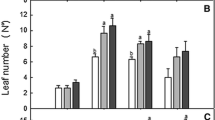
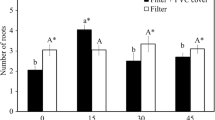
Abstract
The establishment of microplants has been shown to be related to the moisture vapour transmission rate of the culture vessel lid. Lids allowing high moisture vapour loss from the container give increased microplant establishment rates. Further, it has been shown that calcium accumulation in the leaves of microplants is correlated with the moisture vapour transmission rate of the vessel lid and this is related to stomatal function in vitro and ex vitrum and to decreased desiccation in the microplants. It is hypothesized that the increased moisture vapour transmission rate of the lid results in increased transpiration in vitro, which in turn causes increased calcium uptake into the leaves of the microplants with consequential increased stomatal function and reduced losses due to desiccation ex vitrum.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MVTR:
-
moisture vapour transmission rate
References
Brainerd, KE & Fuchigami, LH (1981) Acclimatization of aseptically cultured apple plants to low relative humidity. J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 156: 515–518
Cassells AC (1987) Plant container. European patent no. 87 9025781
Cassells, AC (1991) Screening for pathogens and contaminating organisms in micropropagation. In: Duncan, JM & Torrance, L (Eds) Techniques for the Rapid Diagnosis of Plant Pathogens (pp 179–191) Blackwell, Oxford
Cassells, AC & Minas, GJ (1993) Plant and in vitro factors influencing the micropropagation of ornamental plants by tissue culture. Scientia Hort. 21: 53–65
Cassells, A & Roche, T (1993) The influence of the gas permeability of the vessel lid and growthrooms light intensity on the characteristics of Dianthus microplants in vitro and ex vitrum. In: Lumsden, PJ, Nicholas, JR & Davies, WJ (Eds) Physiology, Growth and Development of Plants and Cells in Culture (in press) Kluwer, Dordrecht
Cassells AC, Walsh C & Periappuram C (1993) Diplontic selection as a positive factor in determining the fitness of mutants of Diantus ‘Mystere’ derived from x-irradiation of nodes in in vitro culture. Euphytzca (in press)
Clarkson, DT (1984) Calcium transport between tissues and its distribution in the plant. Plant Cell Environ. 7: 449–456
Conner, LN & Conner, AJ (1984) Comparative water loss from leaves of Solanum laciniatum plants cultured in vitro and in vivo. Plant Sci. Lett. 36: 241–246
Debergh, P, Aitken-Christie, J, Cohen, D, Grout, B, vonArnold, S, Zimmerman, RH & Ziv, M (1992) Reconsideration of the term ‘vitrification’ as used in micropropagation. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 30: 135–140
Dillen, W & Buysens, S (1989) A simple technique to overcome vitrification in Gypsophila paniculata. Plant Cell. Tiss. Org. Cult. 19: 181–188
Geerts, M, vanCleemput, O & Debergh, PC (1987) Translocation of calcium in micropropagated Prunus avium L. Med. Fac. Landbouww. Rijksuniv. Gent 52: 1449–1456
Ghashghaie, J, Brenckmann, F & Saugier, B (1992) Water relations and growth of rose plants cultured in vitro under various relative humidities. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 30: 51–57
Ho, LC (1989) Environmental effects on the annual accumulation of 45Ca by young fruit and leaves of tomato plants. Ann. Bot. 63: 281–288
Humphries, EC (1956) Mineral components and ash analysis. In: Paech, K & Tracey, MV (Eds) Modern Methods of Plant Analysis (pp 468–503). Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Kerstiens, G (1993) Cuticular development. In: Lumsden, PJ, Nicholas, JR & Davies, WJ (Eds) Physiology, Growth and Development of Plants and Cells in Culture (in press) Kluwer, Dordrecht
Kozai, T (1991) Acclimatization of micropropagated plants. In: Bajaj, YPS (Ed) Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry, Vol 17 (pp 127–141), Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Kurtz, SL, Hartman, RD & Chu, IY (1991) Current methods of commercial micropropagation. In: Vasil, IK (Ed) Scale-up and Automation in Plant Propagation (pp 7–35), Academic Press, New York
