Summary
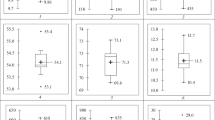
During test baking, the wheat line QT2870, bred from a rye-derived parent, Kavkaz, and having the pedigree Kavkaz/Timgalen//3*Oxley, showed excessive dough stickiness when slightly overmixed. Conventional quality tests on QT2870 and three commercial varieties did not show any major differences which could explain this dough stickiness. However, resistogram data for QT2870 were considerably different from those for the other cultivars. The curves for QT2870 had lower breaking points and sharper curve angles, indicating that it had a lower tolerance to high speed mixing than the other varieties. Dough stickiness and a lack of mixing tolerance are likely to be major problems limiting the use of rye-derived parents in Australian bread wheat breeding programmes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AACC, 1976. Approved methods of the American Association of Cereal Chemists, St. Paul.
Aberham, H., 1975. Wie können sich die Mühlen gegen backunfähigen Massenweizen schützen. DitDeutsche Mueller-Zeitung 7: 173–177.
Bolling, H., 1975a. Zur Problematik der ‘nichtbackfaehigen Weizen’ — eine Schnellmethode zu ihrer Erkennung. Die Muehle und Mischfutrertechnik 112: 256–257.
Bolling, H., 1975b. Possible causes of poor baking quality in some new wheat varieties. Bulletin des anciens Elèves de l'Ecole Française de Meunerie 270: 297–304.
Bolling, H. & P., Gerstenkorn, 1977. Zur Methodik der Erkennung von Weizen, der ‘nicht fuer die Brotherstellung’ geeignet ist. Die Muehle und Mischfuttertechnik 114: 219–220.
Brabender, M., 1973. Resistography. A dynamic quick method to classify wheat and flour quality. Cereal Science Today 18: 206–210.
Douglas, S. G., 1981. A rapid method for the determination of pentosans in wheat flour. Food Chemistry 7: 139–145.
Farrand, E. A., 1964. Flour properties in relation to the modern bread processes in the United Kingdom, with special reference to alpha-amylase and starch damage. Cereal Chemistry 41: 98–111.
Hoeser, K. & E., Wolf, 1976. Vorläufige Ergebnisse von Vergleichsuntersuchungen an Winterweizen-Sortenmehlen mit dem Resistogramm und Schnellextensogram. Getreide, Mehl und Brot 30: 217–219.
ICC, 1968. Standard methods of the International Association for Cereal Chemistry. Moritz Schäfer, Detmold.
Kent-Jones, D. W., A. J., Amos, R. A., Scott & D. G., Elias, 1965. A modern reflectometer for flour and near-white substance. Chemistry and Industry (London) 50: 1490–1493.
Law, C. N. & P. I., Payne, 1983. Genetic aspects of breeding for improving grain protein content and type in wheat. Journal of Cereal Science 1: 79–93.
Mettin, D., W. D. Bluthner & G. Schlegel, 1973. Additional evidence on spontaneous 1B/1R wheat-rye substitutions and translocations. Proc. 4th Wheat Genet. Symp. Columbia: 179–184.
Moonen, J. H. E. & A. C., Zeven, 1984. SDS-Page of the highmolecular-weight subunits of wheat glutenin and the characterization of 1R (1B) substitution and 1BL/1RS translocation lines. Euphytica 33: 3–8.
Parlevliet, J. E., 1981. Disease resistance in plants and its consequences for plant breeding. In: Frey, K. J. (Ed.), Plant breeding II. The Iowa State University Press, Ames: 309–364.
RACI-Cereal Chemistry Division, 1976. Official testing methods of the Royal Australian Chemical Institute, Melbourne.
Seibel, W. & H., Bolling, 1976. Nichtbackfähige Weizen-ein Rohstoffproblem fur das Müllerei-und Backgewerbe. Die Mühle und Mischfuttertechnik 113: 389–391.
Zeller, F. J., 1973. 1B/1R wheat rye chromosome substitutions and translocations. Proc. 4th Wheat Genet. Symp. Columbia: 209–221.
Zeller, F. J., G., Gunzel, G., Fischbeck, P., Gerstenkorn & D., Weipert, 1982. Veränderungen der Backeigenschaften des Weizens durch die Weizen-Roggen-Chromosomen Translokation 1B/1R. Getreide, Mehl und Brot 36: 141–143.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Martin, D.J., Stewart, B.G. Dough mixing properties of a wheat-rye derived cultivar. Euphytica 35, 225–232 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00028561
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00028561