Summary
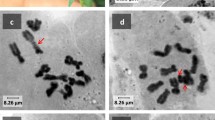
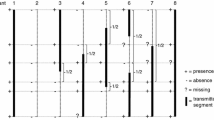
Commercial cultivars of the potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) are widely believed to be cytologically invariable (2n=48), although there are several reports of anomalous counts in experimental material. The presence of two additional chromosomes is reported for the first time in cv. Torridon and their stability in the growing plant examined. The additional chromosomes were found to be completely stable in the shoots but were progressively eliminated from the root tissue. Laggards and bridges were commonly observed during somatic division in the roots. Laggards were also present in the shoots and did not change significantly in frequency in the roots during chromosomal loss. Consequently, they were considered as unlikely to have a central involvement in the elimination process. Somatic bridges on the other hand were only found in the roots and increased in occurrence as elimination increased. A link between the appearance of somatic bridges and the elimination of additional chromosomes in the roots is suggested. The possible origins and mechanism of elimination of the additional chromosomes are briefly discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anon, 1991. Potato Variety Handbook. NIAB, Cambridge, UK.
Austin, S., M. Baer, M. Ehlenfeldt, J.P. Kazmierczak & J.P. Helgeson, 1985. Intra-specific fusions of Solanum tuberosum. Theor. Appl. Genetics 71: 682–690.
Bennett, M.D., R.A. Finch & I.R. Barclay, 1976. The time rate and mechanism of chromosome elimination in Hordeum hybrids. Chromosoma 54: 175–200.
Clulow, S.A., M.J. Wilkinson, R. Waugh, E. Baird, M.J.De Maine & W. Powell, 1991. Cytological and molecular observations on Solanum phureja induced dihaploids. Theor. Appl. Genetics 82: 545–551.
Coleman, M., P. Davie, J. Vessey & W. Powell, 1991. Intraclonal genetic variation for protoplast regenerative ability within Solanum tuberosum cv. Record. Ann. Bot. 67: 459–461.
Creissen, G.P. & A. Karp, 1985. Karyotypic changes in potato plants regenerated from protoplasts. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture 4: 171–182.
De Maine, M.J. & L. Jervis, 1989. The use of dihaploids in increasing the homozygosity of tetraploid potatoes. Euphytica 44: 37–42.
Fish, N. & A. Karp, 1986. Improvements in regeneration from protoplasts of potato and studies on chromosome stability. 1. The effect of initial culture media. Theor. Appl. Genetics 72: 405–412.
Fukuyama, T. & R. Takahashi, 1976. A study of the interspecific hybrid, Hordeum bulbosum (4×) × H. vulgare (4×), with special reference to dihaploid frequency. In: H. Gaul (Ed), Barley genetics III. Thiemig, Munchen, pp 351–360.
Gill, B.S., L.N.W. Kam-Morgan & J.F. Shepard, 1986. Origin of chromosomal and phenetic variation in potato protoclones. J. Heredity 77: 13–16.
Gupta, S.B., 1968. Chlorophyll variegation caused by unstable behaviour of an alien chromosome in hybrid derivatives of Nicotiana species. Genetica 39: 193–208.
Huaman, Z. & H. Stegemann, 1989. Use of electrophoretic analyses to verify morphologically identical clones in a potato collection. Plant Varieties and Seeds 2(3): 155–163.
Ho, K.M. & K.J. Kasha, 1975. Genetic control of chromosome elimination during haploid formation in barley. Genetics 81: 263–275.
Jervis, L., A.L. Shepard & M.J.De Maine, 1986. Variations in soluble tuber proteins in tetraploid, dihaploid and double dihaploid potato (Solanum tuberosum). Biochem. Soc. Trans. 14: 1096–1097.
Jones, G.H., 1978. Giemsa C-banding of Rye meiotic chromosomes and the nature of ‘terminal’ chiasmata. Chromosoma 66: 45–57.
Karp, A., R.S. Nelson, E. Thomas & S.W.J. Bright, 1982. Chromosome variation in protoplast-derived potato plants. Theor. Appl. Genetics 63: 265–272.
Lange, W., 1971. Crosses between Hordeum vulgare L. and H. bulbosum L. 2. Elimination of chromosomes in hybrid tissues. Euphytica 20: 181–194.
Lumsden, J. & J.R. Coggins, 1977. The sub-unit structure of the arom multi-enzyme complex of Neurospora crassa. A possible pentafunctional polypeptide chain. Biochem. J. 161: 599–607.
Newman, L.J., 1966. Bridge and fragment aberrations in Podophyllum peltatum. Genetics 53: 55–63.
Noda, K. & K.J. Kasha, 1981. Chromosome elimination in different meristematic regions of hybrids between Hordeum vulgare L. and H. bulbosum L. Jap. J. Genet. 56: 193–204.
Pijnacker, L.P., M.A. Ferwerda, K.J. Puite & S. Roest, 1987. Elimination of Solanum phureja nucleolar chromosomes in S. tuberosum + S. phureja somatic hybrids. Theor. Appl. Genet. 73: 878–882.
Puite, K.J., S. Roest & L.P. Pijnacker, 1986. Somatic hybrid potato plants after electrofusion of diploid Solanum tuberosum and S. phureja. Plant Cell Rep. 5: 262–265.
Salaman, R.N., 1926. Potato varieties. Cambridge, pp 378.
Schreiter, J., 1988. Variability of chromosome number in sprout-borne roots of the potato Solanum tuberosum 2n=4x=48. Archiv für Zuchtungsforschung 18(3): 169–174.
Smith, H.B., 1927. Chromosome counts in the varieties of S. tuberosum and allied wild species. Genetics 12: 84–92.
Stegemann, H. & V. Loeschcke, 1976. Index Europäischer Kartoffelsorten. Bestimmung durch elektrophoretische Spektren. Zulassungslisten, Bonitierung, genetische Daten. Paul Parey, Berlin, pp 43–213.
Subrahmanyam, N.C. & K.J. Kasha, 1973. Selective chromosomal elimination during haploid formation in barley following interspecific hybridization. Chromosoma 42: 111–125.
Swaminathan, M.S. & H.W. Howard, 1953. The cytology and genetics of the potato (Solanum tuberosum) and related species. Bibliographia Genetica 16: 1–192.
Thomas, H.M. & R.A. Pickering, 1983. Chromosome elimination in Hordeum vulgare × H. bulbosum hybrids. 1. Comparisons of stable and unstable amphidiploids. Theor. Appl. Genet. 66: 135–140.
Walters, M.S., 1950. Spontaneous breakage and reunion of meiotic chromosomes in the hybrid Bromus trinii × B. maritimus. Genetics 35: 11–37.
Visser, R.G.F., A. Hessling-Meinders, E. Jacobsen, H. Nijdam, B. Witholt & W.J. Feenstra, 1989. Expression and inheritance of inserted markers in binary vector carrying Agrobacterium rhizogenes-transformed potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Theor. Appl. Genetics 78: 705–714.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilkinson, M.J. The partial stability of additional chromosomes in Solanum tuberosum cv. Torridon. Euphytica 60, 115–122 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00029666
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00029666