Summary
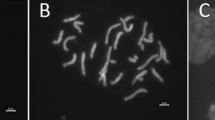
Crossing experiments involving the various groups of Solanum macrocarpon L. complex, including wild (dasyphyllum), semi-wild and cultivars produced fully fertile F1 and F2 hybrids. This confirmed earlier findings that these groups belong to the same biological species. S. macrocarpon complex and S. linnaeanum Hepper ex Jaeger are isolated by reproductive barriers. F1 and F2 hybrids between various groups of S. macrocarpon showed heterosis. F2 superior hybrids were isolated as candidates for the future breeding programmes. Most wild-type traits like prickliness, hairiness were dominant to those possessed by cultivars. Relatively resistant hybrids to pest attack were noted. S. macrocarpon complex and S. linnaeanum are diploids (2n=24). The overall nature of the karyotype suggests that the two are related. The F1 hybrids between the cultivars of S. macrocarpon and the wild group (S. dasyphyllum) showed normal meiosis. A lack of isolating barriers confirmed that S. macrocarpon complex constitute a single biological species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anaso, H.U., 1991. Comparative cytological study of Solanum aethiopicum Gilo group, Solanum aethiopicum Shum group and S. anguivi. Euphytica 53 (2): 81–86.
Anderson, G.J., 1979. Systematic and evolutionary consideration of species of Solanum section Basarthrum. Linnaean Society Symposium 7: 549–562.
Bohs, L., 1989. Solanum allophyllum (Miers) Stand 1. and the genetic delimitation of Cyphomandra and Solanum (Solanaceae). Annals of the Missouri Botanical Garden, 76: 1129–1140.
Brink, R.A. & D.C. Cooper, 1947. The endosperm in seed development. Botanical Review, 13: 423–541.
Bukenya, Z.R., 1980. Studies in Taxonomy of Solanum L. in Southern Ghana. M.Sc. Thesis, University of Ghana, Legon.
Bukenya, Z.R., 1993. Studies in the Taxonomy of genus Solanum in Uganda. Ph.D. Thesis, Makerere University.
Bukenya, Z.R. & J.B. Hall, 1987. Six cultivars of Solanum macrocarpon (Solanaceae) in Ghana. Bothalia, 17: 91–95.
Ganapathi, A., 1987. Phyletic relationship of some tetraploid taxa of the Solanum L. sect Solanum (Maurella). Israel Journal of Botany and Basic Applied Plant Science, 36: 31–39.
Grun, P., 1961. Early stages in the formation of internal barriers to gene exchange between diploid species of Solanum. American Journal of Botany, 48: 79–89.
Kuriachan, P., 1979. Cytogenetic studies on Solanum macrocarpon x Solanum melongena hybrid and its colchiploid. Indian Journal of Botany, 2(2): 159–165.
Lester, R.N., 1989. Evolution under domestication involving disturbance of genic balance. Euphytica, 44: 125–132.
Lester, R.N. & L. Niakan, 1986. Origin and domestication of scarlet eggplant (S. aethiopicum L. from S. anguivi Lam.). In W.G. D'Arcy, Solanaceae: Biology and Systematics: 433–456. Columbia University Press. New York.
Lester, R.N. & G.N.W. Thitai, 1989. Inheritance in Solanum aethiopicum, the scarlet eggplant. Euphytica, 40: 67–74.
Levin, D.A., 1971. The origin of reproductive isolating mechanisms in flowering plants. Taxon, 20: 91–113.
Lopez, L. & J.G. Hawkes, 1991. Cytology and genome constitution of wild tuber-bearing Solanum species in the series Conicibaccata. Solanaceae 111: 327–346. The Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, Richmond, Surrey, U.K.
Narasimha Rao, N. 1979. The barriers to hybridization between Solanum melongena and some other species of Solanum. Linnaean Society Symposium, 7: 605–614. London, Academic Press.
Omidiji, M.O., 1979. Crossability relationships between some species of Solanum, Lycopersicon and Capsicum cultivated in Nigeria. Linnaean Society Symposium, 7: 599–604. London, Academic Press.
Omidiji, M.O., 1986. The role of hybridization in the evolution of Solanum species in the sub-genus Leptostemonum (Dun.) Bitt. In: W.G.D' Arcy (Ed.). Solanaceae: Biology and Systematics. Columbia University Press, New York.
Pearce, K. & R.N. Lester, 1979. Chemotaxonomy of the cultivars of eggplant: A new look at the taxonomic relationships of Solanum melongena L. Linnaean Society Symposium 7: 615–627. London, Academic Press.
Pringle, G.J. & B.G. Murray, 1991. Karyotype diversity and nuclear DNA variation in Cyphomandra. Solanaceae 111: 247–252. The Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, Richmond. Surrey, U.K.
Ramanna, M.S. & J.G. Th. Hermsen, 1979. Genome relationships in tuber bearing Solanums. Linnaean Society Symposium 7: 647–653. London, Academic Press.
Wann, E.V. & K.W. Johnson, 1963. Inter-generic hybridization involving species of Solanum and Lycopersicon. Botanical Gazette, 124: 451–455.
Whalen, M.D., 1984. Conspectus of species Groups in Solanum subgenus Leptostemonum. Gentes Herbarum 12(4): 179–282.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bukenya, Z.R., Carasco, J.F. Crossability and cytological studies in Solanum macrocarpon and Solanum linnaeanum (Solanaceae).. Euphytica 86, 5–13 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00035933
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00035933