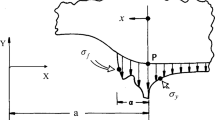
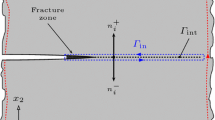
Abstract
A general expression for the energy release rate (G) that arises during steady state crack propagation by diffusion is derived from the standpoint of irreversible thermodynamics. Three contributing components of G are identified: (i) the Griffith energy (G Gr); (ii) heat generated in the process of surface diffution; and (iii) grain-boundary diffusion. Further, the total G is shown to be directly related to the well-known J-integral if formulated in the framework of finite deformation elasticity. This expression for G is valid in general even if the response of the material is not linear and the mass transport kinetics does not follow Fick's law. Quantitative evaluations of each component are made for the linear case where field solutions are available. The results show that component (ii) is approximately equal to G Gr and is independent of the crack velocity (v) whereas component (iii) is a monotonically increasing function with G starting from 0.85 G Gr when v is at threshold value; and that the local strain energy influence on matter diffusion is negligible leading to 229-1. This means that G is not primarily associated with the release of the strain energy at the crack tip but rather, it stems mostly from the (negative) work done (converted to heat) by the normal stresses on the thickening of the grain boundary due to non-uniform deposition of matter along it.
Résumé
Par une approche de thermodynamique irréversible, on a dérivé une expression générale de la vitesse de relaxation de l'énergie (G) au cours d'une propagation de fissure en régime stable occasionné par diffusion.
Trois composantes de G ont été identifiées: l'énergie de Griffith G Gr, la chaleur produite au cours du processus de diffusion en surface et la diffusion aux frontières des grains. En outre, on montre que G est en relation directe avec l'intégrale J bien connue s'il est formulé dans le contexte de l'élasticité à déformations finies. Cette expression de G est d'application générale, même si la réponse du matériau n'est past linéaire, et si la cinétique de transfert de masses ne suit pas la loi de Fick.
On a procédé à des évaluations quantitatives de chacune des composantes citées, dans un cas linéaire ou l'on maîtrise les conditions de champ. Les résultats montrent que la chaleur dégagée est de l'ordre de grandeur de GGr et est indépendante de la vitesse V de la fissure. Par contre, la diffusion aux frontières des grains croit avec G à partir de 0,85 GGr correspondant à une valeur de seuil pour V. L'influence de l'énergie de déformation locale sur la diffusion de matière est négligeable, ce qui conduit à 242-1.
Cela signifie que G n'est pas associé en priorité avec la relaxation de l'énergie de déformation à l'extrémité de la fissure, mais qu'il provient plutôt du travail (négatif, converti en chaleur) effectué par les contraintes normales, qui se traduit par un épaississement des frontières de grain en raison des dépôts non uniformes de matière le long de celle-ci.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.-J. Chuang, K.I. Kagawa, J.R. Rice and L.B. Sills, Acta Metallurgica 27 (1979) 265–284.
T.-J. Chuang, Journal of the American Ceramic Society 65 (1982) 93–103.
J.R. Rice and T.-J. Chuang, Journal of the American Ceramic Society 64 (1981) 46–53.
R. Fuentes-Samaniego and W.D. Nix, Philosophical Magazine A 44 (1981) 601–612.
H.B. Callen, Thermodynamics, John Wiley & Sons, Inc. New York (1960).
I.-W. Chen and A.S. Argon, Acta Metallurgica 29 (1981) 1759–1768.
R.M. Thomson, Chapter 23 in Physical Metallurgy, Ed. by R.W. Cahn and P. Haasen, North-Holland Publishing, Amsterdam (1983).
J.R. Rice and D.C. Drucker, International Journal of Fracture Mechanics 3 (1967) 19–27.
J.R. Rice, in Fracture Vol. II, Academic Press, Inc. New York (1968) 191–311.
J.D. Eshelby, in Inelastic Behavior of Solids, McGraw-Hill, New York (1970) 77–115.
J.R. Rice, Journal of Applied Mechanics 35 (1968) 379–386.
T.-J. Chuang and J.R. Rice, Acta Metallurgica 21 (1973) 1625–1628.
M.V. Speight, W.B. Beere and G. Roberts, Materials Science and Engineering 36 (1978) 155–163.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Work supported by U.S. Department of Energy AR&TD Fossil Energy Materials Program under interagency agreement DE-A105-800R20679 with NBS.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chuang, T.J. On the energy-release rate associated with diffusional crack growth. Int J Fract 23, 229–242 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00028825
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00028825