Abstract
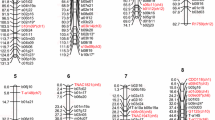
The purpose of this study was to construct a comparative RFLP map of an allotetraploid wild rice species, Oryza latifolia, and to study the relationship between the CCDD genome of O. latifolia and the AA genome of O. sativa. A set of RFLP markers, which had been previously mapped to the AA genome of cultivated rice, were used to construct the comparative map. Fifty-eight F2 progeny, which were derived from a single F1 plant, were used for segregation analysis. The comparative RFLP map contains 149 DNA markers, including 145 genomic DNA markers from cultivated rice, 3 cDNA markers from oat, and one known gene (waxy, from maize). Segregation patterns reflected the allotetraploid ancestry of O. latifolia, and the CC and DD genomes were readily distinguished by most probes tested. There is a high degree of conservation between the CCDD genome of O. latifolia and the AA genome of O. sativa based on our data, but some inversions and translocations were noted.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn S, Tanksley SD: Comparative linkage maps of the rice and maize genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 7980–7984 (1993).
Berhan AM, Hulbert SH, Butler LG, Bennetzen JL: Structure and evolution of the genomes of Sorghum bicolor and Zea mays. Theor Appl Genet 86: 598–604 (1993).
Bonierbale MW, Plaisted Tanksley SD: RFLP maps based on a common set of clones reveal modes of chromosomal evolution in potato and tomato. Genetics 120: 1095–1103 (1988).
Buchberg AM, Brownell E, Nagata S, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG. A comprehensive genetic map of murine chromosome 11 reveals extensive linkage conservation between mouse and human Genetics 122: 153–161 (1989).
Chang C, Bowman JL, DeJohn AW, Lander ES, Meyerowitz EM. Restriction fragment length polymorphism linkage map for Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 6856–6860 (1988).
Chao S, Sharp PJ, Worland AJ, Warham EJ, Koebner RMD, Gale MD: RFLP-based genetic maps of wheat homocologous group-7 chromosoines. Theor Appl Genet 78: 495–504 (1989).
Copeland NG, Jenkins NA, Gilbert DJ, Eppig JT, Maltais LJ, Miller JC, Dietrich WF, Weaver A, Lincoln SE, Steen RG, Stein LD, Nadeau JH, Lander ES. A genetic linkage map of the mouse: current applications and future prospects. Science 262: 57–66 (1993).
Dally AM, Second G: Chloroplast DNA diversity in wild and cultivated species of rice (genus Oryza, section Oryza): cladistic-mutation and genetic-distance analysis. Theor Appl Genet 80: 209–222 (1990).
Feldman M: The effect of chromosome 5B, 5D, and 5A on chromosomal pairing in Triticum aestivum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 55: 1447–1453 (1966).
Gale MD, Chao SM, Sharp PJ: RFLP mapping in wheat: progress and problems. In: Gene Manipulation in Plant Improvement II, pp. 353–363 (1990).
Gebhardt C, Ritter E, Barone A, Debener T, Walkemeier B, Schachtschabel U, Kaufmann H, Thompson RD, Bonierbale MW, Ganal MW, Tanksley SD, Salamini F: RFLP maps of potato and their alignment with the homoeologous tomato genome. Theor Appl Genet 83: 49–57 (1991).
Gopalakrishnan R, Sampath S: taxonomic status and origin of American tetraploid species of the series Latifoliae Tateoka in the genus Oryza. Indian J Agric Sci 37: 465–475 (1967).
Ichikawa H, Hirai A, Katayama T: Genetic analysis of Oryza species by molecular markers for chloroplast genomes. Theor Appl Genet 72: 353–358 (1986).
Jena KK, Kochert G: Restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of CCDD genome species of the genus Oryza L. Plant Mol Biol 16: 831–839 (1991).
Katayama T: Cytogenetical studies on the genus Oryza. 3. Chromosome pairing in the interspecific hybrids with ACD genomes. Nippon Iden Zasshi 41: 317–324 (1967).
Khush GS: Report of meetings to discuss chromosome numbering system in rice. Rice Genet Newsl 7: 12–14 (1990).
