Abstract
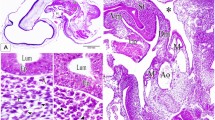
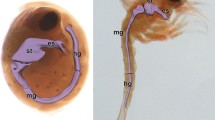
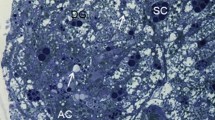
The fine structure of the rudimentary gut of male Asplanchna sieboldi in late stage embryos and at o, 12 and 24 hours after birth is described. The results of histochemical tests for acid phosphatase and glycogen indicate that glycogen, mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, and nuclei are subjected to autolysosomal breakdown, while glycogen remains as the major component of the gut in old males.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buchner, H., Tiefenbacher, L., Kling, R. & Preissler, K. 1970. Über die physiologische Bedeutung des Magen-Darm-Rudimentes des Männchen von Asplanchna sieboldi (Rotatoria, Monogononta). Z. vergl. Physiol. 67: 453–454.
Gilbert, J. J. 1968. Dietary control of sexuality in the rotifer Asplanchna brightwelli Gosse. Physiol. Zool. 41: 14–43.
Gilbert, J. J. & Birky, C. W. Jr. 1971. Sensitivity and specificity of the Asplanchna response to dietary alpha tocopherol. J. Nutrition 101: 113–126.
Hudson, C. T. 1883. On Asplanchna ebbesbornii nov. sp. J. r. microsc. Soc.: 621–628.
Hudson, C. T. & Gosse, P. H. 1886. The Rotifera or Wheel-Animalcules, both British and Foreign. London Vol. L: I–IV + 1–128; Vol. IL: 1–144.
Humason, G. L. 1962. Animal Tissue Techniques. W. H. Freeman and Co., San Francisco: 298–301.
Lange, A. 1911. Zur Kenntnis von Asplanchna sieboldii Leydig. Zool. Anz. 38: 433–441.
Luft, J. H. 1961. Improvements in epoxy embedding methods. J. Biophys. Biochem. Cytol. 9: 409–427.
Miller, F. & Palade, G. E. 1964. Lytic activities in renal protein absorption droplets. An electron microscopical cytochemical study. J. Cell Biol. 23: 519–552.
Powers, J. H. 1912. A case of polymorphism in Asplanchna simulating mutation. Am. Nat. 46: 526–552.
Schiaffino, S. & Hanzlikova, V. 1972. Autophagic degradation of glycogen in skeletal muscles of the newborn rat. J. Cell Biol. 52: 41–51.
Spurr, A. R. 1969. A low viscosity epoxy resin embedding medium for electron microscopy. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 26: 31–43.
Vye, M. V. & Fischman, D. A. 1971. A comparative study of three methods for the ultrastructural demonstration of glycogen in thin sections. J. Cell Sci. 9: 747–749.
Waniczek, H. 1930. Untersuchungen über einige Arten der Gattung Asplanchna Gosse (A. girodi de Guerne, A. brightwellii Gosse, A. priodonta Gosse). Ann. Mus. Zool. Pol. 8: 109–322.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wurdak, E.S., Gilbert, J.J. Ultrastructure and histochemistry of the rudimentary gut of male Asplanchna sieboldi (Rotifera). Hydrobiologia 73, 123–126 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00019434
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00019434