Abstract
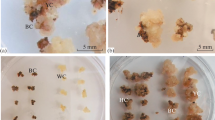
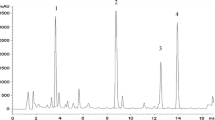
Callus cultures were established from hypocotyl explants of R. bracteosa, R. chalepensis and R. macrophylla. Calli were maintained for more than three years on MS-medium supplemented with 1 mg l-1 of each 2,4-D and kinetin. Acridone and furoquinoline alkaloids and coumarins have been isolated from four week old calli grown on a hormone containing and hormone-free medium. A new chlorinated acridone alkaloid has been detected.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- MS:
-
medium after Murashige & Skoog [6]
References
Baumert A, Gröger D, Schmidt J & Mügge C (1987) Minor alkaloids from Ruta graveolens tissue cultures. Pharmazie 42: 67–68
Baumert A, Gröger D, Schmidt J, Kuzovkina IN & Mügge C (1988) Alkaloids and other constituents from tissue cultures of Ruta graveolens. Fitoterapia 59: 83–88
Eilert U, Engel B, Reinhard E & Wolters B (1983) Acridone epoxides in cell cultures of Ruta species. Phytochemistry 22: 14–15
Hegnauer R (1983) Chemical characters and the classification of the Rutales. In: Waterman PG & Grundon MF (Eds) Chemistry and Chemical Taxonomy of the Rutales. (pp 401–440). Academic Press, London
Mester I (1983) Structural diversity and distribution of alkaloids in the Rutales. In: Waterman PG & Grundon MF (Eds) Chemistry and Taxonomy of the Rutales (pp 31–96). Academic Press, London
Murashige T & Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–497
Nahrstedt A, Wray V, Engel B & Reinhard E (1985) New furoacridone alkaloids from tissue culture of Ruta graveolens. Planta Med. 517–519
N.N. (1971) Chemistry and biology of Rutaceae compounds. International Symposium Herba Hungarica 10, No 2–3: 7–145
Petit-Paly G, Ramawat KG, Chenieux IC & Rideau M (1989) Ruta graveolens: in vitro production of alkaloids and medicinal compounds. In: Bajaj YPS (Ed) Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry, Vol 7. Medicinal and aromatic plants (pp 488–505) Springer, Berlin Heidelberg
Reinhard R, Corduan G & Volk OH (1968) Über Gewebekulturen von Ruta graveolens. Planta Med. 16: 8–16
Reisch J & Gunaherath GMK (1989) Natural products chemistry Part 124. Revised structure and synthesis of a new acridone alkaloid. Hallacridone from Ruta graveolens tissue cultures. J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. I 1047–1051
Rosza Zs, Reisch J, Szendrei K & Minker E (1981) Rutacridone-epoxide and gravacridonol from the roots of Ruta graveolens. Fitoterapia 52: 93–95
Scharlemann W (1972) Acridin-Alkaloide aus Kallus Kulturen von Ruta graveolens L. Z. Naturforsch. 27b: 806–809
White PhR (1943) A Handbook of the Plant Tissue Culture. The Ronald Press Company, New York
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baumert, A., Gröger, D., Kuzovkina, I.N. et al. Secondary metabolites produced by callus cultures of various Ruta species. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 28, 159–162 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00055511
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00055511