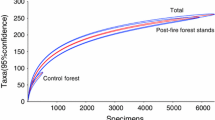
Fire is a common disturbance in the Mediterranean ecosystem. A fire that broke out in the eastern Mediterranean pine forest on Mount Carmel in September 1989 destroyed thousands of hectares of natural forest. We carried out a comparative study of rodent recovery after fire under three different management regimes in order to establish the best treatment for recovery. Rodents were used as ‘bio-indicators’, because of their limited home range, to assess the best management practice to be used in the recovery of the post-fire habitat. Our results show that the three arboreal Palaeoarctic species which lived in this habitat before the fire either died during the fire or left the habitat as a result of its destruction. A succession of rodent species was observed. The untreated burned forest had the highest species diversity in the initial stage, while during a later stage the highest diversity was observed in plots where the burned trees were cut down, the trunks removed and the twigs collected into small piles. The results also suggest that removing the trunks and twigs at the initial stage of recolonization results in a more xeric and warm habitat which will postpone the reinvasion of the forest species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aisner, R. (1984) Aspects of learning of pine cones opening by the black rat (Rattus rattus) and the spread of this behaviour in Israel. MSc thesis, Tel Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel.
Atlas of Israel (1970) Surveys of Israel Ministry of Labour. Amsterdam, Jerusalem: Elsevier.
Bronson, F.H. (1984) The adaptability of the house mouse. Sci. Amer. 250, 90–7.
Broza, M., Poliakov, D., Weber, S. and Izhaki, I. (1993) Soil microarthropods on post-fire pine-forest on Mount Carmel, Israel. Wat. Sci. Tech. 7–8, 533–8.
Fertig, D.S. and Edmonds, V.W. (1969) The physiology of the house mouse. Sci. Amer. 221, 103–10.
Filippucci, M.G., Simson, S. and Nevo, E. (1989) Evolutionary biology of the genus Apodemus Kamp, 1829 in Israel. Allozymic and biometric analysis with description of a new species: Apodemus hermonensis (Rodentia, Muridae). Bull. Zool. 56, 361–376.
Fox, B.J. and Fox, M.D. (1986) Resiliance of animal and plant communities to human disturbance. In: Resiliance in Mediterranean type ecosystems (B. Dell, A.J.M. Hopkins and B.B. Lamont, eds) pp. 65–83. Dodrecht: Dr. W. Junk Publishers.
Granot, Y. (1984) Structure, dynamics and spatial organization in sympatric Apodemus. Re'em 3, 21–9 (in Hebrew).
Haim, A. (1987a) Metabolism and thermoregulation in rodents: are these adaptations to habitat and food quality? S. Afr. J. Sci. 83, 639–42.
Haim, A. (1987b) Thermoregulation and metabolism of Wagner's gerbil (Gerbillus dasyurus): a rock-dwelling rodent adapted to arid and mesic environments. J. Therm. Biol. 12, 45–8.
Haim, A. (1993) Resiliance to fire of rodents in an East-Mediterranean pine forest on Mount Carmel, Israel: the effects of management regimes. In: Fire in Mediterranean ecosystems (L. Trabaud and R. Prodon eds) pp. 293–301. Brussels, Luxembourg: ECSC-EEC-EAEC.
Haim, A. and Tchernov, E. (1974) The distribution of myomorph rodents in the Sinai peninsula. Mammalia 38, 201–23.
Haim, A., Pelaot, I. and Sela, A. (1986) Comparison of ecophysiological parameters between two Apodemus species coexisting in the same habitat. In: Environmental quality and ecosystem stability. Vol 3A (Z. Dobinsky and Y. Steinberger, eds) pp. 33–40. Ramat-Gan: Bar-Ilan University Press.
Haim, A. and Rubal, A. (1992) The coexistence of two Apodemus species in the Mediterranean woodlands of Israel. In: Medecos VI (C.A. Thanos, ed.) pp. 127–32. Athens: University of Athens.
Haim, A. and Izhaki, I. (1993) The ecological significance of resting metabolic rate and non-shivering thermogenesis for rodents. J. Therm. Biol., 18, 71–81.
Hains, H., Ciskowski, C. and Harms, V. (1973) Acclimation to chronic water restriction in the wild house mouse Mus musculus. Physiol. Zool. 46, 110–28.
Harrison, D.L. and Bates, P.J.J. (1991) The mammals of Arabia. Kent: Harrison Zoological Museum Publication, Kent.
