Abstract
Two closely related species of Cenocorixa inhabit saline lakes in British Columbia. C. bifida lives in lakes with a conductivity of 20 to 20 000 µS cm-1, while C. expleta occurs in lakes with a conductivity ranging from 5 000 to 30 000 µS cm-1. The factors limiting the differential distribution of these species in higher salinities, and those governing the exclusion of C. expleta in low salinities have been studied.
Mortality experiments, and an investigation of osmotic and ionic balance, indicate that the two species differ in their ability to tolerate high salinity: these data correlate with the limits computed from field data and suggest that the differential distribution in the high saline lakes is because of physiological differences. However, these same data indicate that both species have a similar ability to live in low salinity lakes. Although C. expleta does not occur in such lakes, it is physiologically capable of doing so and has been reared in freshwater.
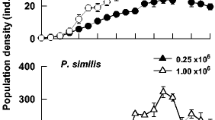
It is proposed that ecological rather than physiological factors exclude C. expleta from low salinity waters. Competitive exclusion by C. bifida might be suggested, but available data do not support this. A study of life cycle phenology, fundamental food niche and realized feeding niche of the two species shows that these are not significantly different. No interactive segregation is evident in sympatry, and so competitive exclusion of C. expleta in freshwater is unlikely.
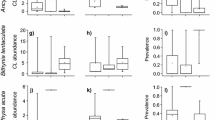
Hence, other biological factors in fresh and low salinity water have been investigated. A marked difference in susceptibility to mite parasitism of the species has been discovered. Although both C. bifida and C. expleta are parasitized by larval Eylais and Hydrachna, C. expleta appears unable to survive such parasitism. It is suggested that this is the biological factor that excludes C. expleta in the fresh and low salinity lakes where water mites are abundant.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cannings, R. A. & Scudder, G. G. E., 1978. The littoral Chironomidae (Diptera) of saline lakes in central British Columbia. Can. J. Zool. 56: 1144–1155.
Cannings, S. G., 1977. The influence of temperature and salinity on the cuticular permeability of some Corixidae. M.Sc. Thesis, Univ. Br. Columbia, 95 pp.
Cannings, S. G., 1978. Successful rearing of Cenocorixa expleta (Hemiptera: Corixidae) in fresh water. Can. Ent. 110: 559.
Cannings, S. G., 1981. The influence of salinity on the cuticular permeability of Cenocorixa bifida hungerfordi Lansbury. Can. J. Zool. 59: 1505–1509.
Davids, C., 1973. The water mite Hydrachna conjecta Koenike, 1895 (Acari, Hydrachnellae), bionomics and relation to species of Corixidae (Hemiptera). Neth. J. Zool. 23: 363–429.
Davids, C. & Schoots, C. J., 1975. The influence of the water mite species Hydrachna conjecta and H. cruenta (Acari, Hydrachnellae) on the egg production of the Corixidae Sigara striata and Cymatia coleoptrata (Hemiptera). Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 19: 3079–3082.
Jansson, A., 1972. Systematic notes and new synonymy in the genus Cenocorixa (Hemiptera: Corixidae). Can. Ent. 104: 449–459.
Jansson, A., 1973. Stridulation and its significance in the genus Cenocorixa (Hemiptera, Corixidae). Behaviour 56: 1–36.
Jansson, A., 1974. Annual periodicity of male stridulation in the genus Cenocorixa (Hemiptera, Corixidae). Freshwat. Biol. 4: 93–98.
Jansson, A. & Scudder, G. G. E., 1972. Corixidae (Hemiptera) as predators: rearing on frozen brine shrimp. J. ent. Soc. Br. Columbia 69: 44–45.
Jansson, A. & Scudder, G. G. E., 1974. The life cycle and sexual development of Cenocorixa species (Hemiptera, Corixidae) in the Pacific Northwest of North America. Freshwat. Biol. 4: 73–92.
Jarial, M. S., 1967. Histophysiological and ultrastructural studies on the hind gut and brain of Cenocorixa bifida (Hemiptera — Insecta). Ph.D. Thesis, Univ. Br. Columbia. 92 pp.
Jarial, M. S. & Scudder, G. G. E., 1970. The morphology and ultrastructure of the Malpighian tubules and hindgut in Cenocorixa bifida (Hung.) (Hemiptera, Corixidae). Z. Morph. Tiere 68: 269–299.
