Abstract
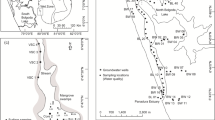
Impoundment behavior was determined for alkalinity, temperature, dissolved oxygen, and conductivity from stations located along the length of a bottom-draining, oligo-mesotrophic, hardwater, deep-storage reservoir located in central Texas. The epilimnion deepened the length of the reservoir throughout the summer as a result of drawdown. Bicarbonate alkalinity and conductivity exhibited both longitudinal and vertical stratification. Alkalinity and conductivity in the epilimnion decreased from the riverine reach downreservoir to the dam. This longitudinal progression was attributed to inflow and photosynthetically induced epilimnetic decalcification.
Hypolimnetic anoxic conditions first occurred in the sedimentation zone in the upreservoir and riverine reaches and then developed in a downreservoir pattern as summer progressed as a result of drawdown. Alkalinity and conductivity in the hypolimnion increased during anoxic conditions and consequently increased in a downreservoir progression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Public Health Association. 1971. Standard methods of the determination of water and wastewater. Washington, D. C. 874 pp.
Chave, K. E. 1965. Carbonates: association with organic matter in surface seawater. Science 148: 1723–1724.
Dowell, C. L. & Petty, R. G. 1971. Engineering data on dams and reservoirs in Texas. Part III. Tex. Water Dev. Board Rep. 126. 198 pp.
Ebel, W. J. & Koski, C. H. 1968. Physical and chemical limnology of Brownlee Reservoir, 1962–64. Fishery Bull. 67 (2): 295–335.
Fish, F. F. & Wagner, F. A. 1950. Oxygen block in the mainstream of the Williamette River. U. S. Fish and Wildl. Serv., Spec. Re. Fish No. 41. 19 pp.
Gnilka, A. 1975. Some chemical and physical aspects of Center Hill Reservoir, Tennessee. J. Tenn. Acad.Sci. 50 (1): 7–11.
Golterman, H. L. 1975. Physiological limnology. An approach to the physiology of lake ecosystems. American Elsevier, New York. 489 pp.
Hannan, H. H. & Broz, L. 1976. The influence of a deep-storage and an underground reservoir on the physicochemical limnology of a permanent central Texas river. Hydrobiologia 51 (1): 43–63.
Hannan, H. H. & Young, W. J. 1974. The influence of a deep-storage reservoir on the physicochemical limnology of a central Texas river. Hydrobiologia 44 (2–3): 177–209.
Holland, P. 1965. Base-flow studies, Guadalupe River, Comal County, Texas, quantity, March 1962. Texas Water Commission Bull. 6503. 7 pp.
Hutchinson, G. E. 1975. A treatise on limnology. Volume I. Geography, physics, and chemistry. Part 2. Chemistry of lakes. John Wiley and Sons, New York. 541–1015 pp.
McCaull, J. & Crossland, J. 1974. Water pollution. Harcourt Brace Jovanovich, New York. 206 pp.
Nicholas, W. R. & Gordon, J. A. 1972. Effects of impoundments on water quality. Observations of several mechanisms of D. O. depletion. A. S. C. E. Annual and National Environmental Meeting, Houston, Texas, 1972.
Nix, J. F. 1974. Distribution of trace metals in a warm water release impoundment. Arkansas Water Resources Res. Center Publ. 12. 377 pp.
Otsuki, A. & Wetzel, R. G. 1972. Coprecipitation of phosphate with carbonates in a marl lake. Limnol. and Oceanog. 17: 763–767.
Otsuki, A. & Wetzel, R. G. 1974. Calcium and total alkalinity budgets and calcium carbonate precipitation of a small hardwater lake. Arch. Hydrobiol. 73 (1): 14–30.
Suess, E. 1970. Interaction of organic compounds with calcium carbonate I. Association phenomena and geochemical implications. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 34: 157–168.
United States Army Corps of Engineers. 1974. Report on sedimentation, Canyon Lake, Guadalupe River, Guadalupe River basin, Texas, resurvey of August, 1972. In: House report of the U. S. Army Corps of Engineers District, Fort Worth, Texas, 66 pp.
Wetzel, R. G. 1975. Limnology. W. B. Saunders Co., Philadelphia. 743 pp.
Wiebe, A. H. 1938. Limnological observations on Norris Reservoir with special reference to dissolved oxygen and temperatures. 3rd. North Am. Wildlife Conf.: 440–457.
Wiebe, A. H. 1939. Dissolved oxygen profiles at Norris Dam and in the Big Creek sector of Norris Reservoir (1937), with a note on the oxygen demand of the water (1938). Ohio J. of Sci. 39 (1):27–36.
Wiebe, A. H. 1940. The effect of density currents upon the vertical distribution of temperature and dissolved oxygen in Norris Reservoir. J. Tenn. Acad. Sci. 15 (3): 301–308.
Wunderlich, W. O. 1971. The dynamics of density-stratified reservoirs. in: G. E. Hall, ed., Reservoir Fisheries and Limnology. American Fish. Soc., Spec. Pub. 8: 219–231.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hannan, H.H., Fuchs, I.R. & Whitenberg, D.C. Spatial and temporal patterns of temperature, alkalinity, dissolved oxygen and conductivity in an oligo-mesotrophic, deep-storage reservoir in central Texas. Hydrobiologia 66, 209–221 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00020902
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00020902