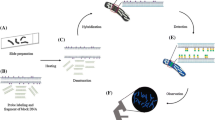
Summary
Fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) has been used to assess the occurrence and frequency of wheat-alien chromosome pairing in a wheat/Thinopyrum bessarabicum hybrid and in wheat/rye hybrids with different levels of chromosome pairing by examining pollen mother cells at metaphase I of meiosis. The use of FISH to identify the presence and size of alien chromatin in a wheat background is also demonstrated.
The value of FISH as an aid to the introgression of alien genetic variation into wheat is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- FISH:
-
fluorescent in situ hybridization
- GISH:
-
genomic in situ hybridization
- PRINS:
-
primer-induced in situ hybridization
References
Abbo S., R.P. Dunford, T.E. Miller, S.M. Reader & I.P. King, 1993a. Primer-mediated in situ detection of the B-Hordein gene cluster on barley chromosome 1H. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 11821–11824.
Abbo S., T.E. Miller & I.P. King, 1993b. Primer-induced in situ hybridization to plant chromosomes. Genome 36: 815–817.
Forster B.P. & T.E. Miller, 1985. A 5B deficient hybrid between Triticum aestivum and Agropyron junceum. Cer. Res. Comm. 13: 93–95.
Gale M.D. & T.E. Miller, 1987. The introducton of alien genetic variation into wheat. p. 173–210. In: F.G.H. Lupton (Ed). Wheat Breeding. Its Scientific Basis. Chapman and Hall, London.
Gerlach W.L. & J.R. Bedbrook, 1979. Cloning and characterization of ribosomal RNA genes from wheat and barley. Nucleic Acid Res. 7: 1869–1885.
Gustafson J.P. & J.E. Dillé, 1992. Chromosome location of Oryza sativa recombination linkage groups. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89: 8646–8650.
Hutchinson J., T.E. Miller & S.M. Reader, 1983. C-banding at meiosis as a means of assessing chromosome affinities in the Triticeae. Can. J. Genet. Cytol. 25: 319–323.
King I.P., R.M.D. Koebner, R. Schlegel, S.M. Reader, T.E. Miller & C.N. Law, 1992. Exploitation of a preferentially transmitted chromosome from Aegilops sharonensis for the elimination of segregation for height in semidwarf bread wheat varieties. Genome 34: 944–949.
King I.P., K.A. Purdie, S.E. Orford, S.M. Reader & T.E. Miller, 1993a. Detection of homoeologous recombination in Triticum durum × Thinopyrum bessarabicum hybrids using genomic in situ hybridization. Heredity 71: 369–372 (Erratum 72: 321).
King I.P., K.A. Purdie, H.N. Rezanoor R.M.D. Koebner, T.E. Miller, S.M. Reader & P. Nicholson, 1993b. Characterization of Thinopyrum bessarabicum chromosome segments in wheat using random amplified polymorphic DNAs (RAPDs) and genomic in situ hybridization. Theor. Appl. Genet. 86: 895–900.
King I.P., S.M. Reader, K.A. Purdie, S.E. Orford & T.E. Miller, 1994. A study of the effect of a homoeologous pairing promoter on chromosome pairing in wheat/rye hybrids using genomic in situ hybridization. Heredity 74: 318–321.
Mettin D., R. Schlegel, W.D. Bluthner & M. Weinrich, 1976. Giemsa-banding von MI-Chromosomen bei Weizen-Roggen-Bastarden. Biol. Zbl. 95: 35–41.
Miller, T.E., S.M. Reader & D. Singh, 1988. Spontaneous non-Robertsonian translocations between wheat chromosomes and an alien chromosome. p. 387–390. In: T.E. Miller & R.M.D. Koebner (Eds). Proc. 7th Int. Wheat Genet. Symp., Cambridge, Institute of Plant Science Research.
Miller T.E., S.M. Reader & M.D. Gale, 1983. The effect of homoeologous group 3 chromosomes on chromosome pairing and crossability in Triticum aestivum. Can. J. Genet. Cytol. 25: 634–641.
Miller T.E., S.M. Reader, K.A. Purdie & I.P. King, 1994. Determinations of the frequency of wheat-rye chromosome pairing in wheat × rye hybrids with and without chromosome 5B. Theor. Appl. Genet. 89: 255–258.
Reader S.M., S. Abbo, K.A. Purdie, I.P. King & T.E. Miller, 1994. Direct labelling of plant chromosomes by rapid in situ hybridization. Trends Genet. 10: 265–266.
Riley R., V. Chapman & G. Kimber, 1959. Genetic control of chromosome pairing in intergeneric hybrids in wheat. Nature, London 183: 1244–1246.
Riley R., V. Chapman & R. Johnson, 1968. The incorporation of disease resistance in wheat by genetic interference with the regulation of meiotic chromosome pairing. Genet. Res. Camb. 12: 199–219.
Schlegel R. & E. Weryszko, 1979. Intergeneric chromosome pairing in different wheat-rye hybrids revealed by giemsa banding technique and some implications on karyotype evolution in the genus Secale. Biol. Zbl. 93: 398–407.
Schwarzacher T., K. Anamathawat-Jonsson, G.E. Harrison, A.K.M.R. Islam, J.Z. Jia, I.P. King, A.R. Leitch, T.E. Miller, S.M. Reader, W.J. Rogers, M. Shi & J.S. Heslop-Harrison, 1992. Genomic in situ hybridization to identify alien chromosome segments in wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 84: 778–786.
Sybenga J., 1983. Rye chromosome nomenclature and homoeology relationships-Workshop report. Z. Pflanzenzüchtg. 90: 297–304.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miller, T.E., Reader, S.M., Purdie, K.A. et al. Fluorescent in situ hybridization as an aid to introducing alien genetic variation into wheat. Euphytica 85, 275–279 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023956
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023956