Abstract
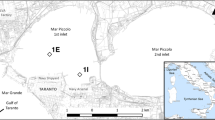
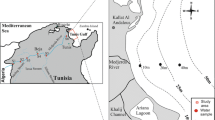
During 1994 net sediment-water fluxes of oxygen, ammonium and inorganic phosphorus as well as sediment profiles of organic matter, nitrogen, phosphorus and iron were determined in three shallow eutrophic environments. Investigations were conducted monthly from March to December at five stations in the Sacca di Goro (Po River Delta, Italy). In the late summer, samples were collected from a single site in the Prévost lagoon (French Mediterranean coast) and three stations in the Bassin d'Arcachon (French Atlantic coast). In the Sacca di Goro, water-sediment exchanges of O2, NH +4 and PO 3−4 were estimated by means of core incubation in the dark. Benthic fluxes for the French lagoons were in part determined experimentally using benthic chambers and in part from the literature.
In general in the Sacca di Goro the highest oxygen uptake and nutrient release rates were found at the central sites, affected by macroalgal growth. At the sampling site adjacent to the freshwater inlet, sediment-water exchanges were principally influenced by tidal activity. In terms of organic matter and nutrient levels, sediments from the Sacca di Goro and from the Prévost lagoon, both colonised by the floating macroalga Ulva rigida C. Agardh, were similar. Sediments from the inner sheltered site in the Bassin d'Arcachon, invaded by the rooted macrophyte Ruppia cirrhosa (Pet.) Grande, showed the highest total N and P content (363 ± 157 µmol N cm−3 and 15 ± 2 µmol P cm−3 as average values in the top 10 cm of sediment), but were low in pore water ammonium and orthophosphate probably due to the high sequestering capacity of the system and/or efficient coupling between bacterial nutrient regeneration and assimilation by the plant roots. In addition the outer tidal stations in the Bassin d'Arcachon, invaded by rooted macrophytes, were low in pore water nutrients. A different trend was evident in the Prévost lagoon where the concentrations of exchangeable inorganic phosphorus and ammonium were appreciable (0.28 ± 0.07 µmol P cm−3 and 2.4 ± 1.4 µmol N cm−3 as average values in the top 10 cm of sediment). High amounts of dissolved organic nitrogen were found in the pore water at all the sites investigated showing the key role of the organic nitrogen in the recycling of nitrogen in these systems.
The hypothesis that iron is a key factor in controlling phosphorus release is discussed since the Sacca di Goro, which is subject to dystrophic crises, is richer in iron than the Bassin d'Arcachon, which is a more buffered system.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvisi, A., D. Marzocchi & S. Edelwais, 1993. Indagine quali-quantitativa delle acque superficiali dei bacini Burana-Volano e Canal Bianco. Dimensione Ambiente, Amm. Prov. Ferrara, Servizio Ambiente, 207 pp.
A.P.H.A., A.W.W.A., W.P.C.F., 1975. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. 14th edn. APHA, Washington, 1193 pp.
Aspila, K. I., H. Agemian & A. S. Y. Chau, 1976. A semiautomated method for the determination of inorganic, organic and total phosphate in sediments. Analyst 101: 187–197.
Bachelet, G., X. de Montaudouin, I. Auby & P. J. Labourg, 1994. A comparative study of the seasonal changes in macrophytes and macrozoobenthos assemblages in three coastal lagoons under varying degrees of eutrophication. In P. Caumette (Coord.) C.L.E.A.N. Progress Report 1994. EU Environment Programme DG XII, Brussels: 353–367.
Barbanti, A., M. C. Bergamini, F. Frascari, S. Miserocchi & G. Rosso, 1993. Investigations on some critical aspects of sedimentary phosphorus chemical fractionation. J. envir. Qual. 23: 1093–1102.
Barbanti, A., F. Frascari, D. Paltrinieri & G. Rosso, 1992. Transport of nutrients in rivers: investigation on the Po river (Italy). Sci. Total. Envir. Suppl. 92: 337–344.
