Abstract
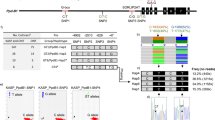
Rice genomic clones containing eight different α-amylase genes have been previously classified into five groups based on DNA hybridization studies and restriction site mapping. This report describes the clustering of three Group 3 genes (RAmy3A, RAmy3B and RAmy3C) within 28 kb of genomic DNA. The genes are separated from each other by about 5 kb and transcribed in the same direction. At the protein level, RAmy3B and RAmy3C are 95% homologous while each is 78% homologous to RAmy3A. All three genes have relatively small introns in the first and third positions. RAmy3A; however, has an additional 409 bp intron in the second intron insertion site. Nucleotide sequence comparisons of the coding and 3′ flanking regions suggest that clustering of the RAmy3 genes occurred by gene duplication resulting from unequal crossing-over at repetitive sequences. A comparison of the 5′ flanking regions revealed several sequences that may be involved in transcription. Expression of RAmy3B/C first appears in the germinating seed after two days and at a higher level after four days. Quantitative primer extension analysis indicates that RAmy3B and RAmy3C contribute 25% and 75%, respectively, of the transcripts from this cluster at four days of germination. No primer extension band specific to RAmy3A transcripts could be detected at this time point. However, RAmy3A PCR products could be amplified from RNA isolated from embryo-derived callus tissue.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akazawa T, Mitsui T, Hayashi M: Recent progress in α-amylase biosynthesis. In: J. Preiss (ed) The Biochemistry of Plants: A Comprehensive Treatise, Vol. 14, pp. 465–492. Academic Press, New York (1988).
Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K: Phenol/SDS method for plant RNA preparation. In: Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (eds) Current Protocols in Molecular Biology, pp. 4.3.1–4.3.4. Green Publishing Associates and Wiley-Interscience, New York (1987).
Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K: T4 polynucleotide kinase. In: Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA, Struhl K (eds) Current Protocols in Molecular Biology, pp. 3.10.2–3.10.5. Greene Publishing Associates and Wiley-Interscience, New York (1987).
Baulcombe DC, Huttly AK, Martienssen RA, Barker RF, Jarvis MG: A novel wheat α-amylase gene (α-Amy3). Mol Gen Genet 209: 33–40 (1987).
Beck E, Ziegler P: Biosynthesis and degradation of starch in higher plants. In: Briggs WR, Jones RL, Walbot V (eds) Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, vol. 40, pp. 95–117. Annual Reviews, Palo Alto, CA (1989).
Bennett MD, Smith JB: Nuclear DNA amounts in angiosperms. Proc R Soc London Ser B 274: 227–274 (1976).
Boer PH, Hickey DA: the α-amylase gene in Drosophila melanogaster: nucleotide sequence, gene structure and expression motifs. Nucl Acids Res 14: 8399–8411 (1986).
Bojsen K, Abildsten D, Jensen EO, Paludan K, Marcker KA: The chromosomal arrangement of six soybean leghemoglobin genes. EMBO J 2: 1165–1168 (1983).
Breathnach R, Chambon P: Organization and expression of eukaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rey Biochem 50: 349–383 (1981).
Brown ADH, Jacobsen JV: Genetic basis and natural variation of α-amylase isozymes in barley. Genet Res Camb 40: 315–324 (1982).
Cross M, Renkawitz R: Repetitive sequence involvement in the duplication and divergence of mouse lysozyme genes. EMBO J 9: 1283–1288 (1990).
Darnell JE: Variety in the level of gene control in eukaryotic cells. Nature 297: 365–371 (1982).
Daussant J, Miyata S, Mitsui T, Akazawa T: Enzymic mechanism of starch breakdown in germinating rice seeds. 15. Immunological study on multiple forms of amylase. Plant Physiol 71: 88–95 (1983).
Dean C, Pichersky E, Dunsmuir P: Structure, evolution, and regulation of RBcS genes in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 40: 415–439 (1989).