Higgs, P. and Fox, B.J. (1993) Interspecific competition: a mechanism for rodent succession after fire in wet heathland. Austr. J. Ecol. 18, 193–201.
Izhaki, I., Lahav, H. and Ne'eman, G. (1992) Spatial distribution patterns of Rhus coriaria seedlings after fire in a Mediterranean pine forest. Acta Oecol. 13, 271–81.
Izhaki, I., Haim, A. and Zohar, O. (1993) Rodent populations recovering from fire in an East-Mediterranean woodland. Wat. Sci. Tech. 7–8, 539–45.
Katz, U. (1973) The effects of water deprivation and hypertonic salt injection on several rodent species compared with the albino rat. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 44A, 473–85.
Kleiber, M. (1961) The fire of life. New York: Wiley.
Komarek, E.V. (1969) Fire and animal behaviour. 9th Annual Tall Timber Fire Ecology conference, Tall Timbers Res. Sta., Tallahassee, pp. 161–207.
Lahav, H. (1988) Renewal of vegetation after fire in natural pine forest on Mt. Carmel. MSc thesis, Tel-Aviv University, Tel-Aviv, Israel.
Lewis, R.D., Lewis, J.H. and Atallah, S.I. (1967) A review of Lebanese mammals Lagomorpha and Rodentia. J. Zool. (Lond), 153, 45–70.
Main, A.R. (1986) Resiliance of the level of individual animal. In: Resiliance in Mediterranean type ecosystems (B. Dell, A.J.M. Hopkins, and B.B. Lamont, eds) pp. 83–94. Dorecht: Dr. W. Junk Publishers.
Naveh, Z. (1984) The vegetation of the Carmel and Nahal Sefunim Prehistoric sites Mount Carmel, Israel. In: Sefunim Prehistoric Sites Mount Carmel, Israel (A. Ronen, ed) pp. 230–63. Oxford: BAB.
Naveh, Z. (1990a) Ancient man's impact on the Mediterranean landscape in Israel-ecological and evolutionary perspectives. In: Man's roles in the shaping of the eastern Mediterranean landscape (S. Bottema, G. Entjes-Nieborg and Zeist, eds) pp. 43–50. Rotterdam: A.A. Balkema.
Naveh, Z. (1990b) Fire in the Mediterranean — a landscape ecological perspective. In: Fire ecosystem dynamics (J.G. Goldammer and M.J. Jenkins, eds) pp. 1–20. Dan Haag: SPB Academic Publishing.
Ne'eman, G., Lahav, H. and Izhaki, I. (1993). Resiliance to fire of vegetation in an East-Mediterranean pine forest on Mount Carmel: the effects of management regimes. In: International Workshop on the role of fire in Mediterranean ecosystems (L. Trabaud and R. Prodon, eds.), pp. 127–40. E Guyot SA: Brussels.
Prodon, R. (1992) Land abandonment, wildfires and fauna in north Mediterranean context. In U.I.M.P. Santander Seminario. (unpublished seminar).
Prodon, R., Fons, R. and Athias-Binche, F. (1987) The impact of fire on animal communities in Mediterranean area. In: The role of fire in ecological systems (L. Trabaud, ed.) pp. 121–57. Dan Haag: SPB Academic Publishing.
Quinn, R.D. (1986) Mammalian herbivory and resilience in Mediterranean-climate ecosystems. In: Resiliance in Mediterranean type ecosystems (B. Dell, A.J.M. Hopkins and B.B. Lamont, eds) pp. 113–28. Dorecht: Dr. W. Junk Publishers.
Sgardelis, S.P. and Margaris, N.S. (1992). Effects of fire on birds and rodents of phryganic (East Mediterranean) ecosystem. Isr. J. Zool. 38, 1–8.
Shkolnik, A. and Borut, A. (1969) Temperature and water relations in two species of spiny mice (Acomys). J. Mammal. 50, 245–55.
Tevis, L.Jr. (1956) Effects of slash burn on forest mice. J. Wild Manag. 20, 405–9.
Vogel, R.J. (1973) Effects of fire on the plants and animals of Florida wetland. Amer. Midl. Nat. 89, 334–47.
Yahav, S., Haim, A. and Shkolnik, A. (1982) Thermoregulation and activity in Apodemus mystacinus (Mammalia: Muridae) on Mount Carmel. Isr. J. Zool. 31, 157–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haim, A., Izhaki, I. Changes in rodent community during recovery from fire: relevance to conservation. Biodivers Conserv 3, 573–585 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00114202
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00114202