Bartoli, M., M. Cattadori, G. Giordani & P. Viaroli, 1994. Oxygen, sulphide and nutrient fluxes in shallow eutrophic lagoons with different primary producer communities. II. Superficial sediment profiles of nutrients, iron and reduced sulfur pools. In P. Caumette (Coord.) C.L.E.A.N. Progress Report 1994. EU Environment Programme DG XII, Brussels: 353–367.
Blackburn, T. H. & N. D. Blackburn, 1993. Rates of microbial processes in sediments. Phil. Trans. r. Soc., Lond. 344: 49–58.
Boynton, W. R. & W. M. Kemp, 1985. Nutrient regeneration and oxygen consumption by sediments along an estuarine salinity gradient. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 23: 45–55.
Buchsbaum, R., I. Valiela, T. Swain, M. Dzierzesky & S. Allen, 1991. Available and refractory nitrogen in detritus of vascular plants and macroalgae. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 72: 131–143.
Castel, J., P. Caumette & R. Herbert, 1996. Eutrophication gradients in coastal lagoons as exemplified by the Bassin d'Arcachon and the Étang du Prévost. Hydrobiologia 329 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 117): xi-xxx.
Caumette, P., 1986. Phototrophic sulphur bacteria and sulphate reducing bacteria causing red waters in a shallow brackish coastal lagoon (Prévost Lagoon, France), FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 38: 113–124.
Dal Cin, R. & P. Pambianchi, 1991. I sedimenti della Sacca di Goro (Delta del Po). In S. Bencivelli & N. Castaldi (eds), Studio integrato dell'ecologia della Sacca di Goro, Francoangeli, Milano: 253–263.
Enoksson, V., 1993. Nutrient recycling by coastal sediments: effects of added algal material. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 92: 245–254.
Escaravage, V., 1990. Daily cycles of dissolvd oxygen and nutrient content in a shallow fishpond: the impact of water renewal. Hydrobiologia 207: 131–136.
Giordani, G., M. Bartoli, M. Cattadori & P. Viaroli, 1996. Sulphide release from anoxic sediments in relation to iron availability and organic matter recalcitrance and its effects on inorganic phosphorus recycling. Hydrobiologia 329 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 117): 205–216.
Golterman, H. L. & A. Booman, 1988. Sequential extraction of iron-phosphate and calcium-phosphate from sediments by chelating agents. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 23: 904–909.
Golterman, H. L., 1995. The role of iron hydroxide-phosphate-sulphide system in the phosphate exchange between sediments and overlying water. Hydrobiologia 297: 43–54.
Hansen, L. S. & T. H. Blackburn, 1991. Aerobic and anaerobic mineralization of organic material in marine sediment microcosms. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 75: 283–291.
Hopkinson, C. S. Jr., 1987. Nutrient regeneration in shallow-water sediments of the estuarine plume region of the nearshore Georgia Bight, USA. Mar. Biol. 94: 127–142.
Johnston, C. A., 1991. Sediment and nutrient retention by freshwater wetlands: effects on surface water quality. Critical Reviews in Environmental Control 21: 491–565.
Koroleff, F., 1970. Direct determination of ammonia in natural waters as indophenol blue. Information on techniques and methods for seawater analysis. I.C.E.S. Interlaboratory. Rep No. 3: 19–32.
Labourg, P. J., 1975. Contribution à l'hydrologie des étangs saumâtres de la région d' Arcachon: description des phénomènes d'eaux blanches. Bull. soc. linn. Bordeaux 5: 3–8.
Lapointe, B., M. M. Littler & D. S. Littler, 1992. Nutrient availability to marine macroalgae in siliciclastic versus carbonate-rich coastal waters. Estuaries 15: 75–82.
Lavery, P. S. & J. A. Mc Comb, 1991. Macroalgal-Sediment nutrient interactions and their importance to macroalgal nutrition in a eutrophic estuary. Estuar. coast. Shelf Sci. 32: 281–295.