Leary, NO, Pembroke, A & Duggan, PF (1992) Single stable reagent (arsenazo III) for optically robust measurements of calcium in serum and plasma. Clin. Chem 38: 904–908
Maerten E (1976) De invloed van enkele hydrocolloiden op de textuur van levensmiddelen. Thesis, Faculty of Agriculture, University of Gent
Mansfield, TA (1993) Stomata. In: Lumsden, PJ, Nicholas, JR & Davies, WJ (Eds) Physiology, Growth and Development of Plants and Cells in Culture (in press) Kluwer, Dordrecht
Mansfield, TA, Hetherington, AM & Atkinson, CJ (1990) Some current aspects of stomatal physiology. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 41: 55–75
Moncousin, C (1991) Rooting of in vitro cuttings. In: Bajaj, YPS (Ed) Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry, Vol 17 (pp 231–261). Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Murashige, T & Skoog, F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio-assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Plant Physiol. 15: 473–497
Preece, JE & Sutter, EG (1991) Acclimatization of micropropagated plants to the greenhouse and field. In: Debergh, PC & Zimmerman, RH (Eds) Micropropagation: Technology and Application (pp 71–93) Kluwer, Dordrecht
Sallanon, H & Maziere, Y (1992) Influence of growth room and vessel humidity on the in vitro development of rose plants. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 30: 121–125
Sha, L, McCown, BH & Peterson, LA (1985) Occurrence and cause of shoot-tip necrosis in shoot cultures. J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 110: 631–634
Singha, S, Townsend, EC & Oberly, GH (1990) Relationship between calcium and agar on vitrification and shoot-tip necrosis of quince (Cydonia oblonga Mill.) shoots in vitro. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 23: 135–142
Sutter, E (1985) Morphological, physical and chemical characteristics of epicuticular wax on ornamentals regenerated in vitro. Ann. Bot. 55: 234–238
Sutter, E & Langhans, RW (1982) Formation of epicuticular wax and its effect on water loss in cabbage plants regenerated from shoot tip culture. Can. J. Bot. 60: 2896–2902
Swietlik, D, Bunce, JA & Miller, SS (1984) Effect of foliar application of mineral nutrients on stomatal aperture and photosynthesis in apple seedlings. J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 109: 306–312
Tanaka, M, Jinno, F & Kozai, T (1988) The use of disposable fluorocarbon polymer film culture vessels on micropropagation. Acta Hort. 230: 73–80
Vanderschaeghe AM & Debergh PC (1987) Technical aspects of the control of the relative humidity on tissue culture containers. In: Ducate G, Jacob M & Simeon A (Eds) Plant Micropropagation in Horticultural Industries (pp 68–76), Presses Universitaires Liege
Wardle, K & Short, KC (1983) Stomatal responses of in vitro cultured plantlets I. Responses in epidermal strips of chrysanthemum to environmental factors and growth regulators. Biochem. Physiol. Pflanzen 178: 619–624
Zeiger, E, Farquar, GD & Cowan, IR (1987) Stomatal Function. Stanford Univ. Press, Stanford.
Ziv, M (1991) Vitrification: morphological and physiological disorder of in vitro plants. In: Debergh, PC & Zimmerman, RH (Eds) Micropropagation: Technology and Application (pp 45–69) Kluwer, Dordrecht
Ziv, M, Schwartz, A & Fleminger, D (1987) Malfunctioning of stomata in vitreous leaves of carnation (Dianthus caryophyllus) plants propagated in vitro; implications for the hardening. Plant Sci. 52: 127–134
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cassells, A.C., Walsh, C. The influence of gas permeability of the culture lid on calcium uptake and stomatal function in Dianthus microplants. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 37, 171–178 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00043612
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00043612