Abstract
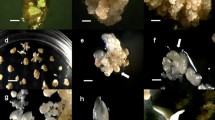
Plantlet regeneration through somatic embryogenesis has been achieved in the apocynaceous medicinal treeThevetia peruviana L. Calluses obtained by culturing young leaf discs on MS medium containing 9 μM 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and 4.6 μM kinetin, when subjected to reduced levels of the growth regulators followed by higher cytokinin treatment, produced numerous somatic embryos. Somatic embryos developed into complete plantlets on a medium devoid of growth regulators. An average of 40–50 plantlets were obtained from 50 mg of embryogenic callus. Survival of transplants was 60% under glasshouse conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Backs-Husemann D & Reinert J (1970) Embryos formation by isolated single cells from tissue culture ofDaucus carota. Protoplasma 70: 49–60
Bhakuni DS (1990) Drugs from plants. Sci. Rep. 8: 12–17
Dasgupta M & Datta SK (1987) Tissue culture, cytology and pharmacognostic evaluation ofThevetia peruviana. In: Chauhan YS (Ed) Biology, Cultivation and Utilization of Some Medicinal and Aromatic Plants (pp 49–57), Meghalaya Science Society, Shillong
Eapen S & George L (1989) High frequency plant regeneration through somatic embryogenesis in finger millet (Eleusine caracana Gaertn.). Plant Sci. 61: 127–130
Guimaraes MLS, Cruz GS & Montezuma-de-Carvalho JM (1988) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration inCyphomandra betacea (Cav.) Sendt. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 15: 161–167
Haccius B (1978) Question of unicellular origin of nonzygotic embryos in callus culture. Phytomorphology 28: 74–81
Halperin W (1969) Morphogenesis in cell cultures. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 21: 395–418
Konar RN, Thomas E & Street HE (1972) Origin and structure of embryoids arising from epidermal cells of the stem ofRanunculus scleratus L. J. Cell Sci. 11: 77–93
Larkin P J & Scowcroft WR (1981) Somaclonal variation — a novel source of variability from cell cultures for plant improvement. Theor. Appl. Genet. 60: 197–214
Mariotti D & Arcioni S (1983) Callus culture ofCoronilia varia L. (Crownvetch): plant regeneration through somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult. 2: 103–110
McWilliam AA, Smith SM & Street HE (1974) The origin and development of embryoids in suspension cultures of carrot. Ann. Bot. 38: 243–250
Murashige T & Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–497
Pierson ES, Van Lemmeren AAM, Schel THN & Staritsky G (1983)In vitro development of embryoids from punched leaf discs ofCoffea canephora. Protoplasma 115: 208–216
Scowcroft WR (1977) Somatic cell genetics and plant improvement. Adv. Agron. 29: 39–81
Thomas E, King PJ & Potrykus I (1979) Improvement of crop plants via single cellin vitro: an assessment. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 82: 1–30
von Arnold S & Wallin A (1988) Tissue culture methods for clonal propagation of forest trees. Intl. Assoc. Plant Tissue Culture Newsl. 56: 2–13
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, A. Somatic embryogenesis and high frequency plantlet regeneration in callus cultures ofThevetia peruviana . Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 31, 47–50 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00043474
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00043474