Mann, K. H., 1988. Production and use of detritus in various freshwater, estuarine, and coastal marine ecosystems. Limnol. Oceanogr. 33: 894–910.
Mesnage, V. & B. Picot, 1995. The distribution of phosphate in sediment and its relation with eutrophication of a Mediterranean coastal lagoon. Hydrobiologia 297: 29–41.
Miller-Way, T., G. S. Boland, G. T. Rowe & R. R. Twilley, 1994. Sediment oxygen consumption and benthic nutrient fluxes on the Louisiana continental shelf: a methodological comparison. Estuaries 17: 809–815.
Nienhuis, P. H., 1992. Eutrophication, water management, and the functioning of Dutch estuaries and coastal lagoons. Estuaries 15: 538–548.
O'Kane, J. P., M. Suppo, E. Todini & J. Turner, 1992. Physical intervention in the lagoon of Sacca di Goro. An examination using a 3-D numerical model. Sci. Total Envir. suppl. 92: 489–510.
Pugnetti, A., P. Viaroli & I. Ferrari, 1992. Processes leading to dystrophy in a Po River Delta lagoon (Sacca di Goro): phytoplancton-macroalgae interactions. Sci. Total Envir. suppl.: 445–456.
Rizzo, W. M., G. J. Lackey & R. R. Christian, 1992. Significance of euphotic, subtidal sediments to oxygen and nutrient cycling in a temperate estuary. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 86: 51–61.
Sand-Jensen, K. & J. Borum, 1991. Interactions among phytoplankton, periphyton, and macrophytes in temperate freshwater and estuaries. Aquat. Bot. 41: 137–175.
Sfriso, A., B. Pavoni, A. Marcomini & A. A. Orio, 1992. Macroalgae, nutrient cycles, and pollutants in the lagoon of Venice. Estuaries 15: 517–528.
Sloth, N. P., N. Risgaard-Petersen, S. Rysgaard, S. Pedret Pelegri, 1993. Nitrification, denitrification and nitrate ammonification in sediments of two coastal lagoons in southern France. In P. Caumette (Coord.), CLEAN Progress Report, European Commission. EU Environment Programme DG XII, Brussels: 159–185.
Valderrama, J. C., 1981. The simultaneous analysis of total nitrogen and total phosphorus in natural waters. Mar. Chem. 10: 109–122.
Val Klump, J. & C. Martens, 1981. Biogeochemical cycling in an organic rich coastal marine basin-II. Nutrient sediment-water exchange processes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 45: 101–121.
Viaroli, P., A. Pugnetti & I. Ferrari, 1992. Ulva rigida growth and decomposition processes and related effects on nitrogen and phosphorus cycles in a coastal lagoon (Sacca di Goro, Po River Delta). In G. Colombo, I. Ferrari, V. U. Ceccherelli & R. Rossi (eds), Marine eutrophication and population dynamics. Olsen & Olsen, Fredensborg: 77–84.
Viaroli, P. & M. Naldi, 1992. Ricerche sui cicli di azoto e fosforo in una laguna costiera eutrofizzata (Sacca di Goro, Delta del Po). S.IT.E ATTI 15: 95–115.
Viaroli, P., M. Naldi, R. R. Christian & I. Fumagalli, 1993. The role of macroalgae and detritus in the nutrient cycles in a shallow water dystrophic lagoon. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 25: 1048–1051.
Viaroli, P., M. Bartoli, C. Bondavalli, R. R. Christian, G. Giordani & M. Naldi, 1996. Macrophyte communities and their impact on benthic fluxes of oxygen, sulpide and nutrients in shallow eutrophic environments. Hydrobiologia 329 (Dev. Hydrobiol. 117): 105–119.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bartoli, M., Cattadori, M., Giordani, G. et al. Benthic oxygen respiration, ammonium and phosphorus regeneration in surficial sediments of the Sacca di Goro (Northern Italy) and two French coastal lagoons: a comparative study. Hydrobiologia 329, 143–159 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00034554
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00034554