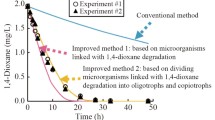
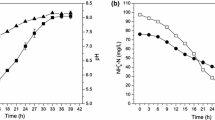
Abstract
The effects of primary electron-donor and electron-acceptor substrates on the kinetics of TCA biodegradation in sulfate-reducing and methanogenic biofilm reactors are presented. Of the common anaerobic electron-donor substrates that were tested, only formate stimulated the TCA biodegradation rate in both reactors. In the sulfate-reducing reactor, glucose also stimulated the reaction rate. The effects of formate and sulfate on TCA biodegradation kinetics were analyzed using a model for primary substrate effects on reductive dehalogenation. Although some differences between the model and the data are evident, the observed responses of the TCA degradation rate to formate and sulfate were consistent with the model. Formate stimulated the TCA degradation rate in both reactors over the entire range of TCA concentrations that were studied (from 50 μg TCA/L to 100 mg TCA/L). The largest effects occurred at high TCA concentrations, where the dehalogenation kinetics were zero order. Sulfate inhibited the first-order TCA degradation rate in the sulfate-reducing reactor, but not in the methanogenic reactor. Molybdate, which is a selective inhibitor of sulfate reduction, stimulated the TCA removal rate in the sulfate-reducing reactor, but had no effect in the methanogenic reactor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson, B & Davies, IJ (1974) The overall rate of substrate uptake (reaction) by microbial films. Part I—A biological rate equation. Trans. Inst. Chem. Engin. 52: 248–259
Bouwer, EJ & McCarty, PL (1983) Transformations of 1-and 2-carbon halogenated aliphatic organic compounds under methanogenic conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 45: 1286–1294
Bouwer, EJ & Wright, JP (1988) Transformation of trace halogenated aliphatics in anoxic biofilm columns. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2: 155–169
Cornish-Bowden, A (1979) Fundamentals of Enzyme Kinetics. Butterworth and Co., Ltd., London
Criddle, CS, DeWitt, JT, Grbić-Galić, D & McCarty, PL (1990) Transformation of carbon tetrachloride by Pseudomonas sp. strain KC under denitrification conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56: 3240–3246
Criddle, CS & McCarty, PL (1991) Electrolytic model system for reductive dehalogenation in aqueous environments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 25: 973–978
Cseh, T, Sanschagrin, S, Hawari, J & Samson, R (1989) Adsorption-desorption characteristics of polychlorinated biphenyls on various polymers commonly found in laboratories. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 55: 3150–3154
Dang, JS, Harvey, DM, Jabbagy, A & Grady, CPLJr (1989) Evaluation of biodegradation kinetics with respirometric data. Res. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 61: 1711–1721
DeWeerd, KA & Suflita, JM (1990) Anaerobic aryl reductive dehalogenation of halobenzoates by cell extracts of Desulfomonile tiedjei. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56: 2999–3005
DeWeerd, KA, Concannon, F & Suflita, JM (1991) Relationship between hydrogen consumption, dehalogenation, and the reduction of sulfur oxyanions by Desulfomonile tiedjei. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57: 1929–1934
Dolfing, J (1988) Acetogenesis. In: Zehnder, AJB (Ed.) Biology of Anaerobic Microorganisms (pp. 417–468). John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York
Egli, C, Scholtz, R, Cook, AM & Leisinger, T (1987) Anaerobic dechlorination of tetrachloromethane and 1,2-dichloroethane to degradable products by pure cultures of Desulfobacterium sp. and Methanobacterium sp. FEMS Microbiol. Let. 43: 257–261
Egli, C, Tschan, T, Scholtz, R, Cook, AM & Leisinger, T (1988) Transformation of CCl4 to CH2Cl2 and CO2 by Acetobacterium woodii. App. Environ. Microbiol. 54: 2819–2824
Egli, C, Stromeyer, S, Cook, AM & Leisinger, T (1990) Transformation of tetra- and trichloromethane to CO2 by anaerobic bacteria is a non-enzymic process. FEMS Microbiol. Letters 68: 207–212
Ensley, BD (1991) Biochemical diversity of trichloroethylene metabolism. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 45: 283–299
Fathepure, BZ & Boyd, SA (1988a) Dependence of tetrachloroethylene dechlorination on methanogenic substrate consumption by Methanosarcina sp. strain DCM. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54: 2976–2980
Fathepure, BZ (1988b) Reductive dechlorination of perchloroethylene and the role of methanogens. FEMS Microbiol. Let. 49: 149–156
Freedman, DL & Gossett, JM (1989) Biological reductive dechlorination of tetrachloroethylene and trichloroethylene to ethylene under methanogenic conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 55: 2144–2151
Gälli, R & McCarty, PL (1989a) Biotransformation of 1,1,1-trichloroethane, trichloromethane, and tetrachloromethane by a Clostridium sp. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 55: 837–844
Gälli, R (1989b) Kinetics of biotransformation of 1,1,1-trichloroethane by Clostridium sp. strain TCAIIB. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 55: 845–851
Gantzer, CJ, Rittmann, BE & Herricks, EE (1988) Mass transfort to streambed biofilms. Water Research 22: 709–722
Gibson, SA & Suflita, JM (1990) Anaerobic biodegradation of 2,4,5-trichlorophenoxyacetic acid in samples from a methanogenic aquifer. Stimulation by short-chain organic acids and alcohols. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56: 1825–1832
Goldman, P (1972) Enzymology of carbon-halogen bonds. In: The degradation of synthetic organic molecules in the biosphere (pp. 147–165). National Academy of Sciences, Washington, DC
Goldman, P, Milne, GWA & Keister, DB (1968) Carbon-halogen bond cleavage. III. Studies on bacterial halidohydrolases. J. Biol. Chem. 243: 428–434.