Devereux J, Haeberli P, Smithies O: A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucl Acids Res 12: 387–395 (1984).
Doolittle WF: The origin and function of intervening sequences in DNA: A review. Am Nat 130: 915–928 (1987).
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B: A technique for radiolabelling DNA restriction fragments to a high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132: 6–13 (1984).
Fincher GB: Molecular and cellular biology associated with endosperm mobilization in germinating cereal grains. In: Briggs WR, Jones RL, Walbot V (eds) Annual Review of Plant Physiology and Plant Molecular Biology, Vol. 40, pp. 305–346. Annual Reviews Palo Alto, CA (1989).
Forde BG, Heyworth A, Pyrell J, Kreis M: Nucleotide sequence of a B1 hordein gene and the identification of possible upstream regulatory elements in endosperm storage protein genes from barley, wheat and maize. Nucl Acids Res 13: 7327–7339 (1985).
Gale MD, Law CN, Chojecki AJ, Kempton RA: Genetic control of α-amylase production in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 64: 309–316 (1983).
Gemmill RM, Levy JN, Doane WW: Molecular cloning of α-amylase genes from Drosophila melanogaster. I. Clone isolation by use of a mouse probe. Genetics 110: 299–312 (1985).
Goodall GJ, Filipowicz W: The minimum functional length of pre-mRNA introns in monocots and dicots. Plant Mol Biol 14: 727–733 (1990).
Groot PC, Bleeker MJ, Pronk JC, Arwert F, Mager WH, Planta RJ, Eriksson AW, Frants RR: The human α-amylase multigene family consists of haplotypes with variable numbers of genes. Genomics 5: 29–42 (1989).
Harada JJ, Barker SJ, Goldberg RB: Soybean β-conglycinin genes are clustered in several DNA regions and are regulated by transcriptional and posttranscriptional processes. Plant Cell 1: 415–425 (1989).
Huang N, Koizumi N, Reinl S, Rodriguez RL: Structural organization and differential expression of rice α-amylase genes. Nucl Acids Res 18: 7007–7014 (1990).
Huang N, Sutliff TD, Litts JC, Rodriguez RL: Classification and characterization of the rice α-amylase multigene family. Plant Mol Biol 14: 655–668 (1990).
Huttly AK, Martienssen RA, Baulcombe DC: Sequence heterogeneity and differential expression of the α-Amy2 gene family in wheat. Mol Gen Genet 214: 232–240 (1988).
Jacobsen A: Purification and fractionation of poly(A)+ RNA. In: Berger SL, Kimmel AR (eds) Methods in Enzymology, Vol. 152, pp. 254–261. Academic Press, New York (1987).
Joshi CP: An inspection of domain between putative TATA box and translation start site in 79 plant genes. Nucl Acids Res 15: 6643–6653 (1987).
Khursheed B, Rogers JC: Barley α-amylase genes. Quantitative comparison of steady-state mRNA levels from individual members of the two different families expressed in aleurone cells. J Biol Chem 263: 18953–18960 (1988).
Klosgen RB, Gierl A, Schwarz-Sommer Z, Saedler H: Molecular analysis of the waxy locus of Zea mays. Mol Gen Genet 203: 237–244 (1986).
Knox CAP, Sonthayanon B, Chandra GR, Muthukrishnan S: Structure and organization of two divergent α-amylase genes from barley. Plant Mol Biol 9: 3–17 (1987).
Landry BS, Michelmore RW: Selection of probes for restriction fragment length analysis from plant genomic clones. Plant Mol Biol Rep 3: 174–179 (1985).
Lauer J, Shen C-K, Maniatis T: The chromosomal arrangement of human α-like globin genes: Sequence homology and α-globin gene deletions. Cell 119: 119–130 (1980).
Leutwiler LS, Meyerowitz EM, Tobin EM: Structure and expression of three light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b binding protein genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nucl Acids Res 14: 4951–4964 (1986).
