Summary
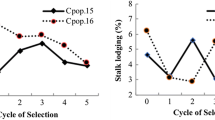
This research evaluated the response to three cycles of mass honeycomb selection based on the grain yields of widely-spaced plants from the F2 generation of a maize (Zea mays L.) single cross hybrid. Frequency distributions of individual plant yields in the selection plots showed strong positive skewness. A significant linear yield increase of 11.23% per cycle compared to the check was obtained. Correlated responses were the significant reduction in days to mid-silking, increases in ear and plant heights and in prolificacy. The selected population was similar to the original hybrid in days to mid-silking, ear and plant heights, but had significantly more ears per plant. It is concluded that mass honeycomb selection at wide spacings was effective in improving grain yield and prolificacy but may produce correlated responses in some other agronomic traits similar to those obtained with other selection schemes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bos, I., 1981. The relative efficiency of honeycomb selection and other procedures for mass selection in winter rye (Secale cereale L.). Doctoral thesis. Agric. Univ., Dept. of Plant Breeding. Wageningen. 172 pp.
Bos, I., 1983. Some remarks on honeycomb selection. Euphytica 32: 329–335.
Burton, G.W., 1983. Utilization of hybrid vigor. In: D.R., Wood (Ed.), Crop breeding. Am. Soc. Agron. and Crop Sci. Soc. Am., Madison, WI. pp. 89–107.
Compton, W.A. & K., Bahadur, 1977. Ten cycles of progress from modified ear-to-row selection in corn. Crop Sci. 17: 378–380.
Comstock, R.E., 1978. Quantitative genetics in maize breeding. In: D.B., Walden (Ed.), Maize breeding and genetics. John Wiley and Sons, New York, pp. 191–206.
Dudley, J.W., D.E., Alexander & R.J., Lambert, 1974. Seventy generations of selections for oil and protein concentration in the maize kernel. In: J.W., Dudley (Ed.), Seventy generations of selection for oil and protein in maize. Crop Sci. Soc. Am. Madison, Wisconsin, pp. 181–212.
Faosulas, A., 1981. Principles and methods of plant breeding. Pub. No. 11. Dept. Gen. Plant Breeding, Aristotelian Univ. of Thessaloniki, Greece, 147 pp.
Gardner, C.O., 1961. An evaluation of the effects of mass selection and seed irradiation with thermal neutrons on yield of corn. Corp Sci. 1: 241–245.
Gardner, C.O., 1978. Population improvement in maize. In: D.B., Walden (Ed.). Maize breeding and genetics. John Wiley and Sons, New York, pp. 207–228.
Genter, C.F., 1982. Recurrent selection for high inbred yields from the F2 of a maize single cross. Proc. 37th Annual Corn and Sorghum Ind. Res. Conf., pp. 67–76.
Hallauer, A.R. & J.B., Miranda FO., 1981. Quantitative genetics in maize breeding. Iowa State Univ. Press, Ames, Iowa. 468 pp.
Johnson, E.C., 1963. Mass selection for yield in a tropical corn variety. Am. Soc. Agron. Abstr. p. 82.
Kyriakou, D.T. & A.C., Fasoulas, 1985. Effects of competition and selection pressure on yield response in winter rye (Secale cereale L.). Euphytica 34: 883–895.
Mareck, J.H. & C.O., Gardner, 1979. Responses to mass selection in maize and stability of resulting populations. Crop Sci. 19: 779–783.
Mitchell, J.W., R.J., Baker & D.R., Knott, 1982. Evaluation of honeycomb selection for single plant yield in durum wheat. Crop Sci. 22: 840–843.
Moll, R.H. & W.D., Hanson, 1984. Comparisons of the effects of intrapopulation vs. interpopulation selection in maize. Crop Sci. 24: 1047–1052.
Motto, M. & R.H., Moll, 1983. Prolificacy in maize: a review. Maydica, 28: 53–76.
Paterniani, E., 1967. Selection among and within half-sib families in a Brazilian population of maize (Zea mays L.). Crop Sci. 7: 212–216.
Russell, W.A., S.A., Eberhart & U.A., Vega, 1973. Recurrent selection for specific combining ability for yield in two maize populations. Crop Sci. 13: 257–261.
Snedecor, G.W. & W.G., Cochran, 1967. Statistical methods, 6th edition. Iowa State Univ. Press, Ames, Iowa, 593 pp.
Webel, O.D. & J.H., Lonnquist, 1967. An evaluation of modified ear-to-row selection in a population of corn (Zea mays L.) Crop Sci. 7: 651–655.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Onenanyoli, A.H.A., Fasoulas, A.C. Yield response to honeycomb selection in maize. Euphytica 40, 43–48 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023295
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023295