Summary
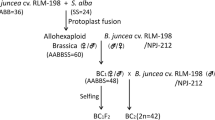
Raparadish, x Brassicoraphanus, the amphidiploid hybrid between Brassica rapa (syn. B.campestris) and Raphanus sativus (fodder radish) was made by Dolstra (1982). Primary hybrid plants grew vigorously, suggesting that the amphidiploid AARR might be useful as a fodder crop. Three populations of this new material were studied, with special attention to improvement of fertility and resistance to beet cyst nematode (Heterodera schachtii), whilst preserving genetic variability. For lack of progress one of the populations was abandoned after the fourth generation. The other two populations were observed through nine or ten generations. Apart from the last two generations mass selection for seed set was carried out on the basis of single plants. This led to a considerable increase in average seed production, without losing a wide variation for this trait. Thus more progress is being expected. Five cycles of mass selection for resistance to beet cyst nematodes led to a considerable increase of the level of resistance of both populations. The prospects of this new agricultural crop are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clauss, E., 1978. Allohexaploide Gattungsbastarde vom Typ Brassico-Raphanobrassica. Archiv Zücht. Forsch. 8: 297–302.
Dolstra, O., 1982. Synthesis and fertility of x Brassicoraphanus and ways of transferring Raphanus characters to Brassica. Agric. Res. Rep. 917, Pudoc, Wageningen, pp. 1–90.
Helm, J., 1957. Über den Typus der Art Raphanus sativus L., deren Gliederung und Synonymie. Kulturpflanze 5: 41–54.
Heyn, F.W., 1978. Introgression of restorer genes from Raphanus sativus into cytoplasmic male sterile Brassica napus and the genetics of fertility restoration. Proc. 5th Intern. Rapeseed Conf., Malmö, Sweden, Vol. 1: 82–83.
Hogenboom, N.G., 1973. A model for incongruity in intimate partner relationships. Euphytica 22: 219–233.
Hogenboom, N.G., 1975. Incompatibility and incongruity: two different mechanisms for the non-functioning of intimate partner relationships. Proc. Royal. Soc. London, B, Biol. Sci. 188: 361–375.
Honing, Y.van der, A., Steg & A.J.H.van, Es, 1977. Feed evaluation for dairy cows: tests on the system proposed in the Netherlands. Livest. Prod. Sci. 4: 95–107.
International Code of Botanical Nomenclature, 1983. Adopted by the 13th International Botanical Congress, Sydney, 1981. (E.G. Voss et al., Eds.), Regnum Vegetabile 111: 472 pp.
Karpechenko, G.D., 1928. Polyploid hybrids of Raphanus sativus L. X Brassica oleracea L. Z. indukt. Abstamm. Vererb. Lehre 48: 1–85.
Krechting, C.F. & W.M.J.van, Gelder, 1983. Automatisering van de bepaling van het stikstofgehalte in gewasmonsters met behulp van een ‘continous-flow’ systeem. Evaluatie van de salicylaatmethode en Nesslermethode. SVP-Rapport, SVP, Wageningen, pp. 1–16 (in Dutch).
McNaughton, I.H., 1976a. Turnip and relatives, Brassica campestris (Cruciferae). In: N.W., Simmonds, (Ed.) Evolution of crop plants, Longman, London, pp. 45–48.
McNaughton, I.H., 1967b. Swedes and rapes Brassica napus (Cruciferae). In: N.W., Simmonds, (Ed.) Evolution of crop plants, Longman, London, pp. 53–56.
McNaughton, I.H., 1979. The current position and problems in the breeding of Raphanobrassica (Radicole) as a forage crop. In: N.P.A. van Marrewijk & H. Toxopeus, (Eds.) Cruciferae 1979, Proc. Eucarpia Conf., SVP & RIVRO, Wageningen, pp. 22–28.
Olsson, G., 1954. Crosses within the campestris group of the genus Brassica. Hereditas 40: 398–418.
Olsson, G., 1986. Allopolyploids in Brassica. In: G., Olsson, (Ed.) Research and results in plant breeding, LTs förlag, Stockholm, pp. 114–119.
Oost, E., 1984. x Brassicoraphanus Sageret or x Raphanobrassica Karpechenko? Cruciferae Newsl. 9: 11–12.
Prakash, S. & S., Tsunoda, 1983. Cytogenetics of Brassica. In: M.S., Swaminathan, P.K., Gupta & U., Sinha, (Eds.) Cytogenetics of crop plants, MacMillan Delhi, pp. 482–513.
Sass, J., 1964. Botanical microtechnique. Iowa State University Ames, Iowa. 228 pp.
Thompson, K.F., 1976. Cabbages, kales etc. Brassica olerace (Cruciferae). In: N.W., Simmonds, (Ed.) Evolution of crop plants, Longman, London, pp. 49–52.
Toxopeus, H., 1974a. Outline of the evolution of turnips and coles in Europe and the origin of winter rape, swede-turnips and rape kales. In: A.B. Wills & C. North, (Eds.) Cruciferae 1974, Proc. Eucarpia Meeting, Scottish Hort. Res. Inst., Dundee, pp. 1–7.
Toxopeus, H., 1974b. The coding of races of Plasmodiophora brassicae (Woron.). In: A.B. Wills & C. North, (Eds.) Cruciferae 1974, Proc. Eucarpia Meeting, Scottish Hort. Res. Inst., Dundee, pp. 80–84.
Toxopeus, H. & E.H., Oost, 1985. A cultivar group classification of Brassica rapa L. Cruciferae Newsl. 10: 6–7.
Toxopeus, H., E.H., Oost & G., Reuling, 1984. Current aspects of the taxonomy of cultivated Brassica species. The use of Brassica rapa L. versus B. campestris L. and a proposal for a new intraspecific classification of B. rapa L. Cruciferae Newsl. 9: 55–58.
Toxopeus, H., 1985. xBrassicoraphanus Sageret, cultivargroup Raparadish. Cruciferae Newsl. 10: 13.
Toxopeus, H. & J.H. Lubberts, 1979. Breeding for resistance to the sugar beet nematode (Heterodera schachtii Schm.) in Cruciferous crops. Proc. Eucarpia Cruciferae Conference, Wageningen (Post Conference Edition): 151.
Tsunoda, S., K., Hinata & C., Gómez-Campo (Eds.), 1980. Brassica crops and wild allies. Biology and breeding. Japan Sci. Soc. Press, Tokyo, 354 pp.
U, N., 1935. Genome analysis in Brassica with special reference to the experimental formation of B. napus and peculiar mode of fertilization. Jap. J. Bot. 7: 389–452.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lange, W., Toxopeus, H., Lubberts, J.H. et al. The development of Raparadish (x Brassicoraphanus, 2n=38), a new crop in agriculture. Euphytica 40, 1–14 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023291
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023291