Abstract
Three Holcus mollis L. populations, one with 2n = 28 chromosomes living in a forest and two with 2n = 35 chromosomes, the first living in a forest, the second in open land, are compared for photosynthesis.
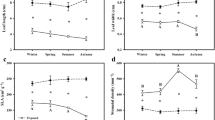
Simultaneous measurements of oxygen and carbon dioxide, either in high light, low light, or dark experiments indicate that the 2n = 28 chromosomes population is photosynthetically well adapted to shade, while 2n = 35 chromosomes forest population, is not.
The 2n = 35 chromosomes plants growing in the forest does not automatically acquire the photosynthetic character of a shade plant, the genome must show an evolution for this. In our study, only the plants with 2n = 28 chromosomes demonstrated the shade adaptation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azcon-Bieto, J., Lambers, M. & Day, D. A. 1983. The effect of photosynthesis and carbohydrate status on respiratory rates and the involvement of the alternative pathway in leaf respiration. Plant Physiol. 72: 598–603.
Badger, M. R. 1987. The CO2 concentrating mechanism in aquatic phototrophs. In the biochemistry of plants: A comprehensive treatise, vol. 10. Photosynthesis (ed M. D.Hatch, N.K.Boardman), pp. 219–274. Academic Press, New York.
Bajon, R. 1989. Etude biosystématique du complexe spécifique du Koeleria cristata (L.) Pers. s.l. (Poacées) en France. Thèse d'Etat. Orsay.
Beuret, F. 1977. Contribution à l'étude de la distribution géographique et de la physiologie de tacons affines di-et polyploïdes. Bibliotheca botanica 133: 1–80.
Bidault, M. 1968. Essai de taxonomie expérimentale et numérique sur Festuca ovina L. s.l. dans le sud-est de la France. Rev. Cytol. et Biol. vég. 31: 217–356.
Byrne, M. C. 1981. Ploïdy effects on anatomy and gas exchange of tall fescue. Plant physiol. 68: 891–893.
Cornic, G., LeGouallec, J.-L., Briantais, J.-M. & Hodges, M. 1989. Effect of dehydration and high light on photosynthesis of two C3 plants (Phaseolus vulgaris L. and Elastostema repens (Lour) Hall f.). Planta 177(1): 84–90.
Evans, J. R. 1987. Quantum yield, Wavelength and irradiance. Austr. J. Plant Physiol. 14: 69–79.
Hiesey, W. M., Mobs, M. A. & Björkman, O. 1971. Experimental studies on the nature of species, V. Biosystematics, genetics and physiological ecology of the Erythranthe section of Mimulus. Carnegie Inst. Wash Publ. no 628.
Jones, K. 1958. Cytotaxonomic studies in Holcus I. The chromosome complex in Holcus mollis L., New Phytologist (vol. 57(2): 191–210.
Khalfallah, N. 1981. Contribution à l'étude biosystématique du genre Arrhenatherum Beauv. en France. Thèse de 3ème cycle. Orsay.
Kirschbaum, M. V. F. & Pearcy, R. W. 1988. Gas exchange analysis of the relative importance of stomatal and biochemical factors in photosynthetic induction in Alocasia macrorrhiza. Plant Physiol. 86: 782–785.
Lamade, E. 1988. Comparison des cytotypes tétraploïde et pentaploïde de l'espèce Holcus mollis L. en région parisienne. Aspects biosystématique et écophysiologique. Thèse de Docteur en sciences. Orsay.
Leclerc, J. C. & Abd el Rahman, N. 1988. Crise de l'intensité de la photosynthèse au cours de la croissance de jeunes plantes de maïs. Etude avec un appareillage nouveau. C.R. Acad. Sci. Paris, 306, série III, 421–426.
Levin, D. A. 1983. Polyploïdy and novelty in flowering plants. The American Naturalist 122(1): 1–25.
Moroney, J. V., Husic, H. D., Tolbert, N. E., Kitayama, M., Manuel, L. J. & Tobasaki, R. K. 1989. Isolation and characterization of a mutant of Chlamydomas reinhardtii deficient in the CO2 concentrating mechanism. Plant Physiol. 89: 897–903.
Osborne, B. A. & Geider, J. 1987. Photorequirement for growth of the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum Bohlin (Bacillariophyceae). Plant cell environ. 10: 141–149.
Prioul, J. L. 1982. Limiting factors in photosynthesis, from the chloroplast to the plant canopy. In Trends in Photobiology (ed. Helène C., Charlier M., Montenay-Garestier Th. & Laustriat G.), p. 633–643. Plenum publishing corporation.
Sharp, R. E., Matthews, M. A. & Boyer, J. S. 1984. The Kok effect and the quantum yield of photosynthesis. Plant Physiol. 75: 95–101.
Teskey, R. O. & Shrestha, R. B. 1985. A relationship between carbon dioxide, photosynthetic efficiency and shade tolerance. Physiol. Plant. 63: 126–132.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leclerc, J.C., Blaise, S. Photosynthetic and genetic differentiation in sun and shade populations of Holcus mollis L.. Vegetatio 92, 85–93 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00047134
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00047134