Grady, CPLJr, Dang, JS, Harvey, DM, Jabbagy, A & Wang, X-L (1989) Determination of biodegradation kinetics through use of electrolytic respirometry. Water Sci. Technol. 21: 957–968
Groenewegen, PEJ, Driessen, AJM, Konings, WN & deBont, JAM (1990) Energy-dependent uptake of 4-chlorobenzoate in the coryneform bacterium NTB-1. J. Bacteriol. 172: 419–423
Henderson, JE, Peyton, GR & Glaze, WH (1976) A convenient liquid-liquid extraction method for the determination of halomethanes in water at the parts-per-billion level. In: Keith, LH (Ed.) Identification and Analysis of Organic Pollutants in Water (pp. 105–111). Ann. Arbor Science Publishers, Inc., Ann Arbor, MI
Holliger, C, Schraa, G, Stams, AJM & Zehnder, AJB (1993) A highly purified enrichment culture couples the reductive dechlorination of tetrachloroethene to growth. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59: 2991–2997
Janssen, DB, Scheper, A, Dijkhuizen, L & Witholt, B (1985) Degradation of halogenated aliphatic compounds by Xanthobacter autotrophicus GJ10. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 49: 673–677
Janssen, DB & Witholt, B (1992) Aerobic and anaerobic degradation of halogenated aliphatics. In: Sigel, H & Sigel, A (Eds) Metal Ions in Biological Systems, Vol. 28 (pp. 299–327). Marcel Dekker, New York
Janssen, DB, Pries, F & van derPloeg, JR (1994) Genetics and biochemistry of dehalogenating enzymes. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 48: 163–191
Jones, WJ, NagleJr, DP & Whitman, WB (1987) Methanogens and the diversity of archaebacteria. Microbiol. Rev. 51: 135–177
Kohler-Staub, D & Leisinger, T (1985) Dichloromethane dehalogenase of Hyphomicrobium sp. strain DM2. J. Bacteriol. 162: 676–681
Krone, UE, Laufer, K, Thauer, RK & Hogenkamp, HPC (1989) Coenzyme F430 as a possible catalyst for the reductive dehalogenation of chlorinated C1 hydrocarbons in methanogenic bacteria. Biochemistry 28: 10,061–10,065
Krone, UE, Thauer, RK, Hogenkamp, HPC & Steinbach, K (1991) Reductive formation of carbon monoxide from CCl4 and FREONs 11, 12, and 13 catalyzed by corrinoids. Biochemistry 30: 2713–2719
Lage, GB, Parsons, FZ, Nasser, RS & Lorenzo, PA (1986) Sequential dehalogenation of chlorinated ethenes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20: 96–99
Lage, GB, Parsons, FZ & Nasser, RS (1987) Kinetics of the depletion of TCE. Environ. Sci. Technol. 21: 366–370
Lam, T & Vilker, VL (1987) Biodehalogenation of bromotrichloroethane and 1,2-dibromo-3-chloropropane by Pseudomonas putida PpG-786. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 29: 151–159
Mikesell, MD & Boyd, SA (1990) Dechlorination of chloroform by Methanosarcina strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56: 1198–1201
Morrison, RT & Boyd, RN (1973) Organic Chemistry. Allyn & Bacon, Inc., Boston, MA
Mosey, FE (1983) Mathematical modelling of the anaerobic digestion process: regulatory mechanisms for the formation of short-chain volatile acids from glucose. Water Sci. Technol. 15: 209–232
Oremland, RS (1988) Biogeochemistry of methanogenic bacteria. In: Zehnder, AJB (Ed.) Biology of Anaerobic Microorganisms (pp. 641–705). John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York
Oremland, RS & Capone, DG (1988) Use of ‘specific’ inhibitors in biogeochemistry and microbial ecology. Adv. Microbial Ecology 10: 285–383
Parsons, F & Lage, GB (1985) Chlorinated organics in simulated groundwater environments. J. Amer. Water Works Assn. 77: 56–59
Rittmann, BE & McCarty, PL (1981) Substrate flux into biofilms of any thickness. J. Environ. Eng. (ASCE) 107: 831–848