Kinzer SM, Schwager SJ, Mutschler MA: Mapping of ripening-related or ripening-specific cDNA clones of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum). Theor Appl Genet 79: 489–496 (1990)
Kosambi DD: The estimation of map distances from recombination value. Ann Eugenet 12: 172–175 (1944).
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newburg L: MAPMAKER. An interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1: 174–181 (1987).
Liu YG, Tsunewaki K: Restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analysis in wheat II. Linkage maps of the RFLP sites in common wheat. Jpn J Genet 66: 617–633 (1991).
Maniatis R, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY (1982).
McCouch SR, Kochert G, Yu ZH, Wang ZY, Khush GS, Coffman WR, Tanksley SD. Molecular mapping of rice chromosomes. Theor Appl, Gen 76: 815–829 (1988).
McCouch SR, Tanksley SD. Development and use of restriction fragment length polymorphism in rice breeding and genetics. In: Khush GS, Toenniessen GH (ed) Rice Biotechnology. pp. 109–113. Commonwealth Agricultural Bureaux, Oxon (1991).
Menancio-Hautea D, Fatokun CA, Kumar L, Danesh D, Young ND: Comparative genome analysis of mungbean (Vigna radiata L. Wilczek) and cowpea (V. unguiculata L. Walpers) using RFLP mapping data. Theor Appl Genet 86: 797–810 (1993).
Morizot DC: Use of fish gene maps to predict ancestral vertebrate genome organization. In: Isozymes, pp. 207–234 (1990).
Nadeau JH: Maps of linkage and synteny homologies between mouse and man. Trends Genet 5: 82–86 (1989).
Nayar NM. Origin and cytogenetics of rice. Adv Genet 17: 153–292 (1973).
Oka HI: Origin of cultivated rice. In: Tsunoda S, Takahashi N (eds) Biology of Rice, pp. 1–3. Elsevier, Amsterdam (1988).
Prince JP, Pochard E, Tanksley SD: Construction of a molecular linkage map of pepper and a comparison of synteny with tomato. Genome 36: 404–417 (1993).
Riley R, Kimber G, Chapman V: Origin of genetic control of diploid-like behavior of polyploid wheat. J Hered 52: 22–25 (1961).
Rognli OA, Devos KM, Chinoy CN, Harcourt RL, Atkinson MD, Gala MD. RFLP mapping of rye chromosome 7R reveals a highly translocated chromosome relative to wheat. Genome 35: 1026–1031 (1992).
Sahi BB, Morishima H, Oka HI. A survey of variation in peroxidase, acid phosphatase and esterase isozymes of wild and cultivated Oryza species. Jpn J Genet 44: 303–319 (1969).
Searle AG, Peters J, Lyon MF, Hall JG, Evans EP, Edwards JH, Buckle VJ. Chromosome maps of man and mouse. IV. Ann Hum Genet 53: 89–140 (1989).
Sears ER: An induced mutant with homoeologous pairing in common wheat. Can J Genet Cytol 19: 585–593 (1977).
Second G: Evolutionary relationships in the sativa group of Oryza based on isozyme data. Génét Sél Evol 17: 89–114 (1985).
Tanksley SD, Bernatzky R, Lapitan NL, Prince JP: Conservation of gene repertoire but not gene order in pepper and tomato. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 6419–6423 (1988).
Tanksley SD, Ganal MW, Prince JP, de Vicente MC, Bonierbale MW, Broun P, Fulton TM, Giovannoni JJ, Grandillo S, Martin GB, Messeguer R, Miller JC, Miller L, Paterson AH, Pineda O, Roder MS, Wing RA, Wu W, Young ND. High density molecular linkage maps of the tomato and potato genomes. Genetics 132: 1141–1160 (1992).
Threadgill DW, Adkison LR, Womack JE: Syntenic conservation between humans and cattle. 2. Human chromosome-12. Genomics 8: 29–34 (1990).
Threadgill DW, Womack JE: Syntenic conservation between humans and cattle. 1. Human chromosome-9. Genomics 8: 22–28 (1990).
Whitkus R, Doebley J, Lee M: Comparative genome mapping of sorghum and maize. Genetics 132: 1119–1130 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, H., Kochert, G. Comparative RFLP mapping of an allotetraploid wild rice species (Oryza latifolia) and cultivated rice (O. sativa). Plant Mol Biol 25, 633–648 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00029602
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00029602