Abstract
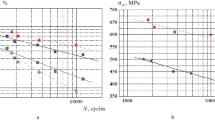
Fatigue crack propagation properties of low-alloy ferritic steel were investigated using 50-mm-wide compact-type (CT) specimens and 200-mm-wide center-cracked-type (CCT) specimens at room temperature and 300°C. Most of the stress ratios were nearly equal to zero. Significant differences in fatigue crack propagation rate in the CCT specimen, which was heated to the test temperature only locally near the crack plane, were compared with the rates for the CT specimen which was enclosed completely by a furnace. It was found that the differences were related to the compressive stresses arising from the thermal gradients.
Résumé
On étudie les propriétés de propagation des fissures de fatigue dans un acier ferritique faiblement allié à l'aide d'éprouvettes de traction compactes CT longues de 50 mm et d'éprouvettes de traction à fissure centrale (CCT) longues de 200 mm, à température ambiante et à 300°C. Dans la plupart des cas, les rapports de contraintes R sont égaux à zéro. On constate et on compose des différences importantes de vitesses de propagation en fatigue sur les éprouvettes CCT où le chauffage jusqu'à température d'essai est appliqué localement au voisinage du plan de la fissure, par rapport aux vitesses de propagation constatées sur les éprouvettes CT complètement insérées dans un four. On trouve que ces différences sont liées aux contraintes de compression associées aux gradiants thermiques.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ASME, Boiler and Pressure Vessel Code, Section XI, Rules for Inspection of Nuclear Power Plant Components, Division 1, Appendix A (1977) 175–188.
S. Matsuoka, E. Takeuchi, M. Kosuge, M. Shimodaira, A. Ohta and S. Nishijima, Journal of Testing and Evaluation 14–6 (1986) 312–317.
J.E. Srawley, International Journal of Fracture 12 (1976) RCR 475–476.
A. Ohta, E. Sasaki, M. Nihei, M. Kosuge, M. Kanao and M. Inagaki, International Journal of Fatigue 4 (1982) 233–237.
W.F. Brown, Jr and J.E. Srawley, in Plane Strain Crack Toughness Testing of High Strength Metallic Materials, ASTM STP 410 (1967) 1–66.
M. Klesnil and M. Lukáš, Materials Science Engineering 9 (1972) 231–240.
A. Ohta and E. Sasaki, Engineering Fracture Mechanics 9 (1977) 307–315.
H. Tada, P.C. Paris and G.R. Irwin, The Stress Analysis of Cracks Handbook, Del Research Corporation, Hellertown (1974) 2.33.
E. Takeuchi, S. Matsuoka and S. Nishijima, JSME International Journal 30–259 (1987) 22–28.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohta, A., Kosuge, M., Matsuoka, S. et al. Significant effect of thermal stresses on fatigue crack propagation properties. Int J Fract 38, 207–216 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00034285
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00034285