Abstract
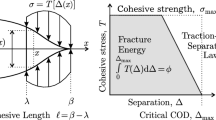
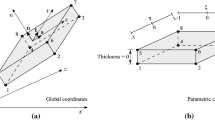
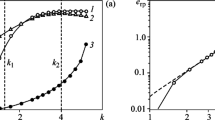
Based on discontinuous displacement approximation of the continuum and ‘shear band’ kinematics, two cohesive crack models are derived within the constitutive framework of coupled damage and plasticity. The models employ the Rankine fracture criterion, and the model parameters are determined from a uniaxial tension test (mode I cracking). Bifurcation analysis is used in order to diagnose critical directions along which the crack will gradually develop and propagate. These directions depend on the actual stress state and are kept fixed after fracture has initiated, whereby a ‘fixed crack’ model is obtained. A ‘discrete crack’ strategy is employed at the finite element implementation in the sense that interfaces (that represent the cohesive crack) are introduced along inter-element boundaries. This implementation strategy calls for gradual realignment of the mesh as a key feature of the algorithm. Numerical results from the analysis of mixed mode fracture in a notched concrete plate are presented.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. Hillerborg, M. Modéer and P.E. Petersson, Cement and Concrete Research 6 (1976) 773–782.
M. Klisinski, K. Runesson and S. Sture, Journal of Engineering Mechanics, ASCE 117 (1991) 575–587.
E.N. Dvorkin, A.M. Cuitino and G. Gioia, International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering 30 (1990) 541–564.
J.G. Rots and R.de Borst, Journal of Engineering Mechanics, ASCE 113 (1987) 1739–1758.
O. Dahlbom and N.S. Ottosen, Journal of Engineering Mechanics, ASCE 116 (1990) 55–76.
R. Larsson, K. Runesson and N.S. Ottosen, International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering 36 (1993) 2087–2105.
B. Halphen and Q.S. Nguyen, Journal de Mecanique 14 (1975) 39–63.
J. Lemaitre, A Course on Damage Mechanics, Springer-Verlag, Berlin (1992).
K. Runesson, N.S. Ottosen and D. Peric, International Journal of Plasticity 7 (1991) 99–121.
Z.P. Bazant and B.H. Oh, Materials and Structures (RILEM) 16 (1983) 155–177.
R. Hill, Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 10 (1962) 1–16.
J. Mandel, in Proceedings of IUTAM Symposium on Rheology and Soil-Mechanics, J. Kravtchenko and P.M. Siryies (eds.), Springer, Berlin (1964) 58–68.
J.R. Rice, in Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, Proceedings of 14th IUTAM Congress, W.T. Koiter (ed.), North-Holland, Amsterdam (1977) 207–220.
R. Larsson, International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering (1993) submitted.
R. Hill, Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 6 (1958) 236–249.
K. Runesson and R. Larsson, Journal of Engineering Mechanics, ASCE 119 (1993) 647–666.
R. Larsson, K. Runesson and S. Sture, Archive of Applied Mechanics 66 (1991) 305–317.
M.B. Nooru-Mohamed, Mixed Mode Fracture of Concrete: An Experimental Approach, Ph.D. dissertation, Delft University of Technology (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larsson, R., Runesson, K. Cohesive crack models for semi-brittle materials derived from localization of damage coupled to plasticity. Int J Fract 69, 101–122 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00035025
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00035025