function oxidase induction in Great Blue Herons. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 30, 33–52.
Benoit, R., Des, Granges, J.L. and McNeil, R. (1993) Directions of arrivals of Great Blue Herons (Ardea herodias) at nests with large chicks near Montréal, Québec. Can. J. Zool. 71, 2250–7.
Boersma, D.C., Ellenton, J.A. and Yagminas, A. (1986) Investigation of hepatic mixed-function oxidase system in Herring Gull embryos in relation to environmental contaminants. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 5, 309–18.
Bosveld, A.T.C., Van den, Berg, M. and Theelen, R.M.C. (1992) Assessment of the EROD inducing potency of eleven 2,3,7,8-substituted PCDD/Fs and three coplanar PCBs in the chick embryo. Chemosphere 25, 911–16.
Braune, B.M. and Norstrom, R.J. (1989) Dynamics of organochlorine compounds in Herring Gulls: III. Tissue distribution and bioaccumulation in Lake Ontario (Canada, USA) gulls. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 8, 957–68.
Brunström, B. (1990) Mono-ortho-chlorinated chlorobiphenyls: toxicity and induction of 7-ethoxyresorufin O-deethylase (EROD) activity in chick embryos. Arch. Toxicol. 64, 188–92.
Brunström, B., Andersson, L., Nikolaidis, E. and Dencker, L. (1990) Non-ortho- and mono-ortho-chlorine-substituted polychlorinated biphenyls-embryotoxicity and inhibition of lymphoid development. Chemosphere 20, 1125–8.
Chu, I., Secours, V.E., Villeneuve, D.C. and Valli, V.E. (1982) Acute and subacute toxicity of octachlorostyrene in rat. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 10, 285–96.
Des, Granges, J.L. (1993) Grand Héron. In Gauthier, J. and Aubry, Y. eds. Atlas des oiseaux nicheurs du Québec méridional. Région de Québec: Service canadien de la faune.
Des, Granges, J.L. and Laporte, P. (1983) Quatrième et cinquième tournées d'inspection des héronnières du Québec, 1980–1981. Service canadien de la faune, région de Québec. Cahiers de biologie 139, 1–11.
Ellenton, J.A., Brownlee, L.J. and Hollebone, B.R. (1985) Aryl hydroxylase levels in Herring Gull embryos from different locations on the Great Lakes. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 4, 615–22.
Fleming, W.J., Pullin, B.P. and Swineford, D.M. (1984) Population trends and environmental contaminants in Herons in the Tennessee Valley, 1980–81. Col. Waterbirds 7, 63–73.
Gibbs, J.P. (1991) Spatial relationships between nesting colonies and foraging areas of Great Blue Herons. The Auk 108, 764–70.
Gibbs, J.P., Woodward, S., Hunter, M.L. and Hutchinson, A.E. (1987) Determinants of Great Blue Heron colony distribution in coastal Maine. The Auk 104, 38–47.
Gilbertson, M., Kubiak, T.J., Ludwig, J.P. and Fox, G.A. (1991) Great Lakes embryo mortality, edema, and deformities syndrome (GLEMEDS) in colonial fish-eating birds: similarity to chick-edema disease. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 33, 455–520.
Gilman, A.P., Fox, G.A., Peakall, D.B., Teeple, S.M., Carroll, T.R. and Haymes, G.T. (1977) Reproductive parameters and contaminant levels of Great Lakes Herring Gulls. J. Wildl. Manage. 41, 458–68.
Gilman, A.P., Peakall, D.B., Hallett, D.J., Fox, G.A. and Norstrom, R.J. (1979) Herring Gulls (Larus argentatus) as monitors of contaminants in the Great Lakes. In Nielsen, S.W., Migaki, G. and Scarpelli, D.G. eds. Animals as monitors of environmental pollutants, pp. 280–98. Washington, DC: National Academy of Sciences.
Hancock, J. and Kushlan, J. (1984) The Heron Handbook. London: Croom Helm.
Hebert, C.E., Haffner, G.D., Weis, I.M., Lazar, R. and Montour, L. (1990) Organochlorine contaminants in duck populations of Walpole Island. J. Great Lakes Res. 16, 21–6.
Jones, P.D., Giesy, J.P., Newsted, J.L., Verbrugge, D.A., Beaver, D.L., Ankley, G.T., Tillitt, D.E., Lodge, K.B. and Niemi, G.J. (1993) 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin equivalents in tissues of birds at Green Bay, Wisconsin, USA. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 24, 345–54.