Jarial, M. S. & Scudder, G. G. E., 1971. Neurosecretion and water balance in Cenocorixa bifida (Hung.) (Hemiptera, Corixidae). Can. J. Zool. 49: 1369–1375.
Jarial, M. S., Scudder, G. G. E. & Teraguchi, S., 1969. Observations on the labium of Corixidae (Hemiptera). Can. J. Zool. 47: 713–715.
Komnick, H. & Schmitz, M., 1977. Cutane Chloridaufnahme aus hypo-osmotischer Konzentration durch die Chloridzellen von Corixa punctata. J. Insect Physiol. 23: 165–173.
Komnick, H. & Wichard, W. 1975. Histochemischer Nachweis von Chloridzellen bei Wasserwanzen (Hemiptera: Hydrocorisae) und ihre Feinstruktur bei Hesperocorixa sahlbergi Fieb. (Hemiptera: Corixidae). Int. J. Insect Morphol. Embryol. 4: 89–105.
Maddrell, S. H. P. & Phillips, J. E., 1975a. Secretion of hypoosmotic fluid by the lower Malpighian tubule of Rhodnius prolixus. J. exp. Biol. 62: 671–683.
Maddrell, S. H. P. & Phillips, J. E., 1975b. Active transport of sulphate ions by the Malpighian tubules of larvae of the mosquito Aedes campestris. J. exp. Biol. 62: 367–378.
Oloffs, P. C. & Scudder, G. G. E., 1966. The transition phenomenon in relation to the penetration of water through the cuticle of an insect, Cenocorixa expleta (Uhler). Can. J. Zool. 44: 621–630.
Reynolds, J. D., 1974. Aspects of the ecology of two species of Cenocorixa (Corixidae: Hemiptera) in allopatry and sympatry. Ph.D. Thesis, Univ. Br. Columbia. 280 pp.
Reynolds, J. D., 1975. Feeding in corixids (Heteroptera) of small alkaline lakes in central B.C. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 19: 3073–3078.
Reynolds, J. D., 1980. Crustacean zooplankton of some saline lakes of central British Columbia. Syesis 12 (1979): 169–173.
Scudder, G. G. E., 1966. The immature stages of Cenocorixa bifida (Hung.) and C. expleta (Uhler) (Hemiptera: Corixidae). J. ent. Soc. Br. Columbia 63: 33–40.
Scudder, G. G. E., 1969a. The distribution of two species of Cenocorixa in inland saline lakes of British Columbia. J. ent. Soc. Br. Columbia 66: 32–41.
Scudder, G. G. E., 1969b. The fauna of saline lakes on the Fraser Plateau in British Columbia. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 17: 430–439.
Scudder, G. G. E., 1975. Field studies on the flight muscle polymorphism in Cenocorixa (Hemiptera: Corixidae). Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 19: 3064–3072.
Scudder, G. G. E., 1976. Water-boatmen of saline waters (Hemiptera: Corixidae). In: L. Cheng. (ed.), Marine Insects. North Holland Publ. Co., Amst. 263–289.
Scudder, G. G. E., Jarial, M. S. & Choy, S. K., 1972. Osmotic and ionic balance in two species of Cenocorixa (Hemiptera). J. Insect Physiol. 18: 883–895.
Smith, B. P., 1977. Water mite parasitism of water boatmen (Hemiptera: Corixidae). M.Sc. Thesis, Univ. Br. Columbia. 117 pp.
Szibbo, C. M., 1977. Physiology of secretion of the segmented Malpighian tubules of Cenocorixa bifida (Hemiptera — Insecta). M.Sc. Thesis, Univ. Br. Columbia. 102 pp.
Szibbo, C. M. & Scudder, G. G. E., 1979. Secretory activity of the segmented Malpighian tubules of Cenocorixa bifida (Hung.) (Hemiptera, Corixidae). J. Insect Physiol. 25: 931–937.
Topping, M. S., 1975. Effects of environmental factors on standing crop of plankton in British Columbia lakes. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 19: 524–529.
Topping, M. S. & Scudder, G. G. E., 1977. Some physical and chemical features of saline lakes in central British Columbia. Syesis 10: 145–166.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scudder, G.G.E. A review of factors governing the distribution of two closely related corixids in the saline lakes of British Columbia. Hydrobiologia 105, 143–154 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00025184
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00025184