Abstract
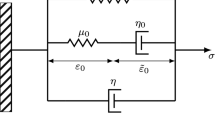
Non-linear equations governing the temporal evolution of the vector of instantaneous rotation are developed for an Earth with a homogeneous mantle having a viscoelastic Maxwell rheology and with a homogeneous inviscid fluid core.
This general theory is investigated using the angular momentum theorem applied to the coupled core-mantle system. It allows to study the influence upon the planetary rotation of a quasi-rigid rotational motion in the liquid core. It also enables to investigate the consequences of excitation sources (e.g. pressure), located at the core-mantle interface. Especially, the influence of viscoelastic variations in the inertia tensors resulting from the rotation itself or from various excitation sources are detailed with the help of a Love number formalism. The equations of the linear theory for an elastic Earth with a liquid core, and the non-linear theory for a viscous planet with a quasi-fluid behavior are shown to be particular cases of our generalized system of equations. Some planetological applications may be derived from the quasi-fluid approximation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alterman, Z., H. Jarosch and C.H. Pekeris: 1959, ‘Oscillation of the Earth’, Proc. R. Soc. London A 252, 80–95.
Capitaine, N. and N. Xiao: 1982, ‘Some terms of nutation derived from the BIH data’, Geophys. J. R. astr. Soc. 68, 805–814.
Daillet, S.: 1981, ‘Contribution à l'interprétation du mouvement du pôle par des phénomènes géophysiques, météorologiques et océanographiques’, Thesis, University Paul Sabatier, Toulouse, France.
Darwin, G.H.: 1877, ‘On the influence of Geological Changes on the Earth's Axis of Rotation’, Phil. Trans. R. Soc. London 167, part I, 271–312.
Euler, L.: 1749, Recherche sur la précession de équinoxes et sur la nutation de l'axe de la Terre, Berlin, H & M, 1749, 289.
Gwinn, C.R., T.A. Herring and I.I. Shapiro: 1986, ‘Geodesy by radiointerferometry: studies of forced nutations of the Earth 2, Interpretation’, J. Geophys. Res. 91, 4755–4765.
Hinderer, J., H. Legros and M. Amalvict: 1982, ‘A search of Chandler and nearly diurnal free wobbles using Liouville equations’, Geophys. J. R. astr. Soc. 71, 303–322.
Hinderer, J., D. Jault, H. Legros and J.L.Le Mouel: 1990, ‘Core-mantle topogrpahic torque: a spherical harmonic approach and implications for excitation of the Earth's rotation by core motions’, Phys. Earth Planet. Int. 59, 329–341.
Hough, B.A.: 1895, ‘The Oscillations of a Rotating Ellipsoidal Shell containing Fluid’, Phil. Trans. R. Soc. London 186, 469–505.
Lambeck, K.: 1980, The Earth's Variable Rotation, Cambridge University Press, 449 pp.
Landau, L. and E. Lifchitz: 1966, Mécanique, Edition de Moscou, 227 pp.
Legros, H.: 1987, ‘Sur quelques problèmes de dynamique planétaire’, Thesis, Université Louis Pasteur, Strasbourg, France.
Liouville, M.J.: 1859, Développements sur un chapitre de la Mécanique de Poisson, Additions à la connaissance des temps.
Merriam, J.B.: 1985, ‘Toroidal Love Numbers and transverse stress at the Earth's surface’, J. Geophys. Res. 90, B9, 7795–7802.
Milankovitch, M.: 1934, ‘Der Mechanismus des Polverlagerungen and die daraus sich ergebenden Polbahnkurven’, Gerlands Beitr. Geophys. 42, 70–97.
Molodensky, M.S.: 1961, ‘The theory of nutation and diurnal Earth tides’, Commun. Observ. Roy. Belg. 188, 25–56.
Munk, W.H. and G.J.F. Mac Donald: 1960, The rotation of the Earth, Cambridge University Press, London, 323 pp.
Neuberg, J., Hinderer J. and W. Zurn: 1987, ‘Stacking gravity tide observations in Central Europe for the retrieval of the complex eigenfrequency of the nearly diurnal free wobble’, Geophys. J. R. asir. Soc. 91, 853–868.
