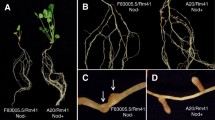
Abstract
Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar trifolii strain TA1 nodulates a range of Trifolium plants including red, white and subterranean clovers. Nitrogen-fixing nodules are promptly initiated on the tap roots of these plants at the site of inoculation. In contrast to these associations, strain TA1 has a ‘Nod-’ phenotype on a particular cultivar of subterranean clover called Woogenellup (A.H. Gibson, Aust J Agric Sci 19: (1968) 907–918) where it induces rare, poorly developed, slow-to-appear and ineffective lateral root nodules. By comparing the nodulation gene region of strain TA1 with that of another R. leguminosarum bv. trifolii strain ANU843, which is capable of efficiently nodulating cv. Woogenellup, we have shown that the nodT gene (B.P. Surin et al., Mol Microbiol 4: (1990) 245–252) is essential for nodulation on cv. Woogenellup. The nodT gene is naturally absent in strain TA1. A cosmid clone spanning the entire nodulation gene region of strain TA1 was capable of conferring nodulation ability to R.l. bv. trifolii strains deleted for nodulation genes, but only on cultivars of subterranean clovers nodulated by strain TA1. This shows that cultivar recognition events are, in part, determined by genes in the nodulation region of strain TA1. Complementation studies also indicated that strain TA1 contains negatively-acting genes located on the Sym plasmid and elsewhere, which specifically block nodulation of cv. Woogenellup.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appelbaum E, Chartrain N, Thompson D, Johanson K, O'Connell M, McLoughlin T. Genes of Rhizobium japonicum involved in the development of nodules. In: Evans H, Bottomley P (eds) Nitrogen Fixation Research Progress, pp. 101–107. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, Dordrecht (1985).
Appelbaum E, McLoughlin T, O'Connell M, Chartrain N: Expression of symbiotic genes of Rhizobium japonicum USDA191 in other rhizobia. J Bact 63: 385–388 (1985).
Bender G, Goydych W, Rolfe B, Nayudu M: The role of the Rhizobium conserved and host specific nodulation genes in the infection of the non-legume Parasponia andersonii. Mol Gen Genet 210: 299–306 (1987).
Canter-Cremers HCJ, Spaink HP, Wijfjes AHM, Pees E, Wijffelman CA, Okker RJH, Lugtenberg BJJ: Additional nodulation genes on the Sym plasmid of Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae. Plant Mol Biol 13: 163–174 (1989).
Davis EO, Evans IJ, Johnston AWB: Identification of nodX, a gene that allows Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae strain TOM to nodulate Afghanistan peas. Mol Gen Genet 212: 531–535 (1988).
Ditta G, Stanfield S, Corbin D, Helinski DR: Broad host range DNA cloning system for gram negative bacteria: construction of a gene bank of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77: 7346–7351 (1980).
Djordjevic MA, Innes RW, Wijffelman CA, Schofield PR, Rolfe BG: Nodulation of specific legumes is controlled by several loci in Rhizobium trifolii. Plant Mol Biol 6: 389–403 (1986).
Djordjevic MA, Schofield PR, Rolfe BG: Tn5 mutagenesis of Rhizobium trifolii host-specific nodulation genes result in mutants with altered host range ability. Mol Gen Genet 200: 463–471 (1985).
Djordjevic MA, Zurkowski W, Shine J, Rolfe BG: Symplasmid transfer to various symbiotic mutants of Rhizobium trifolii, R. leguminosarum and R. meliloti. J Bact 156: 1035–1045 (1983).
Dretzen G, Bellard M, Sassone-Corsi P, Chambon P: A reliable method for the recovery of DNA fragments from agarose and acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem 112: 295 (1981).
Ellingboe A: Changing concepts in host-pathogen genetics. Ann Rev Phytopath 19: 125–143 (1981).
Faucher C, Camut S, Denarie J, Truchet G: The nodH and nodQ host range genes of Rhizobium meliloti behave as avirulence genes in R. leguminosarum bv. viciae and determine changes in the production of plant-specific extracellular signals. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 2: 291–300 (1989).
Flor HH: Inheritance of reaction to rust in flax. J Agric Res 74: 241–262 (1947).
Friedman A, Long S, Brown S, Buikema W, Ausubel F: Construction of a broad host range cloning vector and its use in the genetic analysis of Rhizobium mutants. Gene 18: 289–296 (1982).
Gabriel DW: Genetics of plant parasite populations and host-parasite specificity. In: Kosuge T, Nester EW (eds) Plant-Microbe Interactions: Molecular and Genetic Perspectives, pp. 343–379 Macmillan Publishing Company, New York (1989).
Gibson A: Nodulation failure in Trifolium subterraneum L. cv. Woogenellup (Syn. Marrar). Aust J Agric Sci 19: 907–918 (1968).
