Summary
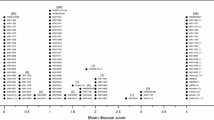
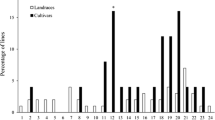
Hordeum chilense is a wild barley with high crossability with Triticum, Hordeum and Secale. Its amphiploid with wheat, tritordeum, has potential as a new crop. H. chilense is highly resistant to the powdery mildew diseases of both wheat and barley. Whereas tritordeum is resistant to barley powdery mildew, its reaction to wheat powdery mildew is similar to that of its wheat parent. However H. chilense contributes to a reduced density of mildew colonies. This quantitative resistance of tritordeum is diluted at higher ploidy levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AlvarezJ.B., J.Ballesteros, J.A.Sillero & L.M.Martín, 1992. Tritordeum: a new crop of potential importance in the food industry. Hereditas 116: 193–197.
AsherM.J.C. & C.E.Thomas, 1983. The expression of partial resistance to Erysiphe graminis in spring barley. Plant Pathology 32: 79–89.
BennettF.G.A., 1984. Resistance to powdery mildew in wheat: a review of its use in agriculture and breeding programmes. Plant Pathology 33: 279–300.
Bothmer, R., N. Jacobsen, C. Baden, E.B. Jorgensen & I. Linde-Laursen, 1991. An ecogeographical study of the genus Hordeum. Rome IBPGR.
CuberoJ.I., A.Martín, T.Millán, A.Gómez-Cabrera & A.deHaro, 1986. Tritordeum: a new alloploid of potential importance as a protein source crop. Crop Science 26: 1186–1190.
DosbaF., A.M.Tanguy & G.Donaire, 1980. Study of the characteristics linked to an Mv chromosome of Aegilops ventricosa in an addition line wheat x Aegilops. Cereal Res. Comm. 8: 501–507.
FinchR.A. & M.D.Bennett, 1980. Mitotic and meiotic chromosome behaviour in new hybrids of Hordeum with Triticum and Secale. Heredity 44: 201–209.
GustafssonM. & L.Claesson, 1988. Resistance to powdery mildew in wild species of barley. Hereditas 108: 231–237.
HeunM. & B.Friebe, 1990. Introgression of powdery mildew resistance from rye into wheat. Phytopathology 80: 242–245.
JahoorA. & G.Fishbeck, 1987. Genetical studies of resistance of powdery mildew in barley lines derived from Hordeum spontaneum collected from Israel. Plant Breeding 99: 265–273.
JohnsonR., 1984. A critical analysis of durable resistance. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 22: 309–330.
JorgensenJ.H., 1992. Sources and genetics of resistance to fungal pathogens. In: P.R.Shewry (Ed.) Barley: Genetics, Biochemistry, Molecular Biology and Biotechnology. C.A.B. International, U.K., pp. 441–457.
Linde-LaursenI., 1977. Reaction of triticale, wheat and rye to the powdery mildew fungi, Erysiphe graminis f. sp. tritici and E. graminis f. sp. secalis. Z. Planzenzüchtg. 79: 110–121.
MartínA., 1988. Tritordeum: the first ten years. Rachis 7: 12–15.
Martín, A., 1991. Cytology of a hybrid between barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) and tritordeum (x Tritordeum Ascherson et Gaebner). Barley Genetics VI, pp. 83–84.
MartínA. & J.I.Cubero, 1981. The use of Hordeum chilense in cereal breeding. Cereal Res. Comm. 9: 317–323.
MosemanJ.G., R.C.F.Macer & L.W.Greeley, 1965. Genetic studies with cultures of Erysiphe graminis f. sp. hordei virulent on Hordeum spontaneum. Trans Br. Mycol. Soc. 48: 479–489.
ParlevlietJ.E., 1978. Race-specific aspects of polygenic resistance of barley to leaf rust Puccinia hordei. Neth. J. Plant Pathol. 84: 121–126.
RiginB. & T.V.Lebedeva, 1990. (Interaction of the wheat and rye genomes in the control of resistance to powdery mildew). (Genetike i Seletktsii) Plant Breeding Abstracts 61: 1279, abstract 9969.
RoyerM.H., R.R.Nelson, D.R.MacKenzie & D.A.Diehle, 1984. Partial resistance of near-isogenic wheat lines compatible with Erysiphe graminis f. sp. tritici. Phytopatology 74: 1001–1006.
RubialesD., J.Ballesteros & A.Martín, 1991. The reaction of x Tritordeum and its Triticum spp. and Hordeum chilense parents to rust diseases. Euphytica 54: 75–81.
RubialesD., J.Ballesteros & A.Martín, 1992a. Resistance to Septoria tritici in Hordeum chilense x Triticum spp. amphiploids. Plant Breeding, 109: 281–286.
RubialesD., R.E.Niks, R.G.Dekens & A.Martín, 1993. Histology of the infection of x Tritordeum and its parents by cereal brown rusts. Plant Pathology 42: 93–99.
RubialesD., M.C.Ramírez & R.E.Niks, 1992b. The contribution of Hordeum chilense to partial resistance of tritordeum to wheat brown rust. Euphytica 59: 129–133.
SinigovetsM.E. & G.D.Lapchenko, 1975. (Location of resistance to Erysiphe graminis f.sp. tritici in the chromosomes of Agropyron intermedium). (Tsitologiya i Genetika 9: 439–442) Plant Breeding Abstracts 46: 180. Abstract num. 2224.
WahlI., E.Nava, E.Sega & Z.Sobel, 1978. Significance of wild relatives of small grains and other wild grasses in cereal powdery mildews. In: D.M.Spencer (Ed.), The powdery mildews, pp. 83–100. Academic Press, London.
XuJ. & J.W.Snape, 1989. The resistance of Hordeum bulbosum and its hybrids with H. vulgare to common fungal pathogens. Euphytica 41: 273–276.
XuJ. & K.J.Kasha, 1992. Transfer of a dominant gene for powdery mildew resistance and DNA from Hordeum bulbosum into cultivated barley (H. vulgare). Theor. Appl. Genet. 84: 771–777.
ZellerF.J. & M.Heun, 1985. The incorporation and characterization of powdery mildew resistance from Aegilops longissima in common wheat (T. aestivum L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 71: 513–517.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rubiales, D., Brown, J.K.M. & Martín, A. Hordeum chilense resistance to powdery mildew and its potential use in cereal breeding. Euphytica 67, 215–220 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00040623
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00040623