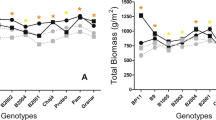
Summary
Although many selection indices have been used to screen rices (Oryza sativa L.) for drought resistance, there has been little comparison of the relative merits of these indices. Research was conducted to compare drought resistance as estimated from grain yields, canopy-temperature-based stress indices, visual scoring, and uprooting force for 30 rice genotypes grown in the field with a puddled Maahas clay (Typic Tropaquept) and to evaluate traits related to drought resistance from nonstressed plants grown in the field and in aeroponic culture. Water deficit was imposed in the field by withholding irrigation from 45 to 75 days after transplanting compared to a continuously flooded control. Grain yields in the stress treatment were most strongly correlated with visual assessment of drought stress symptoms according to a standard evaluation system (r = 0.66). Canopy-temperature-based indices were also significantly correlated with grain yields of the stress treatment (r from −0.55 to −0.63). No trait of aeroponically grown plants was correlated with traits of stressed plants in the field. We conclude that visual scoring of stressed plants was the best method of screening for drought resistance, but if controlled water deficit cannot be imposed, then drought resistance may be estimated by measuring both uprooting force and grain yield.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadi, N., 1983. Variabilité génétique et hérédité de méchanismes de tolérance à la sécheresse chez le riz Oryza sativa L.: I. Dévelopment du système racinaire. L'Agronomie Tropicale 38: 10–117.
Armenta-Soto, J.L., P.L., Steponkus & J.C., O'Toole, 1982. Aeroponic technique for root system studies of rice Oryza sativa L. Int. Rice Res. Newsletter 7: 22.
Chang, T.T., J.L., Armenta-Soto, C.X., Mao, R., Peris & G.C., Loresto, 1987. Genetic studies on the components of drought resistance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). In: Rice Genetics, pp. 387–398. Int. Rice Res. Inst., Los Baños, Philippines.
Chang, T.T. & G.C., Loresto, 1986. Screening techniques for drought resistance in rice. In: Chopra & Paroda (Eds.), Approaches for Incorporating Drought and Salinity Resistance in Crop Plants, pp. 108–129. Oxford & IBH, New Delhi.
Chang, T.T., G.C., Loresto, J.C., O'Toole & J.L., Armenta-Soto, 1982. Strategy and methodology of breeding rice for drought-prone areas. In: Drought Resistance in Crops with Emphasis on Rice, pp. 217–244. Int. Rice Res. Inst., Los Baños, Philippines.
De Datta, S.K. & D.V., Seshu, 1982. Evaluating rices for drought tolerance using field screening and multilocation trials. In: Drought Resistance in Crops with Emphasis on Rice, pp. 245–263. Int. Rice Res. Inst., Los Baños, Philippines.
Ekanayake, I.J., D.P., Garrity, T.M., Masajo & J.C., O'Toole, 1985. Root pulling resistance in rice: inheritance and association with drought resistance. Euphytica 34: 905–913.
Idso, S.B., R.D., Jackson, P.J., Pinter Jr., R.J., Reginato & J.L., Hatfield, 1981. Normalizing the stress-degree-day parameter for environmental variability. Agric. Meteorol. 24: 45–55.
International Rice Testing Program (IRTP), 1975. Standard Evaluation System for Rice. Int. Rice Res. Inst., Los Baños, Philippines.
Jackson, R.D., S.B., Idso, R.J., Reginato & P.J., Pinter Jr., 1981. Canopy temperature as a crop water stress indicator. Water Resources Res. 17: 1133–1138.
Maguling, M.A., J.C., O'Toole, R.P., Novero & D.P., Garrity, 1982. A rainfed lowland yield nursery for drought-prone areas: testing genetic materials for unfavorable shallow rainfed rice environments. Philipp. J. Crop Sci. 7: 37–43.
O'Toole, J.C. & T.T., Chang, 1979. Drought resistance in cereals—rice: a case study. In: Mussell & Staples (Eds.), Stress Physiology in Crop Plants, pp. 373–405. J. Wiley & Sons, New York.
O'Toole, J.C. & S.K. De Datta, 1986. Drought resistance in rainfed lowland rice. In: Progress in rainfed lowland rice, pp. 145–158. Int. Rice Res. Inst., Los Baños, Philippines.
O'Toole, J.C. & J.G., Real, 1986. Estimation of aerodynamic and crop resistances from canopy temperature. Agron. J. 78: 305–310.
O'Toole, J.C. & Soemartono, 1981. Evaluation of a simple technique for characterizing rice root systems in relation to drought resistance. Euphytica 30: 283–290.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ingram, K.T., Real, J.G., Maguling, M.A. et al. Comparison of selection indices to screen lowland rice for drought resistance. Euphytica 48, 253–260 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023658
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023658