Rittmann, BE, Crawford, LA, Tuck, CK & Namkung, E (1986) In situ determination of kinetic parameters for biofilms. Isolation and characterization of oligotrophic biofilms. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 28: 1753–1760
Sáez, PB & Rittmann, BE (1992) Model-parameter estimation using least squares. Water Research 26: 789–796
Scholz-Muramatsu, H, Szewzyk, R, Szewzyk, U & Gaiser, S (1990) Tetrachloroethylene as electron acceptor for the anaerobic degradation of benzoate. FEMS Microbiol. Let. 66: 81–86
Semprini, L, Hopkins, GD, McCarty, PL & Roberts, PV (1992) In situ transformation of carbon tetrachloride and other halogenated compounds resulting from biostimulation under anoxic conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 26: 2454–2461
Stanley, TJ, WardIII, WJ & Alger, MM (1989) CH2Cl2 permeation in polycarbonate using a 14C-tracer. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 28: 1494–1497
Stromeyer, SA, Stumpf, K, Cook, AM & Leisinger, T (1992) Anaerobic degradation of tetrachloromethane by Acetobacterium woodii: Separation of dechlorinative activities in cell extracts and roles for vitamin B12 and other factors. Biodegradation 3: 113–123
Suidan, MT, Rittmann, BE & Traegner, UK (1987) Criteria establishing biofilm-kinetic types. Water Research 21: 491–498
vanGenuchten, MT (1982) Analytical solutions for chemical transport with simultaneous adsorption, zero-order production and first-order decay. J. Hydrol. 49: 213–233
Vogel, TM & McCarty, PL (1985) Biotransformation of PCE to TCE, DCE, VC, and CO2 under methanogenic conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 49: 1080–1083
Vogel, TM & McCarty, PL (1987) Abiotic and biotic transformations of 1,1,1-TCA under methanogenic conditions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 21: 1208–1213
Vogel, TM, Criddle, CS & McCarty, PL (1987) Transformations of halogenated aliphatic compounds. Environ. Sci. Technol. 21: 722–736
Wackett, L, Logan, MSP, Blocki, FA & Bao-li, C (1992) A mechanistic perspective on bacterial metabolism of chlorinated methanes. Biodegradation 3: 19–36
Wade, RS & Castro, CE (1973) Oxidation of iron(II) porphyrins by alkyl halides. J. Amer. Chem. Soc. 95: 226–230
Widdel, F (1988) Microbiology and ecology of sulfate- and sulfur-reducing bacteria. In: Zehnder, AJB (Ed.) Biology of Anserobic Microorganisms (pp. 468–585). John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York
Wolin, MJ (1982) Hydrogen transfer in microbial communities. In: Bull, AT & Slater, JH (Eds) Microbial Interactions and Communities, Vol. 1 (pp. 323–356) Academic Press, New York
Wrenn BA (1992) Substrate interactions during the anaerobic biodegradation of 1,1,1-trichloroethane. Ph.D. Thesis, Dept. of Civil Engr., University of Illinois, Urbana, IL
Wrenn BA & Rittmann BE (in press) A model for the effects of primary substrates on reductive dehalogenation kinetics. Biodegradation
Zeikus, JG (1980) Microbial populations in digesters. In: Stafford, DA, Wheatley, BI & Hughes, DE (Eds) Anaerobic Digestion (pp. 61–87) Applied Science Publishers, Ltd., London
Zeikus JG (1983) Metabolic communications between biodegradative populations in nature. In: Slater JH, Whittenbury R & Wimpenny JWT (Eds) Microbes in Their Natural Environments (pp. 423–461) Cambridge University Press
Zeikus, JG, Kerby, R & Krzycki, JA (1985) Single-carbon chemistry of acetogenic and methanogenic bacteria. Science 227: 1167–1173
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wrenn, B.A., Rittmann, B.E. Evaluation of a model for the effects of substrate interactions on the kinetics of reductive dehalogenation. Biodegradation 7, 49–64 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00056558
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00056558