Summary
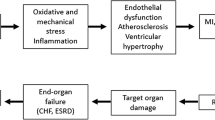
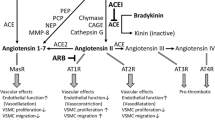
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors have played a highly beneficial role in the therapy of hypertension and congestive heart failure. Detailed analysis of some of the heart failure trials in patients with these diseases has uncovered unexpected benefits in the prevention of cardiovascular events. Paralleling these observations are the rapidly accruing basic studies describing important molecular and cellular effects of these agents. For example, ACE inhibition will prevent stimulation of smooth muscle cell angiotensin II receptors, thereby blocking both contractile and proliferative actions. In addition, ACE inhibition of kininase II inhibits the breakdown of bradykinin. Bradykinin is a direct stimulant of nitric oxide release from the intact endothelial cell. Thus, at the cellular level ACE inhibition shifts the balance of ongoing mechanisms in favor of those promoting vasodilatory, antiaggregatory, antithrombotic, and antiproliferative effects. These effects underlie the potential benefits of ACE inhibition in the therapy of coronary artery disease and atherosclerosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lonn, EM, Yusuf, S, Jha, P, Montague, TJ, Teo, KK, Benedict, CR, Pitt, B. Emerging role of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in cardiac and vascular protection. Circulation 1994;90:2056–2069.
Rubanyi, G. The role of endothelium in cardiovascular hemeostasis and diseases. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 1993; 22(Suppl. 4):S1-S14.
Ludmer, PL, Selwyn, AP, Shook, TL, et al. Paradoxical vaso-construction induced by acetylcholine in atherosclerotic coronary arteries. N Engl J Med 1986;315:1046–1051.
Werns, SW, Walton, JA, Hsia, HH, et al. Evidence of endothelial dysfunction in angiographically normal coronary arteries of patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation 1989;79:287–291.
Vita, JA, Treasure, CV, Nabel, EG, et al. Coronary vasomotor response to acetylcholine relates to risk factors for coronary artery disease. Circulation 1990;81:491–497.
vonLutterotti, N, Caranzara, DF, Sealy, JE, Laragh, JH. Renin is not synthesized by cardiac and extrarenal vascular tissues. A review of experimental evidence. Circulation 1994;89:458–470.
Dzau, V, Re, R. Tissue angiotensin system in cardiovascular medicine: A paradigm shift? Circulation 1994;89:493–498.
Naftilin, AJ, Pratt, RE, Dzau, VJ. Induction of platelet-derived growth factor A chain and c-myc gene expressions by angiotensin II in cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest 1989;83:1419–1474.
Naftilin, AJ, Pratt, RE, Eldridge, CS, Lin, HD, Dzau, VJ. Angiotensin II induces c-fos expression in smooth muscle cell via transcriptional control. Hypertension 1989:13: 706–711.
Chobanian, AV, Haudenschild, CC, Nickerson, C. Drago, R. Antiatherogeic effect of captopril in the Watanabe heritable hyperlipidemic rabbit. Hypertension 1992;20:473–477.
Aberg, G, Ferrer, P. Effects of captopril on atherosclerosis in cynomolgus monkeys. J Cardiovas Pharmacol 1990; 15(Suppl. 5):S65-S72.
Rolland, PH, Charpiot, P, Friggi, A, et al. Effects of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition with perindolol on hemodynamics, arterial structure, and wall rheology in the hindquarters of atherosclerotic mini-pigs. Am J Cardiol 1993;71:22E-27E.
Farber, HW, Center, DM, Rounds, S, Danilov, SM. Components of the angiotensin system cause release of neutrophil chemoattractant from cultural bovine and human endothelial cells. Eur Heart J 1990;11(Suppl. B):100–107.
Lüscher, TF, Boulanger, CM, Dohi, Y, Zang, Z. Endothelium-derived contracting factors. Hypertension 1992;19:117–130.
James, IM, Dickenson, EJ, Burgoyne, W, Jeremy, JY, Barrados, MA, Mikhailidis, DP, Dandona, P. Treatment of hypertension with captopril: Preservation of regional blood flow and reduced platelet aggregation. J Human Hypertens 1988;2:21–5.
Ridker, PM. An epidemiologic assessment of thrombotic risk factors for cardiovascular disease. Curr Opin Lipidol 1992; 3:285–290.
MacMahon, S, Peto, R, Culter, R, et al. Blood pressure, stroke and coronary heart disease. I: Effects of prolonged differences in blood pressure: Evidence from nine prospective observational studies corrected for the regression dilution bias. Lancet 1989;335:765–774.
Collins, R, Peto, R, MacMahon, S, et al. Blood pressure, stroke and coronary heart disease. II: Effect of short-term reductions in blood pressure: An overview of randomized drug trials in an epidemiological context. Lancet 1990;335: 827–838.
Yusuf, S, Pepine, CJ, Garces, C, et al. Effect of enalapril on myocardial infarction and unstable angina in patients with low ejection fractions. Lancet 1992;340:1173–1178.
Rutherford, JD, Pfeffer, MA, Moyé, LA, et al. Effects of captopril on ischemic events after myocardial infarction: Results of the Survival and Ventricular Enlargement Trial. Circulation 1994;90:1731–1738.
Treasure, CB, Klein, JL, Weintraub, WS, et al. Beneficial effects of cholesterol-lowering therapy on the coronary endothelium in patients with coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 1995;332:481–487.
Anderson, T, Meredith, IT, Yeung, AC, Frei, B, Selwyn, A, Ganz, P. The effect of cholesterol-lowering and antioxidant therapy on endothelium-dependent coronary vasomotion. N Engl J Med 1995;332:488–493.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
John Mancini, G.B. Emerging concepts: Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in coronary artery disease. Cardiovasc Drug Ther 10 (Suppl 2), 609–612 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00052506
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00052506