Summary
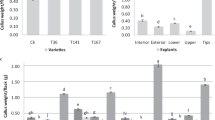
Twenty-five mulberry genotypes were studied for callus induction, to evaluate the effectiveness of hormones in promoting callus growth and to identify genotypes capable of regenerating plants. Fifteen genotypes showed callus initiation. Genotypic variation was also noted for longevity and rate of growth of callus cultures. Calli of different genotypes were maintained for more than one year. Frequency of callus initiation was high on Murashige & Skoog's modified medium incorporated with 2.0 mg/l 2,4-D, 100 mg/l casein acid hydrolysate and 150 ml/l coconut water. Regeneration through organogenesis was achieved in six genotypes indicating genotypic specificity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bajaj, Y.P.S., 1986. Biotechnology of tree improvement for rapid propagation and biomass energy production. In: Y.P.S. Bajaj (Ed). Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry, Vol. 1. Trees, pp. 1–22. Springer Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg.
Bapat, V.A., M. Mhatre & P.S. Rao, 1987. Propagation of Morus indica L. (Mulberry) by encapsulated shoot buds. Plant Cell Rep. 6: 393–395.
Gupta, P.K., 1988. Advances in biotechnology of conifers. Curr. Sci. 20: 629–637.
Jones, O.P., 1983. In vitro propagation of tree crops. In: S.J. Mantell & S. Smith (Eds). Plant Biotechnology, pp. 109–140. Cambridge University Press.
Kim, H., K.R. Patel & T.A. Thorpe, 1985. Regeneration of mulberry plantlets through tissue culture. Bot. Gaz. 146: 335–340.
Kumar, A., 1992. Morphogenesis in foliar callus of an apocynaceous tree, Thevetia peruviana L. Indian J. Expt. Biol. 30: 749–750.
Linsmaier, E.M. & F. Skoog, 1965. Organic growth factor requirement for tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant 18: 100–127.
Mhatre, M., V.A. Bapat & P.S. Rao, 1985. Regeneration of plants from the culture of leaves and axillary buds in mulberry (Morus indica L.). Plant Cell Rep. 4: 78–80.
Murashige, T. & F. Skoog, 1962. A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco cultures. Physiol. Plant 15: 473–497.
Oka, S. & K. Ohyama, 1981. In vitro initiation of adventitious buds and its modification by high concentration of benzyladenine in leaf tissues of mulberry (Morus alba L.). Can. J. Bot. 59: 68–74.
Oka, S. & K. Ohyama, 1986. Mulberry (Morus alba L.). In: Y.P.S. Bajaj (Ed). Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry Trees, pp. 384–392. Springer Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg.
Pratap Narayan, S. Chakraborty & S. Subba Rao, 1989. Regeneration of plantlets from the callus of stem segments of mature plants of Morus alba L. Proc. Indian Nat. Sci. Acad. 55: 469–472.
Rao, P.S., V.A. Bapat, M. Mhatre & G.K. Patel, 1989. Application of plant cell, tissue and organ culture in mulberry improvement programme. In: K. Sengupta & S.B. Dandin (Eds). Genetic Resources of Mulberry and Utilization, pp. 125–131. Central Sericultural Research & Training Institute, India.
Sommer, E., C.L. Brown & P.P. Kormanic, 1975. Differentiation of plantlets in long leaf pine (Pinus palustris Mill.) tissue culture in vitro. Bot. Gaz. 136: 196–200.
Sree Ramulu, K. & P. Dijkhuis, 1984. Growth and differentiation of callus derived from leaf and stem internodes of Haplopappus gracilis (Nutt.) Gray. J. Plant Physiol. 115: 245–251.
Stains, V.A., 1983. Effect of growth regulators on organogenesis in perennial ryegrass tissue culture. Soviet Plant Physiol. 30: 325–329.
Tanimoto, S. & H. Harada, 1982. Physiological and hormonal factors influencing organogenesis in Rudbeckia bicolor explants cultured in vitro. Plant Cell Physiol. 23: 107–113.
Yakuwa, H. & S. Oka, 1988. Plant regeneration through meristem culture from vegetative buds of mulberry (Morus bombycis Koidz) stored in liquid nitrogen. Ann. Bot. 62: 79–82.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Susheelamma, B.N., Shekar, K.R., Sarkar, A. et al. Genotype and hormonal effects on callus formation and regeneration in mulberry. Euphytica 90, 25–29 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00025156
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00025156