Joshi, P.S., Mathur, S.N., Murthy, S.K. and Ganguly, J. (1973) Vitamin A economy of the developing chick embryo and of the freshly hatched chick. Biochem. J. 136, 757–61.
Kubiak, T.J., Harris, H.J., Smith, L.M., Schwartz, T.R., Stalling, D.L., Trick, J.A., Sileo, L., Docherty, D.E. and Erdman, T.C. (1989) Microcontaminants and reproductive impairment of the Forster's Tern on Green Bay, Lake Michigan-1983. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 18, 706–27.
Laporte, P. (1982). Organochlorine residues and eggshell measurements of Great Blue Heron eggs from Quebec. Col. Waterbirds 5, 95–103.
Mineau, P., Fox, G.A., Norstrom, R.J., Weseloh, D.V., Hallett, D.J. and Ellenton, J.A. (1984) Using the Herring Gull to monitor levels and effects of organochlorine contamination in the Canadian Great Lakes. In Nriagu, J.O. and Simmons, M.S. eds. Toxic contaminants in the Great Lakes, p. 437. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Mitchell, C.A., White, D.H. and Kaiser, T.E. (1981) Reproductive success of Great Blue Herons at Nueces Bay, Corpus Christi, Texas. Bull. Texas Ornithol. Soc. 14, 18–21.
Moore, F.R. (1957) Vitamin A. New York: Elsevier Publishing.
Noble, R.C. (1987) Lipid metabolism in the chick embryo: some recent ideas. J. Exp. Zool. Suppl. 1, 65–73.
Parrish, D.B., Williams, R.N. and Sanford, P.E. (1951) The state of vitamin A in livers and unabsorbed yolks of embryonic and newly hatched chicks. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 34, 64–6.
Peakall, D. (1992) Animal Biomarkers as Pollution Indicators. London: Chapman & Hall.
Powell, G.V.N. and Powell, A.H. (1986) Reproduction by Great White Heron Ardea herodias in Florida Bay as an indicator of habitat quality. Biol. Conservat. 36, 101–13.
Spear, P.A., Moon, T.W. and Peakall, D.B. (1986) Liver retinoid concentrations in natural populations of herring gulls (Larus argentatus) contaminated by 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo p-dioxin and in ring doves (Streptopelia risoria) injected with a dioxin analogue. Can. J. Zool. 64, 204–8.
Spear, P.A., Bourbonnais, D.H., Peakall, D.B. and Moon, T.W. (1989) Dove reproduction and retinoid (vitamin A) dynamics in adult females and their eggs following exposure to 3,3′,4,4′-tetrachlorobiphenyl. Can. J. Zool. 67, 908–13.
Spear, P.A., Bourbonnais, D.H., Norstrom, R.J. and Moon, T.W. (1990) Yolk retinoids (vitamin A) in eggs of the Herring Gull and correlations with polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins and dibenzofurans. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 9, 1053–61.
Spear, P.A., Bilodeau, A.Y. and Branchaud, A. (1992) Retinoid: from metabolism to environmental monitoring. Chemosphere 25, 1733–8.
Tanabe, S., Kannan, N., Ono, M. and Tatsukawa, R. (1989) Toxic threat to marine mammals: increasing toxic potential of non-ortho and mono-ortho coplanar PCBs from land to ocean. Chemosphere 18, 485–90.
Tarkpea, M., Hagen, I., Carlberg, G.E., Kolsaker, P. and Storflor, H. (1985) Mutagenicity, acute toxicity, and bioaccumulation potential of six chlorinated styrenes. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 35, 525–30.
Thaller, C. and Eichele, G. (1987) Identification and spatial distribution of retinoids in the developing chick limb bud. Nature 327, 625–8.
Thompson, J.N. (1970) The role of vitamin A in reproduction. In De, Luca, H.F. and Suttie, J.W. eds. The fat-soluble vitamins. p. 267. Madison: University of Wisconsin Press.
Thompson, J.N. (1976) Fat-soluble vitamins. Comp. Anim. Nutr. 1, 99–135.
Tremblay, J. and Ellison, L.N. (1980) Breeding success of the Black-Crowned Night Heron in the St. Lawrence estuary. Can. J. Zool. 58, 1259–63.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boily, M.H., Champoux, L., Bourbonnais, D.H. et al. β-carotene and retinoids in eggs of Great Blue Herons (Ardea herodias) in relation to St Lawrence River contamination. Ecotoxicology 3, 271–286 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00117992
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00117992