Abstract
The protein, carbohydrate and lipid contents of the food ingested and their absorption in the intestine of Heterotis niloticus inhabiting a small man-made lake; Awba Lake, in Ibadan were investigated.
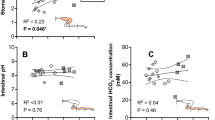
The ingested food had mean total protein, mean total carbohydrate and mean total lipid contents of 53.0%, 28.8% and 15.5% of the organic content, respectively. Calculated percentages absorbed were 56.4–72.7% (mean — 64.9%) total protein, 32.2–50.8% (mean — 40.3%) total carbohydrates and 71.9–87.3% (mean = 78.3%) lipid.
Absorption mostly occurred in the fore-gut (the first one-third of the intestine) and least in the hind-gut (the last one-third of the intestine). Different sizes of fish showed different dietary protein, carbohydrate and lipid contents. Absorptive capacity for these components of the food also varied with fish size.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akintunde, E. A., 1982. Intestinal absorption by Sarotherodon galilaeus (Syn: Tilapia galilaea) of Kainji Lake, Nigeria. Proceedings of the second annual conference of the fisheries society of Nigeria (FISON), Calabar, 25th–27th January 1982: 235–243.
Al-Hussaini, A. H., 1949. Functional morphology of the alimentary tract of some fishes in relation to their feeding habits. Part I. Quart J. Micr. Sci. 90: 109–140.
Al-Hussaini, A. H. & A. A. Kholy, 1953. On the functional morphology of the alimentary tract of some omnivorous fish. Proc. Egypt. Acad. Sci. 9: 17–39.
Bligh, E. G. & W. J. Dyer, 1959. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 39: 911–917.
Bowen, S. H., 1981. Digestion and assimilation of periphytic detrital aggregate by T. mossambica. Trans. am. Fish. Soc. 110: 239–245.
Bowen, S. H., 1982. Feeding, Digestion and Growth — Qualitative Considerations. pp. 141–156. In R. S. V. Pullin and R. H. Lowe McConnel (eds). The Biology and Culture of Tilapias. ICLARM Conference Proceedings 7: 432 pp.
Bullock, W. L., 1963. Intestinal histology of some salmonid fishes with particular reference to the histopathology of acanthocephalan infections. J. Morph. 112: 23–44.
Caulton, M. S., 1978. The importance of habitat temperatures for growth in the tropical cichlid Tilapia rendalli Boulenger. J. Fish. Biol. 13: 99–112.
Clark, J., 1983. A preliminary investigation of the digestive enzymes of the dover sole (Solea solea L.). Heriot-Watt University, Edinburgh, 30 pp.
Green, C. W., 1913. The fat absorbing function of alimentary tract of king salmon. Bull. U.S. Bur. Fish. 33: 149–175.
Kaushik, N. K. & H. B. N. Hynes, 1968. Experimental study on the role of autumn-shed leaves in aquatic environment. J. Ecol. 65: 229–243.
Mathew, L. H. & H. W. Parker, 1950. Notes on the anatomy and biology of the basking shark (Cetorhinus maximus) (Gunner). Proc. Zool. Soc., Lond. 120: 535–576.
Miller, G. L., 1959. Protein determination for large numbers of samples. Analyt. chem. 31: 964.
Moriarty, D. J. W., 1973. The physiology of digestion of blue-green algae in T. nilotica. J. Zool., Lond. 171: 25–39.
Sivadas, P., 1965. Absorption of fat in the alimentary canal of Tilapia mossambica (Peters) (Teleostei). J. Cell. Comp. Physiol. 65: 249–254.
Thomas, L. C. & G. J. Chambelin, 1974. Colorimetric Chemical Analytical Methods 8th Edition. The Tintometer Ltd., Salisbury, England and at Tintometer 9M6H W. Germany.
Ugwumba, A. A. A., 1989. Carbohydrases in the digestive tract of Sarotherodon melanotheron (Ruppell) (Pisces: Cichlidae) in Lake Awba, Ibadan, Nigeria. J. Expt. Appl. Biol. 1: 44–56.
Ugwumba, A. A. A., 1990. Food and feeding ecology of Oreochromis niloticus, Sarotherodon melanotheron and Heterotis niloticus (Pisces: Osteichthyes) in Awba Reservoir, Ibadan, Ph.D. Thesis, University of Ibadan, 395 pp.
Ugwumba, A. A. A., 1992. The food and feeding habits of Heterotis niloticus (Teleostei: Osteoglossidae) in a small tropical man-made lake in Ibadan, Nigeria. J. Afr. Zool. 106: 113–123.
Ugwumba, A. A. A., 1993. Carbohydrases in the digestive tracts of the African bony-tongue Heterotis niloticus (Pisces: Osteoglossidae). Hydrobiologia 257: 95–100.
Van Slyke, D. D. & G. F. White, 1911. Digestion of protein in the stomach and intestine of the dogfish. J. Biol. Chem. 9: 209–217.
Winberg, G. G., 1956. Rate of Metabolism of Food Requirements of Fishes. Belorussian State University, Minsk. (Translated from Russian by Fish Res. Bd. Can. Transl. Ser. No. 194 (1960).
Yamamoto, T., 1966. An electron microscopic study of the columnar epithelial cell in the intestine of freshwater teleost goldfish (Carassius auratus) and rainbow trout (Salmo irideus) Z. Zellfrosch Mikrosk Anat. 72: 66–87.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ugwumba, A.A.A. Absorption of food in Heterotis niloticus (Cuvier) (pisces: osteoglossidae) from a small tropical man-made lake in Ibadan, Nigeria. Hydrobiologia 330, 55–58 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00020823
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00020823