Summary
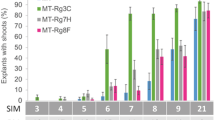
Adventitious shoots of Zinnia marylandica, an amphidiploid with limited genetic segregation, were regenerated from cotyledonary tissue on Murashige-Skoog (MS) media containing 0.2 or 22.2 μM thidiazuron (TDZ) and grown through flowering. Fisher's Test for Equal Variance indicated tissue culture induced plants had more variation than seed-derived control plants. Twelve of 149 (8%) plants derived from 0.2 μM TDZ and three of 23 (13%) plants from 22.2 μM TDZ had variant characters. Aberrant characteristics in self-pollinated variants included plant height, fertility, flower color and morphology, and were sexually transmitted, indicating genetic change had occurred. Aberrant characteristics not observed in regenerated plants arose in progeny.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- TDZ:
-
thidiazuron
References
Boyle T.H. & D.P. Stimart, 1982. Interspecific hybrids of Zinnia elegans Jacq. and Z. angustifolia HBK: embryology, morphology and powdery mildew resistance. Euphytica 31: 857–867.
Broertjes C. & A. Keen, 1980. Adventitious shoots: do they develop from one cell? Euphytica 29: 73–87.
D'Amato F., 1977. Cytogenetics of differentiation in tissue and cell culture. In: J. Reinert & Y.P.S. Bajaj (Eds.), Applied and Fundamental Aspects of Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture, pp. 343–357. Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Evans D.A. & J.E. Bravo, 1986. Phenotypic and genotypic stability of tissue cultured plants. In: R.H. Zimmerman, R.J. Griesbach, F.A. Hammerschlag & R.J. Lawson (Eds.). Tissue Culture as a Plant Production System for Horticultural Crop, pp. 73–94. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, Boston.
Evans D.A. & W.R. Sharp, 1983. Single gene mutations in tomato plants regenerated from tissue culture. Science 221: 949–951.
Fincham J.R.S., 1987. Patterns of flower pigmentation. Nature 325: 390–391.
Groose R.W. & E.T. Bingham, 1986. An unstable anthocyanin mutation recovered from tissue culture of alfalfa (Medicago sativa). 1. High frequency of reversion upon reculture. Plant Cell Rep. 5: 104–107.
Larkin P.J. & W.R. Scowcroft, 1981. Somaclonal variation—a novel source of variability from cell cultures for plant improvement. Theor. Appl. Genet. 60: 197–214.
Lee M. & R.L. Phillips, 1988. The chromosomal basis of somaclonal variation. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 39: 413–437.
Lentini Z., E.D. Earle & R.L. Plaisted, 1990. Insect-resistant plants with improved horitcultural traits from interspecific potato hybrids grown in vitro. Theor. Appl. Genet. 80: 95–104.
Lima-De-Faria A., 1969. DNA replication and gene amplification in heterochromatin. In: A. Lima-De-Faria (Ed.), Handbook of Molecular Cytology, pp. 234–282. North Holland, Amsterdam/London.
McClintock B., 1983. Trauma as a means of initiating change in genome organization and expression. In Vitro 19: 283–284 (Abstr.).
McClintock B., 1984. The significance of responses of the genome to challenge. Science 226: 792–800.
McCoy T.J., R.L. Phillips & H.W. Rines, 1982. Cytogenetic analysis of plants regenerated from oat (Avena sativa L.) tissue cultures and sectoring in some regenerated plants. Can. J. Genet. Cytol. 24: 559–565.
Murashige T. & F. Skoog, 1962. A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–497.
Orton T.J., 1980. Haploid barley regenerated from callus cultures of Hordeum vulgare x H. jubatum. J. Hered. 71: 280–282.
Reisch B., 1983. Genetic variability in regenerated plants. In: D.A. Evans, W.R. Sharp, P.V. Ammirato & Y. Yamada (Eds.), Handbook of Plant Cell Culture, Vol. 1, pp. 748–769. Macmillan Publ. Co., New York.
Sacristan M.D., 1971. Karyotypic changes in callus cultures from haploid and diploid plants of Crepis capillaris (L.) Wallr. Chromosoma 33: 273–283.
Scowcroft W.R., 1985. Somaclonal variation: The myth of clonal uniformity. In: B. Hohn & E.S. Dennis (Eds.), Genetic Flux in Plants, pp. 217–245. Springer-Verlag, New York.
Skirvin R.M. & J. Janick, 1976a. Tissue culture-induced variation in scented Pelargonium spp. J. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 101: 281–290.
Skirvin R.M. & J. Janick, 1976b. ‘Velvet Rose’ Pelargonium, a scented geranium. HortScience 11: 61–62.
Snedecor G.W. & W.G. Cochran, 1980. Statistical Methods, Seventh Edition, pp. 98–99. Iowa State University Press, Ames, Iowa.
Spooner D.M., D.P. Stimart & T.H. Boyle, 1991. Zinnia marylandica (Asteraceae: Heliantheae), a new disease resistant ornamental hybrid. Brittonia 430: 7–10.
Stebbins G.L., 1950. Variation and Evolution in Plants. Columbia University Press, New York.
Stieve, S.M., 1991. Adventitious shoot formation and somaclonal variation in Zinnia marylandica. M.S. thesis, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI.
Terry-Lewandowski V.M., G.R. Bauchan & D.P. Stimart, 1984. Cytology and breeding behavior of interspecific hybrids and induced amphiploids of Zinnia elegans and Zinnia angustifolia. Can. J. Genet. Cytol. 26: 40–45.
Wijsman H.J.W., 1986. Evidence for transposition in petunia. Theor. Appl. Genet. 71: 791–796.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stieve, S.M., Stimart, D.P. & Yandell, B.S. Heritable tissue culture induced variation in Zinnia marylandica . Euphytica 64, 81–89 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023541
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023541