Abstract
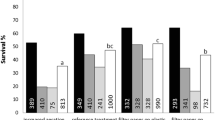
The maturation of somatic embryos of Sitka spruce [Picea sitchensis (Bong.) Carr.] was found to be highly dependent on the method used to seal plastic Petri dishes. Large numbers of well-formed mature embryos developed if dishes were sealed with PVC cling-film (CF) whilst sealing with Parafilm M (PF) greatly reduced the numbers of embryos forming. Inclusion of potassium permanganate oxidation traps, normally used to deplete the atmospheric ethylene, greatly stimulated somatic embryo maturation under PF sealing. Similarly, traps of adsorption agents (Tenax, activated charcoal or soft white paraffin), capable of removing volatiles from the culture vessel head-space, stimulated somatic embryo maturation under PF sealing although to a lesser extent than the oxidation traps. Incorporation of silver nitrate or 2-chloroethylphosphonic acid (ethephon) in the culture medium indicated that ethylene was not the agent supressing somatic embryo maturation under PF sealing.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
abscisic acid
- CF:
-
PVC cling-film
- PF:
-
Parafilm M
References
Adkins SW (1992) Cereal callus-cultures — control of head-space gases can optimize the conditions for callus proliferation. Aus J Bot 40: 737–749
Auboiron E, Carron M-P and Michaux-Ferrière N (1990) Influence of atmospheric gases, particularly ethylene, on somatic embryogenesis of Hevea brasiliensis. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 21: 31–37
Biddington NL (1992) The influence of ethylene in plant tissue culture. Plant Growth Reg 11: 173–187
Cronin DA and Caplan PJ (1987) Applications of GC/MS to identification of flavour compounds in foods. In: Gilbert J (ed) Applications of Mass Spectrometry in Food Science, pp 1–71. London: Elsevier Applied Science
Dimasi-Theriou K, Economou S and Sfakiotakis M (1993) Promotion of petunia (Petunia hybrida L.) regeneration in vitro by ethylene. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 32: 219–225
Dunstan DI, Bekkaoui F, Pilon M, Fowke LC and Abrams SR (1988) Effect of abscisic acid and analogues on the maturation of white spruce (Picea glauca) somatic embryos. Plant Sci 58: 77–84
Flores HE, Dai Y-R, Freyer AJ and Michaels PJ (1994) Biotransformation of butylated hydroxytoluene in “hairy root” cultures. Plant Physiol Biochem 32: 511–519
Fournioux J-C and Bessis R (1986) Influence de la teneur et gaz corbonique sur la morphogenèse de la vigne en culture in vitro. Can J Bot 64: 2608–2616
George EF and Sherrington PD (1984) Plant Propagation by Tissue Culture. Handbook and Directory of Commercial Laboratories. Reading, Berkshire: Eastern Press
Heath D (1995) An Introduction to Experimental Design and Statistics for Biology. London: UCL Press
Hébert D, Kikkert JR, Smith FD and Reisch BI (1993) Optimization of biolistic transformation of embryogenic grape cell suspensions. Plant Cell Rep 12: 585–589
Jackson MB, Abbot AJ, Belcher AR, Hall KC, Butler R and Cameron J (1991) Ventilation in plant tissue cultures and the effects of poor aeration on ethylene and carbon dioxide accumulation, oxygen depletion and explant development. Ann Bot 67: 229–237
Jackson MB, Belcher AR and Brain P (1994) Measuring the shortcomings in tissue culture aeration and their consequences for explant development. In: Lumsden PJ, Nicholas JR and Davies WJ (eds) Physiology, Growth and Development of Plants in Culture, pp 191–203. The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers
John A, Drake P and Selby C (1995) Somatic embryogenesis in Sitka spruce (Picea sitchensis (Bong.) Carr.). In: Jain S, Gupta P and Newton R (eds) Somatic Embryogenesis in Woody Plants, pp 125–143. The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers
Kochba J, Spiegel-Roy P, Neumann H and Saad S (1978) Stimulation of embryogenesis in Citrus ovular callus by ABA, ethephon, CCC and Alar and its suppression by GA3. Z Pflanzenphysiol 89: 427–432
