Abstract
Change of hybrid dysgenesis potentials in P-M system of Drosophila melanogaster — In the P-M system of hybrid dysgenesis, three types of Drosophila melanogaster strains have been described in relation to hybrid gonadal sterility: P, Q and M. When M strain females were mated with P strain males, the P factors resulted in variable level of sterility in their progeny. The Q strain had no significant potential for sterility in any hybrid strain combination. To observe the dynamics of chromosomal contamination, due to the P transposable elements in different genetic context, mixed populations of these three types of strains were set up and monitored for their gonadal sterility potential during at least 30 generations.
A first set of 16 experimental populations was set up; each of these was initiated with a mixture of 50% of individuals from the Harwich strain (a strong P strain) and 50% of individuals from a M or Q strain collected in natural populations. The M activity levels of these strains corresponded to a range from 100% to 0%. For all of these populations, the M activity potential disappeared during the five first generations. However, the P activity potential reached an equilibrium level positively correlated with the M activity potential level introduced at the beginning. It is proposed that the force of invasion of the P type by chromosomal contamination through the transposition of the P elements is dependent on the copy number of P sequences present on the chromosome of the M′ strain in competition.
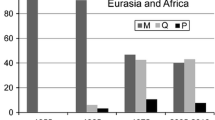
A second set of 18 experimental populations was set up with a mixture of P, M or Q strains collected in France between 1965 and 1982 (this period probably corresponds to the invasion of the P elements in France). After 30 generations, all of these populations (except one) had lost all dysgenic sterility potentiality and seemed to be of the Q type. Taking into account the results obtained from the two sets of experimental populations, the temporal and geographical distribution of P elements in the world could be explained by a progressive diffusion of autonomous P elements, from America with an accompanying decrease of their ability to transpose.
Similar content being viewed by others
Références
Anxolabéhère, D., Girard, P., Palabost, L. & Périquet, G., 1976. Stabilité des polymorphismes morphologique et enzymatique d'une population naturelle de Drosophila melanogaster. Arch. Zool. exp. gén. 117: 169–179.
Anxolabéhère, D., Nouaud, D. & Périquet, G., 1982a. Etude de la variabilité du système P-M de dysgénésie des hybrides entre populations de Drosophila melanogaster. C.r. Acad. Sc. Paris 294: 913–918.
Anxolabéhère, D., Nouaud, D. & Périquet, G., 1982b. Cytotype polymorphism of the P-M system in two wild populations of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79: 7801–7803.
Anxolabéhère, D. & Périquet, G., 1983. Système P-M de dysgénésie des hybrides, polymorphisme génétique et évolution des populations de Drosophila melanogaster. Génét. Sél. Evol. 15: 31–44.
Anxolabéhère, D., Hu, Kai, Nouaud, D., Périquet, G & Ronsseray, S., 1984. The geographical distribution of P-M hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Génét. Sél. Evol. 16(1): 15–26.
Anxolabéhère, D., Nouaud, D., Périquet, G. & Tchen, P., 1985. P element distribution in Eurasian populations of Drosophila melanogaster: a genetic and molecular analysis. Proc. natn. Acad. Sc. U.S.A. 82: 5418–5422.
Bingham, P. M., Kidwell, M. G. & Rubin, G. M., 1982. The molecular basis of P-M hybrid dysgenesis: the role of the P element, a P-strain specific transposon family. Cell 29: 995–1004.
Bregliano, J. C., Picard, G., Bucheton, A., Pelisson, A., Lavige, J. M. & L'Héritier, P., 1980. Hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. Science 207: 606–611.
Bregliano, J. C. & Kidwell, M. G., 1983. Hybrid dysgenesis determinants. In: J. A.Shapiro (ed.), Mobile genetic elements. Academic Press, New-York.
Engels, W. R., 1979a. Hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster: rules of inheritance of female sterility. Genet. Res. Camb. 33: 219–236.
