Summary
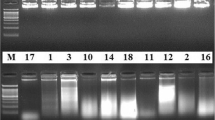
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR), with single ten-base-long nucleotide primers, was used to amplify random regions of genomic DNA from eleven diploid meiotic mutants (2n egg, 2n pollen and jumbo pollen producers) of the Medicago sativa-coerulea-falcata complex. Electrophoretic patterns of the resulting random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD) fragments were evaluated to develop a graphical representation of amplification products from which conserved and individual-specific markers could be readily identified. Oligonucleotide primers differed significantly in their capacity of detecting polymorphism. Jumbo pollen (jp) mutants showed higher levels of similarity, as proportion of shared amplification products, than 2n pollen mutants. A diploid plant of alfalfa, tested for the occurrence of two mechanisms of unreduced egg formation (second division restitution and apomeiosis) was analyzed to obtain genome specific fingerprints. This PCR-based characterization could be used to determine whether the apomeiotic 2n eggs develop through parthenogenesis. The application of RAPD markers for germplasm evaluation and alfalfa improvement programs is also discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barcaccia, G., 1994. Development, comparability and potential applications of RAPD markers in the genus Medicago. J. Genet. & Breed. 48: 161–168.
Bingham, E.T., 1980. Maximizing heterozygosity in autopolyploids. In: W.H., Lewis (Ed.) Polyploidy: biological relevance, pp. 471–489. Plenum Press, New York.
Busbice, T.H. & C.P., Wilsie, 1966. Inbreeding depression and heterosis in autotetraploids with application to Medicago sativa L. Euphytica 15: 52–67.
Dellaporta, S.L., J., Wood & J.B., Hicks, 1983. A plant DNA minipreparation: Version II. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 4: 19–21.
Echt, C.S., L.A., Erdahl & T.J., McCoy, 1992. Genetic segregation of random amplified polymorphic DNA in diploid cultivated alfalfa. Genome 35: 84–87.
Mariani, A., S., Tavoletti & F., Veronesi, 1993. Abnormal macrosporogenesis in five alfalfa (Medicago sativa) mutants producing 4n pollen. Theor. Appl. Genet. 85: 873–881.
McCoy, T.J. & L.Y., Smith, 1983. Genetics, cytology, and crossing behavior of an alfalfa (Medicago sativa) mutant resulting in failure of the postmeiotic cytokinesis. Can. J. Genet. Cytol. 25: 390–397.
McCoy, T.J. & C.S. Echt, 1992. Chromosome manipulations and genetic analysis in Medicago. In: J.W. Dudley, A.R. Hallauer, R.E. Veilleux (Eds). Plant Breeding Reviews, Vol. 10: 169–197.
Nei, M. & W.H., Li, 1979. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76: 5269–5273.
Nogler, G.A., 1984. Gametophytic apomixis. In: B.M., Johri (Ed.). Embryology of angiosperms, pp. 475–518 Springer-Verlag, New York.
Pfeiffer, T.W. & E.T., Bingham, 1983. Abnormal meiosis in alfalfa, Medicago sativa: cytology of 2n eggs and 4n pollen formation. Can. J. Genet. Cytol. 25: 107–112.
Tavoletti, S., A., Mariani & F., Veronesi, 1991. Cytological analysis of macro- and microsporogenesis of a diploid alfalfa clone producing male and female 2n gametes. Crop Sci. 31: 1258–1263.
Tavoletti, S., 1994. Cytological mechanisms of 2n egg formation in a diploid genotype of Medicago sativa subsp. falcata. Euphytica 75: 1–8.
Veronesi, F., A., Mariani & E.T., Bingham, 1986. Unreduced gametes in diploid Medicago and their importance in alfalfa breeding. Theor. Appl. Genet. 72: 37–41.
Veronesi, F., A., Mariani & S., Tavoletti, 1988. Screening for 2n gamete producers in diploid species of genus Medicago. Genet. Agr. 42: 187–200.
Vorsa, N. & E.T., Bingham, 1979. Cytology of 2n pollen formation in diploid alfalfa, Medicago sativa. Can. J. Genet. Cytol. 21: 525–530.
Waugh, R. & W., Powell, 1992. Using RAPD markers for crop improvement. Trends Biotech. 10: 186–191.
Welsh, J. & M., McClelland, 1990. Fingerpringting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 24: 7213–7218.
Wilde, J., R., Waugh & W., Powell, 1992. Genetic fingerprinting of Theobroma clones using randomly amplified polymorphic DNA markers. Theor. Appl. Genet. 83: 871–877.
Williams, J.G.K., A.R., Kubelik, K.J., Livak, J.A., Rafalski & S.V., Tingey, 1990. DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 22: 6531–6535.
Yu, K. & K.P., Pauls, 1992. Optimization of the PCR program for RAPD analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 10: 2606.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barcaccia, G., Tavoletti, S., Pezzotti, M. et al. Fingerprinting of alfalfa meiotic mutants using RAPD markers. Euphytica 80, 19–25 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00039294
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00039294