Levy JN, Gemmill RM, Doane WW: Molecular cloning of α-amylase genes from Drosophila melanogaster. II. Clone organization and verification. Genetics 110: 313–324 (1985).
Maeda N, Smithies O: The evolution of multigene families: Human haptoglobin genes. Ann Rev Genet 20: 81–108 (1986).
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Habor, NY (1982).
McClure BA, Hagen G, Brown CS, Gee MA, Guilfoyle TJ: Transcription, organization, and sequence of an auxin-regulated gene cluster in soybean. Plant Cell 1: 229–239 (1989).
Miyata S, Akazawa T: Enzymic mechanism of starch breakdown in germinating rice seeds 12. Biosynthesis of α-amylase in relation to protein glycosylation. Plant Physiol 70: 147–153 (1982).
Montoliu L, Rigau J, Puigdomenech P: A tandem of α-tubulin genes preferentially expressed in radicular tissues from Zea mays. Plant Mol Biol 14: 1–15 (1989).
Muthukrisknan S, Gill BS, Swelge M, Chandra GR: Structural genes for α-amylase are located on barley chromosomes 1 and 6. J Biol Chem 259: 13637–13639 (1984).
Nielsen NC, Dickinson CD, Chou T-J, Thanh VH, Scallon BJ, Fischer RL, Sims TL, Drews GN, Goldberg RB: Characterization of the glycinin gene family in soybean. Plant Cell 1: 313–328 (1989).
Nishikawa K, Nobuhara M: Genetic studies of α-amylase isozymes of wheat 1. Location of genes and variation in tetra- and hexaploid wheat. Jpn J Genet 46: 345–358 (1971).
Oppenheimer DG: Haas N, Silflow CD, Snustad DP: The β-tubulin gene family of Arabidopsis thaliana: preferential accumulation of the β1 transcript in roots. Gene 63: 87–102 (1988).
Rahmatullah RJ, Huang JK, Clark KL, Reeck GR, Chandra GR, Muthukrishnan S: Nucleotide and predicted amino acid sequences of two different genes for high-pI α-amylases from barley. Plant Mol Biol 12: 119–121 (1989).
Rogers JC, Milliman C: Isolation and sequence analysis of a barley α-amylase cDNA clone. J Biol Chem 258: 8169–8174 (1983).
Saghai-Marrof MA, Soliman KM, Jorgensen RA, Allard RW: Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: Mendelian inheritance, chromosomal location, and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 8014–8018 (1984).
Shen S, Slighton JL, Smithies O: A history of the human fetal globin gene duplication. Cell 26: 191–203 (1981).
Tabor S, Richardson CC: DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84: 4767–4771 (1987).
Tobin AJ: Evaluating the contribution of posttranscriptional processing to differential gene expression. Develop Biol 68: 47–58 (1979).
Weibauer K, Gumucio DL, Jones JM, Caldwell RM, Hartle HT, Meisler MH: A 78-kilobase region of mouse chromosome 3 contains salivary and pancreatic amylase genes and a pseudogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 82: 5446–5449 (1985).
Whittier RF, Dean DA, Rogers JC: Nucleotide sequence analysis of α-amylase and thiol protease genes that are hormonally regulated in barley aleurone cells. Nucl Acids Res 15: 2515–2535 (1987).
Wingender R, Rohrig H, Horicke C, Wing D, Schell J: Differential regulation of soybean chalcone synthase genes in plant defense, symbiosis and upon environmental stimuli. Mol Gen Genet 218: 315–322 (1989).
Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K, Mundy J, Chua N-H: Four tightly linked genes are differentially expressed in rice. Plant Mol Biol 14: 29–39 (1989).
Yanisch-Perron C, Vieira J, Messing J: Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene 33: 103–119 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sutliff, T.D., Huang, N., Litts, J.C. et al. Characterization of an α-amylase multigene cluster in rice. Plant Mol Biol 16, 579–591 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023423
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023423