Engels, W. R., 1979b. Extrachromosomal control of mutability in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 76: 4011–4015.
Engels, W. R., 1981a. Germline hypermutability and its relation to hybrid dysgenesis and cytotype. Genetics 98: 565–587.
Engels, W. R., 1981b. Hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila and the stochastic loss hypothesis. Cold Spring Harbor Symp. quant. Biol. 45; 561–565.
Engels, W. R. & Preston, C. R., 1981. Characteristics of a neutral strain in the P-M system of hybrid dysgenesis. Dros. Inf. Serv. 56: 35–37.
Karess, R. E. & Rubin, G. M., 1984. Analysis of P transposable element functions in Drosophila. Cell 38: 135–146.
Kidwell, M. G., Kidwell, J. F. & Sved, J. A., 1977. Hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster: a syndrome of aberrant traits including mutation, sterility and male recombination. Genetics 86: 813–833.
Kidwell, M. G., 1979. Hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster: the relationship between the P-M and the I-R systems. Genet. Res. Camb. 33: 204–217.
Kidwell, M. G., Novy, J. B. & Feeley, S. M., 1981a. Rapid unidirectionnal change of hybrid dysgenesis potential in Drosophila. J. Hered. 72: 32–38.
Kidwell, M. G., 1981b. Hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster: the genetics of cytotype determination in a neutral strain. Genetics 98: 275–290.
Kidwell, M. G., 1983a. Hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster: factors affecting chromosomal contamination in the P-M system. Genetics 104: 317–341.
Kidwell, M. G., 1983b. Evolution of hybrid dysgenesis determinants in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80: 1655–1659.
Kidwell, M. G., Frydryk, T. & Novy, J. B., 1983c. The hybrid dysgenesis potential of Drosophila melanogaster strains of diverse temporal and geographical natural origins. Dros. Inf. Serv. 59: 63–68.
O'Hare, K. & Rubin, G. M., 1983. Structures of P transposable elements and their sites of insertion and excision in the Drosophila melanogaster genome. Cell 34: 25–35.
Périquet, G. & Anxolabéhère, D., 1982. Elements causing hybrid dysgenesis on the second chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol. gen. Genet. 186: 309–314.
Picard, G., Bucheton, A., Lavige, J. M. & Pélisson, A., 1976. Répartition géographique des trois grands types de souches impliquées dans un phénomène de stérilité à déterminisme non-mendélien chez Drosophila melanogaster. C.r. Acad. Sc. Paris 282: 1813–1816.
Ronsseray, S., Anxolabéhère, D. & Périquet, G., 1984. Hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster: influence of temperature on cytotype determination in the P-M system. Mol. gen. Genet. 196: 17–23.
Rubin, G. M., Kidwell, M. G. & Bingham, P. M., 1982. The molecular basis of P-M hybrid dysgenesis: the nature of induced mutations. Cell 29: 987–994.
Schaeffer, R. E., Kidwell, M. G. & Fausto-Sterling, A., 1979. Hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster: morphological and cytological studies of ovarian dysgenesis. Genetics 92: 1141–1152.
Spradling, A. C. & Rubin, G. M., 1982. Transposition of cloned P elements into Drosophila germ line chromosomes. Science 218: 341–347.
Yamamoto, A., Hihara, F. & Watanabe, T. K., 1984. Hybrid dysgenesis in Drosophila melanogaster: predominance of Q factors in Japanese populations and its change in the laboratory. Genetica 63: 71–77.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Ce travail a été réalisé dans le cadre de l'A.T.P. Biologie des populations et de l'UA 693 du C.N.R.S.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Anxolabéhère, D., Nouaud, D., Périquet, G. et al. Evolution des potentialités dysgénésiques du système P-M dans des populations expérimentales mixtes P, Q, M et M′ de Drosophila melanogaster . Genetica 69, 81–95 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00115127
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00115127