Summary
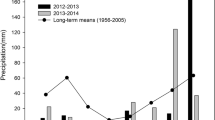
Distribution and accumulation of dry matter (d.m.) and nitrogen (N) were investigated within ears of a semidwarf, a gigas, and a normal wheat genotype grown under controlled environments. A high harvest index was linked with a small pre-anthesis N-storage (and vice versa) but this did not affect N amounts in grains because of compensation by prolonged N uptake during grain filling. N distribution within and between spikelets roughly paralleled that of d.m. Nevertheless, the two processes appeared to be rather independent as became evident from comparisons of the time courses in and between the genotypes. Final distribution of d.m. and N within and between spikelets mainly depended on different rates during the linear phases of accumulation and less on the duration. Maximum of d.m. and N weights per grain as well as maximum of grain number were observed in spikelets below the middle of the ear axis. This ‘submedian dominance’ suggested a pre-anthesis determination of the accumulation potential of grains in different spikelets. N percentage within spikelets disclosed that N accumulation was hampered more than that of d.m. in those positions unfavourable to the latter process. This principal pattern was not affected by genotypes in spite of considerable differences in numbers and weights of grains.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austin, R. B., J. A. Edrich, M. A. Ford & R. D. Blackwell, 1977. The fate of dry matter, carbohydrates and 14C lost from the leaves and stems of wheat during grain filling. Ann. Bot. 41: 1309–1321.
Austin, R. B., C. L. Morgan, M. A. Ford & R. D. Blackwell, 1980. Contribution to grain yield from pre-anthesis assimilation in tall and dwarf barley phenotypes in two contrasting seasons. Ann. Bot. 45: 309–319.
Bremner, P. M., 1972. Accumulation of dry matter and nitrogen by grains in different positions of the wheat ear as influenced by shading and defoliation. Aust. J. Biol. Sci. 25: 657–668.
Bremner, P. M. & H. M. Rawson, 1978. The weight of individual grains of the wheat ear in relation to their growth potential, the supply of assimilate and interaction between grains. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 5: 61–72.
Brunori, A., H. Axmann, A. Figueroa & A. Micke, 1980. Kinetics of nitrogen and dry matter accumulation in the developing seed of some varieties and mutant lines of Triticum aestivum. Z. Pflanzenzüchtg 84: 201–218.
Evans, L. T. & I. F. Wardlaw, 1976. Aspects of comparative physiology of grain yield in cereals. Advances Agron. 28: 301–359.
Fisher, J. E., 1973. Developmental morphology of the inflorescence in hexaploid wheat cultivars with and without the cultivar Norin-10 in their ancestry. Can. J. Plant Sci. 53: 7–15.
Fischer, R. A. & D. Hille Ris Lambers, 1978. Effect of environment and cultivar on source limitation to grain weight in wheat. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 29: 443–458.
Fussell, L. K. & C. J. Pearson, 1978. Course of grain development and its relationship to black region appearance in Pennisetum americanum. Field Crop Res. 1: 21–31.
Hanif, M. & R. H. M. Langer, 1972. The vascular system of spikelet in wheat. Ann. Bot. 36: 721–727.
Herzog, H., 1982. Source and sink development during kernel filling of two spring wheats as affected by root size and cytokinin applications. Z. Pflanzenern. Bodenk. 145: 128–139.
Herzog, H. & P. Stamp, 1982. Chlorophyll content and RuBP carboxylase activity in assimilating organs in relation to grain growth of ‘gigas’ semidwarf and normal spring wheats. Z. Pflanzenzüchtg 88: 127–136.
Martinez-Carrasco, R. & G. N. Thorne, 1979. Physiological factors limiting grain size in wheat. J. exp. Bot. 30: 669–679.
McNeal, F. H., M. A. Berg & C. A. Watson, 1966. Nitrogen and dry matter in five spring wheat varieties at successive stages of development. Agron. J. 58: 605–608.
McNeal, F. H., M. A. Berg, C. F. McGuire, V. R. Stewart & O. E. Balridge, 1972. Grain and plant nitrogen relationship in eight spring wheat crosses. Crop Sci. 12: 599–602.
Mikesell, M. E. & G. M. Paulsen, 1971. Nitrogen translocation and the role of individual leaves in protein accumulation in wheat grain. Crop Sci. 11: 919–922.
Nass, H. G. & B. Reiser, 1975. Grain filling period and grain yield relationships in spring wheat. Can. J. Plant Sci. 55: 673–678.
Nátr, L., P. Apel & I. Kousalová, 1978. Mathematical description of nitrogen and phosphorus accumulation in developing barley kernels. Biologia Plant. 20: 248–255.
Pinthus, M. J. & Y. Sar-Shalom, 1978. Dry matter accumulation in the grains of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars differing in grain weight. Ann. Bot. 42: 469–471.
Simmons, S. R. & D. N. Moss, 1978a. Nitrogen and dry matter accumulation by kernels formed at specific florets in spikelets of spring wheat. Crop Sci. 18: 131–143.
Simmons, S. R. & D. N. Moss, 1978b. Nitrate reductase as a factor affecting N assimilation during the grain filling period in spring wheat. Crop Sci. 18: 584–586.
Sofield, I., I. F. Wardlaw, L. T. Evans & S. Y. Zee, 1977. Nitrogen, phosphorus, and dry matter contents during grain development and maturation in wheat. Aust. J. Plant Physiol. 4: 799–810.
Spiertz, J. H. H., 1974. Grain growth and distribution of dry matter in the wheat plant as influenced by temperature, light energy and ear size. Neth. J. agric. Sci. 22: 207–220.
Spiertz, J. H. H., 1977. The influence of temperature and light intensity on grain growth in relation to carbohydrate and nitrogen economy of the wheat plant. Neth. J. agric. Sci. 25: 182–197.
Spiertz, J. H. H. & J. Ellen, 1978. Effects of nitrogen on crop development and grain growth of winter wheat in relation to assimilation and utilization of assimilates and nutrients. Neth. J. agric. Sci. 26: 210–231.
Stamp, P. & G. Geisler, 1978. Die Stickstoffaufnahme und das Wachstum der Körner bei zwei Sommerweizensorten. Z. Acker-und Pflanzenb. 147: 255–263.
Stamp, P., U. Rave, W. Diepenbrock, H. Herzog, O. Krippgans & G. Geisler, 1982. Comparative analysis of dry matter accumulation in caryopses and seeds of aestivum wheats, durum wheat, rye, triticale, rape seed and pea by means of a growth function. Z. Acker-und Pflanzenb. 151: 224–234.
Stoy, V., 1965. Photosynthesis respiration and carbohydrate accumulation in spring wheat in relation to yield. Physiol. Plant. Suppl. IV: 1–125.
Tietze, U., 1970. Untersuchungen zur Gliederung der Weizenähre und der damit zusammenhängenden Kornbeschaffenheit. Z. Acker-und Pflanzenb. 132: 85–106.
Walpole, P. R. & D. G. Morgan, 1970. A quantitative study in grain filling in Triticum aestivum L., cultivar Maris Widgeon. Ann. Bot. 34: 309–318.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Herzog, H., Stamp, P. Dry matter and nitrogen accumulation in grains at different ear positions in ‘gigas’, semidwarf and normal spring wheats. Euphytica 32, 511–520 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00021463
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00021463