Kumar PP, Joy RW and Thorpe TA (1989) Ethylene and carbon dioxide accumulation, and growth of cell suspension cultures of Picea glauca (white spruce). J Plant Physiol 135: 592–596
Kvaalen H and vonArnold S (1991) Effects of various partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide on different stages of somatic embryogenesis in Picea abies. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 27: 49–57
Leshem YY, Rapoport D, Frimer AA, Strul G, Asaf U and Felner I (1993) Buckminsterfullerene (C60 Buckyball) inhibition of ethylene release from senescing legume foliage and cut carnations. In: Pech JC, Latché A and Balagué C (eds) Cellular and Molecular Aspects of the Plant Hormone Ethylene, pp 174–181. The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers
Matthys D, Gielis J and Debergh P (1995) Chapter 19. Ethylene. In: Aitken-Christie J, Kozai T and Smith L (eds) Automation and Environmental Control in Plant Tissue Culture, pp 473–491. The Netherlands: Kluwer Academic Publishers
Ono Y, Takahata Y and Kaizuma N (1994) Effect of genotype on shoot regeneration from cotyledonary explants of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Plant Cell Rep 14: 13–17
Pius J, George L, Eapen S and Rao PS (1993) Enhanced plant regeneration in pearl millet (Pennisetum americanum) by ethylene inhibitors and cefotaxime. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 32: 91–96
Robinson KEP and Adams DO (1987) The role of ethylene in the regeneration of Helianthus annuus (sunflower) plants from callus. Physiol Plant 71: 151–156
Roustan JP, Latche A and Fallot J (1989) Stimulation of Daucus carota somatic embryogenesis by inhibitors of ethylene synthesis: cobalt and nickel. Plant Cell Rep 8: 182–185
Roustan JP, Latche A and Fallot J (1990) Control of carrot somatic embryogenesis by AgNO3, an inhibitor of ethylene action: effect on arginine decarboxylase. Plant Sci 67: 89–95
Roustan JP, Latche A and Fallot J (1994) Role of ethylene on induction and expression of carrot somatic embryogenesis: relationship with polyamine metabolism. Plant Sci 103: 223–229
Saito T and Nishimura S (1994) Improved culture conditions for somatic embryogenesis using an aseptic ventilative filter in egg plant (Solanum melongena L.). Plant Sci 102: 205–211
Snedecor GW and Cochran WG (1967) Statistical Methods. Ames, Iowa: Iowa State University Press
Tisserat B and Murashige T (1977) Effects of ethephon, ethylene and 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid on asexual embryogenesis in vitro. Plant Physiol 60: 437–439
Vain P, Filament P and Soudain P (1989) Role of ethylene in embryogenic callus initiation and regeneration in Zea mays L. J Plant Physiol 135: 537–540
Vain P, Yean H and Flament P (1989) Enhancement of production and regeneration of embryogenic type II callus in Zea Mays L by AgNO3. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 18: 143–151
Webb DT, Arias W and deHostos E (1986) Callus formation by Ginkgo biloba embryos on hormone-free media controlled by closures and media components. Phytomorph 36: 121–127
Webb DT, Torres LD and Fobert P (1984) Interactions of growth regulators, explant age, and culture environment controlling organogenesis from lettuce cotyledons in vitro. Can J Bot 62: 586–590
Wochok ZS and Wetherell DF (1971) Suppression of organized growth in cultured wild carrot tissue by 2-chloroethyl-phosphonic acid. Plant Cell Physiol 12: 771–774
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Selby, C., McRoberts, W.C., Hamilton, J.T.G. et al. The influence of culture vessel head-space volatiles on somatic embryo maturation in Sitka spruce [Picea sitchensis (Bong.) Carr.]. Plant Growth Regul 20, 37–42 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00024055
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00024055