Gough J, Murray N: Sequence diversity among related genes for recognition of specific targets in DNA molecules. J Mol Biol 166: 1–19 (1983).
Heron DS, Ersek T, Krishnan HB, Peuppke SG: Nodulation mutants of Rhizobium fredii USDA257. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 2: 4–10 (1989).
Holl FB: Host plant control of the inheritance of dinitrogen fixation in the Pisum-Rhizobium symbiosis. Euphytica 24: 767–770 (1975).
Hombrecher G, Gotz R, Dibb NJ, Downie JA, Johnston AWB, Brewin J: Cloning and mutagenesis of nodulation genes from Rhizobium leguminosarum TOM, a strain with extended host range. Mol Gen Genet 194: 293–298 (1984).
Iismaa S, Ealing P, Scott K, Watson J: Molecular linkage of the nif/fix and nod gene regions in Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar. trifolii. Mol Microbiol 3: 1753–1764 (1989).
Innes R, Hirose M, Kuempel P: Induction of nitrogen-fixing nodules on clover requires only 32 kilobase pairs of DNA from the Rhizobium trifolii symbiosis plasmid. J Bact 170: 3793–3802 (1988).
Innes RW, Kuempel PL, Plazinski J, Canter-Cremers H, Rolfe BG, Djordjevic MA: Plant factors induce expression of nodulation and host range genes in Rhizobium trifolii. Mol Gen Genet 201: 426–432 (1985).
Keen NT, Staskawicz B: Host range determinants in plant pathogens and symbionts. Ann Rev Microbiol 42: 421–440 (1988).
Klement Z, Goodman RN: The hypersensitive response to infection by bacterial pathogens. Ann Rev Phytopathol 5: 17–44 (1967).
Lie TA: Host genes in Pisum sativum L. conferring resistance to European Rhizobium leguminosarum strains. Plant Soil 82: 415–425 (1984).
Long SR: Rhizobium-legume nodulation: life together in the underground. Cell 56: 203–214 (1989).
Maniatis T, Fritsch E, Sambrook J: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY (1989).
Rolfe BG, Gresshoff PM, Shine J, Vincent JM: Interaction between a non-nodulating and an ineffective mutant of Rhizobium trifolii resulting in effective (nitrogen-fixing) nodulation. Appl Environ Microbiol 39: 449–452 (1980).
Ruvkun GB, Long SR, Meade HM, van den Bos RC, Ausubel FM: ISRm1: A Rhizobium meliloti insertion sequence that transposes preferentially into nitrogen fixation genes. J Mol Appl Genet 1: 405–418 (1982).
Sargent L, Huang SZ, Rolfe BG, Djordjevic MA: Split root assays using Trifolium subterraneum show that Rhizobium infection induces a systemic response that can inhibit nodulation of another invasive Rhizobium strain. Appl Envir Microbiol 53: 1611–1619 (1987).
Schofield PR, Djordjevic MA, Rolfe BG, Shine J, Watson JM: A molecular linkage map of nitrogenase and nodulation genes in Rhizobium trifolii. Mol Gen Genet 192: 459–465 (1983).
Schofield PR, Ridge RW, Rolfe BG, Shine J, Watson JW: Host-specific nodulation is encoded on a 14 Kb DNA fragment in Rhizobium trifolii. Plant Mol Biol 3: 3–11 (1984).
Schofield PR, Watson JW: DNA sequence of Rhizobium trifolii genes reveals a reiterated and potentially regulatory sequence preceding nodABC and nodFE. Nuc Acid Res 14: 2891–2903 (1986).
Spaink HP, Weinman JJ, Djordjevic MA, Wijffelman CA, Okker RJH, Lugtenberg BJJ: Genetic analysis and cellular localization of the Rhizobium host specificity-determining NodE protein. EMBO J 8: 2811–2818 (1989).
Staskawicz B, Dahlbeck D, Keen N, Napoli C: Molecular characterization of cloned avirulence genes from race O and race 1 of Pseudomonas syringae pv. glycinea. J Bact 169: 5789–5794 (1987).
Surin B, Watson J, Hamilton W, Economou A, Downie J: Molecular characterisation of the nodulation gene, nodT, from two biovars of Rhizobium leguminosarum. Mol Microbiol 4: 245–252 (1990).
Vincent JM: Factors controlling the legume-Rhizobium symbiosis. In: Newton WE, Orme-Johnson WH (eds) Nitrogen Fixation, pp. 103–129. University Park Press, Baltimore (1980).
Whitfield P, Seeburg P, Shine J: The human proopiomelanocortin gene: organisation, sequence and interspersion with repetitive DNA. DNA 1: 133–143 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lewis-Henderson, W.R., Djordjevic, M.A. nodT, a positively-acting cultivar specificity determinant controlling nodulation of Trifolium subterraneum by Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar trifolii . Plant Mol Biol 16, 515–526 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023418
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023418