Newcomb, S.: 1892, ‘On the Dynamics of the Earth's Rotation with Respect to Periodic Variations of Latitude’, Monthly Not. R. Astr. Soc. 52, 336–341.
Peltier, WR.: 1974, ‘Impulse response of a Maxwell Earth’, Rev. Geophysics and Space physics 12, No 4, November 1974.
Poincare, H.: 1902, Figure d'équilibre d'une masse fluide, Paris, C. Naud Editeur.
Poincare, H.: 1910, ‘Sur la precession des corps déformables’, Bull. astr. 27, 321–356.
Rochester, M.G., O.G. Jensen and D.E. Smylie: 1974, ‘A search for the Earth's nearly diurnal free wobble’, Geophys. J. R. astr. Soc. 38, 349–363.
Runcorn, S.K.: 1984, ‘The primeval axis of rotation of the Moon’, Phil. Trans. R. Soc. London A 313, 77–83.
Runcorn, S.K., G.A. Wilkins, E. Groten, H. Lenhardt, J. Campbell, R. Hide, B.F. Chao, A. Souriau, J. Hinderer, H. Legros, J.L.Le Mouel and M. Feissel: 1988, ‘The excitation of the Chandler wobble’, Surveys in Geophysics 9, 419–449.
Sabadini, R. and W.R. Peltier: 1981, ‘Pleistocene deglaciation and the Earth's rotation implications for mantle viscosity’, Geophys. J. R. astr. Soc. 66, 553–578.
Sabadini, R., D. Yuen and E. Boschi: 1982, ‘Polar wandering and the forced responses of a rotating, multilayered, viscoelastic Earth’, J. Geophys. Res. 87, B4, 2885–2903.
Sabadini, R., D. Yuen and E. Boschi: 1984, ‘A comparison of the complete and truncated versions of the polar wander equations’, J. Geophys. Res. 89, B9, 7609–7620.
Sabadini, R., B. Smith and D. Yuen: 1987, ‘Consequences of experimental transient rheology’, Geophys. Res. Lett. 14, 8, 816–819.
Sabadini, R. and D. Yuen: 1989, ‘Mantle stratification and long-term polar wander’, Nature 339, June 1989.
Sasao, T., J. Okamoto and S. Sakai: 1977, ‘Dissipative core-mantle coupling and nutational motion of the Earth’, Publ. Astron. Soc. Japan 29, 83–105.
Sasao, T., S. Okubo and S. Masanori: 1980, ‘A simple theory on the dynamical effects of a stratified fluid core upon nutational motion of the Earth’, Proc. IAU symposium No 78, 1980.
Schultz, P.: 1986, ‘Le déplacement des poles sur Mars’, Pour la Science, Fevrier 1986.
Toomre, A.: 1974, ‘On the ‘nearly diurnal wobble’ of the Earth’, Geophys. J. R. astr. Soc. 38, 335–348.
Vondrak, J.: 1985, ‘Long-period behaviour of polar motion between 1900.0 and 1984.0’, Annales Geophysicae 3, 3, 351–356.
Wahr, J.M.: 1982, ‘The effects of the atmosphere and oceans on the Earth's wobble. I. Theory’, Geophys. J. R. astr. Soc. 70, 349–372.
Wahr, J.M.: 1983, ‘The effects of the atmosphere and oceans on the Earth's wobble and on seasonal variations in length of day, II Results’, Geophys. J. R. asir. Soc. 74, 451–487.
Wu, P. and W. Peltier: 1982, ‘Viscous gravitational relaxation’, Geophys. J. R. astr. Soc. 70, 435–485.
Yuen, D., R. Sabadini and E. Boschi: 1982, ‘Viscosity of the lower mantle as inferred from rotational data’, J. Geophys. Res. 87, B13, 10, 745–10, 762.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lefftz, M., Legros, H. & Hinderer, J. Non-linear equations for the rotation of a viscoelastic planet taking into account the influence of a liquid core. Celestial Mech Dyn Astr 52, 13–43 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00048585
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00048585