Abstract
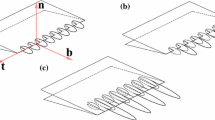
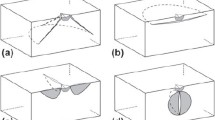
Cone fractures have been produced in epoxy resin samples in four different test configurations using a cylindrical indenter. The shapes of the cracks were determined using optical microscope focusing methods and it was found that they were strongly dependent on test geometry. Large changes in cone angle with crack length were observed. The evolution of the cracks was determined by mapping the fine river line markings on the fracture surface. In all cases crack nucleation occurred at point sources close to the edge of the indenter and then the crack grew in the material round the base of the indenter before expanding outwards. Numerous crack arrest markings were also mapped. It was found that the number and distribution of crack arrests was dependent on the test configuration and re-nucleation occurred after each arrest. The results are interpreted in terms of the no-twist growth constraint, which applies to crack growth in brittle solids. This leads to characteristic patterns on the fracture surface. It is shown that point nucleation results in a strongly non-symmetric fracture path and that the requirement that nucleation occurs at a point has a significant effect on the interpretation of fracture data in other test configurations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H.H.Hertz, Hertz's Miscellaneous Papers, Macmillan, London (1896).
B.R.Lawn, Fracture of Brittle Solids, 2nd edn., Cambridge University Press, Cambridge (1993).
D.Bahat and M.R.Sharpe, Journal of Materials Science 17 (1982) 1167–1170.
I. Finnie and S. Vaidyanathan, in Fracture Mechanics of Ceramics, Vol. 1, R.C. Bradt, D.P.H. Hasselman and F.F. Lange (eds.), Plenum Press (1974) 231–244.
M.M.Chaudhri and C.R.Kurkjian, Journal of the American Ceramic Society 69 (1986) 404–410.
D.Hull, International Journal of Fracture 62 (1993) 119–138.
D.Purslow, Composites 17 (1986) 289–303.
R.E.Robertson and V.E.Mindroiu, Polymer Engineering and Science 27 (1987) 55–61.
R.J. Young, in Developments in Reinforced Plastics-1, G. Pritchard (ed.), Applied Science Publishers (1980) 257–283.
M.M.Chaudhri and P.A.Brophy, Journal of Materials Science 15 (1980) 345–352.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Emeritus Goldsmiths' Professor of Metallurgy, University of Cambridge, U.K.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hull, D. The evolution of ‘cone’ cracks under axi-symmetric loading conditions. Int J Fract 66, 295–312 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00018436
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00018436