Abstract
Biological control of schistosomiasis by means of introduction of a competitor, Helisoma duryi, of the intermediate host snails has been proposed. In the present laboratory studies the competitive relationships between H. duryi and two Biomphalaria species were investigated both when direct interference between the two competing species was possible and when not. A reduction of growth and reproduction of Biomphalaria was found when direct interference was involved but the effect of competition was lessened when the two species were separated by a mesh.
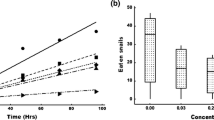
The data showed that despite continuous presence of food in the aquaria food competition was involved in the direct interference between the two species, while the role of chemical interactions could not be evaluated conclusively from the present experiments.
The role of food is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdallah, A. & Nasr, T. 1973. Helisoma duryi as a means of biological control of schistosomiasis vector snails. J. Egypt. Med. Assn. 56: 514–520.
Ayad, N., Mousa, A. H., Ishak, M. M., Yousif, F. & Zaghloul, S. 1970. A preliminary study on biological control of the snail intermediate hosts of schistosomiasis in U.A.R. by Helisoma duryi snails. Hydrobiologia, 35: 197–202.
Berrie, A. D. & Visser, S. A. 1963. Investigations of a growth inhibiting substance affecting a natural population of freshwater snails. Physiol. Zool. 36: 167–173.
Branch, G. M. 1976. Interspecific competition experienced by South African Patella species. J. Anim. Ecol. 45: 507–529.
Calow, P. 1970. Studies on the natural diet of Lymnaea pereger obtusa (Viobelt) and its possible ecological implications. Proc. Malac. Soc. Lond. 39: 203–215.
Doremus, C. M. & Harman, W. N. 1977. The effects of grazing by physid and planorbid fresh water snails on periphyton. Nautilus. 91: 92–96.
Eisenberg, R. M. 1966. The regulation of density in a natural population of the pond snail, Lymnaea elodes. Ecology. 47: 889–906.
Eisenberg, R. M. 1970. The role of food in the regulation of the pond snail Lymnaea elodes. Ecology. 51: 680–684.
El-Hassan, A. A. A. 1974. Helisoma tenue and Physa acuta snails as biological means of control against Bulinus truncatus and Biomphalaria alexandrina, snail intermediate hosts of schistosomiasis in Egypt. Proc. 3rd Intern. Cong. Parasit. Munchen. 3: 1597–1598.
Ferguson, F. F. 1977. The role of biological agents in the control of schistosome-bearing snails. U.S. Department of Health, Education, and Welfare/ Public Health Service/Center for Disease Control/Bureau of Laboratories/Atlanta, Georgia 30333.
Frandsen, F. 1976. The suppression by Helisoma duryi of the cercarial production of Schistosoma mansoni-infected Biomphalaria pfeifferi. Bull. WHO. 53, 385–390.
Frandsen, F. & Madsen, H. 1979. A review of Helisoma duryi in biological control. Acta Tropica, 36: 67–84.
Hairston, N. G., Smith, F. E. & Slobodkin, L. B. 1960. Community structure, population control and competition. Amer. Naturalist. 94: 421–425.
Hald, A. 1973. Statistiske Metoder. Akademish Forlag, København.
Haven, S. B. 1973. Competition for food between the intertidal gastropods Acmaea scabra and A. digitalis. Ecology. 54: 143–151.
Hira, P. R. & Muller, R. 1966. Studies on the ecology of snails transmitting urinary schistosomiasis in Western Nigeria. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasit. 60: 198–211.
Hubendick, B. 1958. Factors conditioning the habitats of freshwater snails. Bull. WHO. 18: 1072–1080.
Madsen, H. & Frandsen, F. 1978. Studies on the interspecific competition between Helisoma duryi (Wetherby) and Biomphalaria camerunensis (Boettger). Size-weight relationships and laboratory competition experiments. Hydrobiologia. in press.
Malek, E. A. 1958. Factors conditioning the habitat of bilharziasis intermediate hosts of the family Planorbidae. Bull. WHO. 18: 785–818.
Malek, E. A. & Malek, R. R. 1978. Potential biological control of schistosomiasis intermediate hosts by helisome snails. Nautilus. 92: 15–18.
Mandahl-Barth, G. 1965. A possible biological method of controlling bilharzia snails. Unpub. lecture given at Ain Shan's Univ., Cairo 23 Nov.
Mandahl-Barth, G. 1970. Biological control of bilharziasis vector snails by Helisoma. OAU Symposium on Schistosomiasis, Nov. Addis Ababa. p. 233.
Mooij-Vogelaar, J. W. & Steen, E. J. van der. 1973. Effects of density on feeding and growth in the pond snail Lymnaea stagnalis (L.). Proc. K. Ned. Akad. Wet. 76: 47–60.
Standen, O. D. 1949. Experimental schistosomiasis. I. The culture of the snail vectors Planorbis boissyi and Bulinus truncatus. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasit. 43: 13–22.
Thomas, J. D. 1973. Schistosomiasis and control of molluscan hosts of human schistosomes with particular reference to self-regulatory mechanisms. Advances in Parasitology. 2: 307–394.
Underwood, A. J. 1978. An experimental evaluation of competition between three species of intertidal prosobranch gastropods. Oecologia (Berl.) 33: 185–202.
Wright, C. A. 1960. The crowding phenomenon in laboratory colonies of freshwater snails. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasit. 54: 224–232.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madsen, H. Further laboratory studies on the interspecific competition between Helisoma duryi (Wetherby) and the intermediate hosts of schistosoma mansoni sambon: Biomphalaria alexandrina (Ehrenberg) and B. camerunensis (Boettger). Hydrobiologia 66, 181–192 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00032048
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00032048