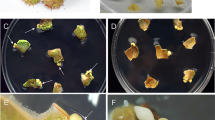
Abstract
Somatic embryogenesis and plantlet formation were obtained from 60–75 day old cell cultures of carnation. Callus was generated on MS basal medium supplemented with 2,4-dichchlorophenoxy acetic acid (2,4-D). Removal of 2,4-D during subsequent subculturing of cell suspensions resulted in formation of embroids. These somatic embryos originated from single cells and their early development proceeded normally with clearly defined apical and root meristems. Some embryos developed into plants and were acclimatized to ex vitro conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BAP:
-
6-benzylaminopurine
- Kinetin:
-
6-furfurylamino purine
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-dichlorophenoxy acetic acid
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog
References
Ammirato P (1983) Embryogenesis. In: Evans D, Sharp W, Ammirato P and Yamada Y (eds) Handbook of plant cell culture, Vol 1, pp 82–123. New York: Mac Millan publishing company
Boulary MP, Gupta PK, Krogstrup P and Durzan DJ (1988) Development of somatic embryos from cell suspension culture of Norway spruce (Picea abies Karst). Plant Cell Rep 7: 134–137
Choudhary ML (1991) Vegetative propagation of carnation in vitro through multiple shoot development. Indian J Hort 48(2): 1–3
Choudhary ML and Prakash P (1991) Effect of different levels of agar and MS macrosalts on the production of hardened Carnation in vitro. New Agriculturist 1 (2): 191–193
Charles HM and Edmundo B (1991) High frequency somatic embryogenesis from leaf tissue of Populus spps. Plant Science 77: 111–118
Chin YL, Greg N and Terese W (1990) Efficient direct regeneration from stem segments of Chrysanthemum. Plant Cell Rep 8: 733–736
Erler and Siegmund (1986) Yearbook of the International Horticultural Statistics. WH Freeman and Company, New York, pp 44
Gerg N, Terse WR and Chin YL (1991) Plant regeneration from stem and petal of Carnation (Dianthus Caryophyllus). Plant Cell Report 10: 477–480
Murashige T and Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassay with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15: 473–497
Vasil IK (1985) In: Henke RR, Hughes KW, Constanin MJ and Hollaender A (eds) Tissue Culture in Forestry & Agriculture, pp 31–48. New York: Plenum Press
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choudhary, M.L., Chin, CK. Somatic embryogenesis in cell suspension culture of carnation (Dianthus caryophyllus L.). Plant Growth Regul 16, 1–4 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00040500
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00040500