Abstract
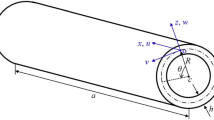
Finite axisymmetric deformation of a hollow circular cylinder with a finite length, composed of a neo-Hookean material, is studied. The inner surface of the tube is subjected to both normal and tangential tractions, while the outer surface is free of tractions. The cylinder will undergo both radial and axial deformations. An asymptotic-expansion method is used to determine the stress and shape of the deformed tube. The deformed radial and axial coordinates, the stress tensor and the surface tractions are expanded into a power series of an appropriate thickness parameter. A hierarchy of equilibrium equations, boundary conditions and constitutive equation are derived following the usual procedure. The theories corresponding to the lowest two order members in this hierarchy are studied in detail. It is shown that the zeroth-order theory corresponds to the membrane theory. The shape of the deformed tube, up to the second-order in the thickness parameter, is determined in terms of the zeroth-order radial and axial deformations. The zeroth-order radial and axial deformations are governed by a coupled pair of nonlinear ordinary differential equations, both of which are of second order. For illustrative purposes the present approach is then applied to a simple representative problem: simultaneous extension and inflation of a cylindrical elastic tube. Finally, the solutions corresponding to the zeroth and first-order approximations of the present theory and the exact solutions obtained from finite elasticity theory are compared for the above-mentioned problem.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A.E. Green and W. Zerna, Theoretical Elasticity, Second edition, Oxford University Press, London (1968).
A.E. Green and J.E. Adkins, Large Elastic Deformations, Second edition, Clarendon Press, Oxford (1970).
R.W. Ogden, Non-Linear Elastic Deformations, Ellis Horwood Limited, West Sussex (1984).
A.D. Kydoniefs and A.J.M. Spencer, Finite deformation analysis of a thin-walled tube sliding on a rough rigid rod. J. Engng. math. 21 (1987) 363–377.
Y.C. Fung, Biodynamics: Circulation, Springer-Verlag, New York (1984).
V.G. Hart and J. Shi, Joined dissimilar elastic thin tubes containing steady viscous flow. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 40 (1992) 1507–1527.
Z. Rigbi and Y. Hiram, An approximate method for the study of large deformations of membranes. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 23 (1981) 1–10.
W.H. Yang and W.W. Feng, On axisymmetrical deformations of nonlinear membranes. J. Appl. Mech. ASME 37 (1970) 1002–1011.
A.D. Kydoniefs and A.J.M. Spencer, Finite axisymmetric deformations of an initially cylindrical elastic membrane. Quart. J. Mech. Appl. Math. 22 (1969) 87–95.
C.H. Wu, On certain integrable nonlinear membrane solutions. Quart. Appl. Math. 28 (1971) 81–90.
R.E. Khayat, A. Derdouri and A. Garcia-Rejon, Inflation of an elastic cylindrical membrane: non-linear deformation and instability. Int. J. Solids Structures 29 (1992) 69–87.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erbay, H.A., Demiray, H. Finite axisymmetric deformations of elastic tubes: An approximate method. J Eng Math 29, 451–472 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00043978
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00043978