Abstract
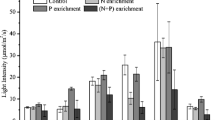
A series of water samples from Lake Kinneret was supplemented with 100 µM N (as NH4 or as NO3 and/or 10 µM orthophosphate-P. The yield of phytoplankton both as chlorophyll and in cell numbers of major species was determined after a two-week incubation. During these experiments, some of the algae present initially never multiplied (e.g. Peridinium and Peridiniopsis spp. Cryptomonas spp., Rhodomonas spp. and Crysochromulina parva); others e.g. Anomoeoneis exilis, Synedra sp., Chlamydomonas sp., Elakatothrix gelatinosa), undetected in the original sample, grew out during the incubation. Chlorophyte species (the majority of commonly observed forms in the lake) responded most readily to added nutrients.
The results of these enrichment experiments were related to the long-term record of phytoplankton populations observed in the lake and suggest that through summer and fall, when ambient levels of both P and N are minimal, P was generally, but not always, the most limiting nutrient for algal growth. In the spring, after the decline of the Peridinium bloom, P appeared to be limiting the growth of Chlorophyta. Although most algal species grew equally well on NH4 or NO3, some species appeared to respond preferentially either to the former (Coelastrum, Chodatella) or to the latter (Chroococcus, Anomoeoneis) source of N.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berman, T., 1970. Phosphatase and phosphorus availability in Lake Kinneret. Limnol. Oceanogr. 15: 663–674.
Berman, T., 1984. Phosphorus and the cultural eutrophication of lakes: reality and illusion. Proc. LECS Shiga Conf., Pref. Govt., Otsu, Japan: 122–127.
Berman, T. & Z. Dubinsky, 1985. The autoecology of Peridinium cinctum fa. westii from Lake Kinneret. Verh. Int. Ver. Limnol. 22: 2850–2853.
Berman, T. & U. Pollingher, 1974. Annual and seasonal variations of phytoplankton, chlorophyll and photosynthesis in Lake Kinneret. Limnol. Oceanogr. 19: 31–54.
Berman, T., B. F. Sherr, E. Sherr, D. Wynne & J. J. McCarthy, 1984. The characteristics of ammonium and nitrate uptake by phytoplankton in Lake Kinneret. Limnol. Oceanogr. 29: 287–297.
Edmondson, W. T., 1972. Nutrients and phytoplankton in Lake Washington. In G. E. Likens (ed.), Nutrients and Eutrophication. Spec. Symp. 1, Am. Soc. Limnol. Oceanogr.: 172–188.
Gophen, M., 1976. Temperature dependence of food intake, ammonia excretion and respiration in Ceriodaphnia reticulata (Jurine) (Lake Kinneret, Israel) Freshwat. Biol. 6: 451–455.
Henry, R., J. G. Tundisi & P. R. Curie, 1984. Effects of phosphorus and nitrogen enrichment on the phytoplankton in a tropical reservoir (Lobo Reservoir, Brazil). Hydrobiologia 118: 177–185.
Holm-Hansen, O., C. Lorenzen, R. W. Holmes & J. D. H. Strickland, 1965. Fluorometric determination of chlorophyll. J. Cons. Int. Explor. Mer 30: 3–15.
Jordan, R. A. & M. E. Bender, 1973. Stimulation of phytoplankton growth by mixtures of phosphate, nitrate and organic chelators. Wat. Res. 7: 189–195.
McCarthy, J. J., D. Wynne & T. Berman, 1982. The uptake of dissolved nitrogenous nutrients by Lake Kinneret (Israel) microplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 27: 673–680.
Megard, R., 1977. Phytoplankton, phosphorus and sewage effluents in Lake Minnetonka. In L. Seyb and K. Randolph (eds), North America Project Study of U.S. Water Bodies, EPA-600/3-77-086: 91–116.
Moss, B., 1969. Limitation of algal growth in some central African waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 14: 591–601.
Pollingher, U., 1978. The phytoplankton of Lake Kinneret. In C. Serruya (ed.), Lake Kinneret. Monographiae Biologicae 32. Junk, The Hague: 229–242.
Pollingher, U., 1981. The structure and dynamics of the phytoplankton assemblages in Lake Kinneret, Israel. J. Plankton Res. 3: 93–105.
Pollingher, U., 1986. Phytoplankton periodicity in a subtropical lake (Lake Kinneret, Israel). Hydrobiologia 138: 127–138.
Pollingher, U. & T. Berman, 1977. Quantitative and qualitative changes in the phytoplankton of Lake Kinneret, Israel, 1972–1975. Oikos 29: 418–428.
Pollingher, U. & T. Berman, 1982. Relative contribution of net and nano phytoplankton to primary production in Lake Kinneret (Israel). Arch. Hydrobiol. 96: 33–46.
Pollingher, U., A. Ehrlich & S. Serruya, 1987. The planktonic diatoms of Lake Kinneret (Israel) during the last 5 000 years. Their contribution to the algal biomass. In Proc. 8th Int. Symp. M. Ricard (ed.). Koeltz Scient. Books. Koenigstein FRG: 459–470.
Pollingher, U. & E. Zemel, 1981. In situ and experimental evidence of the influence of turbulence on cell division processes of Peridinium cinctum forma westii (Lemm.) Lefevre. Br. Phycol. J. 16: 281–287.
Robarts, R. D. & G. S. Southall, 1977. Nutrient limitation of phytoplankton growth in seven tropical man-made lakes, with special reference to Lake McIlwaine, Rhodesia. Arch. Hydrobiol. 79: 1–35.
Schelske, C., E. D. Rothman, E. F. Stoermer & M. A. Santiago, 1974. Responses of phosphorus limited Lake Michigan phytoplankton to factorial enrichments with nitrogen and phosphorus. Limnol. Oceanogr. 19: 409–419.
Schelske, C. L. & E. F. Stoermer, 1972. Phosphorus, silica and eutrophication of Lake Michigan. In G. E. Likens (ed.), Nutrients and Eutrophication. Spec. Symp. 1, Am. Soc. Limnol. Oceanogr.: 157–171.
Schindler, D. W., 1974. Eutrophication and recovery in experimental lakes: implications for lake management. Science 184: 897–899.
Serruya, C., 1975. Nitrogen and phosphorus balances in Lake Kinneret. Verh. Int. Ver. Limnol. 19: 1357–1369.
Serruya, C. & T. Berman, 1975. Phosphorus,nitrogen and the growth of algae in Lake Kinneret. J. Phycol. 11: 155–162.
Stoermer, E. F., B. G. Ladewsky & C. L. Schelske, 1978. Population responses of Lake Michigan phytoplankton to nitrogen and phosphorus enrichment. Hydrobiologia 57: 249–265.
Talling, J. F., 1966. The annual cycle of stratification and phytoplankton growth in Lake Victoria (East Africa). Int. Revue Ges. Hydrobiol. 51: 545–621.
Toerien, D. F. & D. Y. Steyn, 1975. The eutrophication levels of four South African impoundments. Verh. Int. Ver. Limnol. 19: 1947–1956.
Utermohl, H., 1958. Zur Vervollkommnung der quantitativen Phytoplankton — methodik. Mitt. Int. Ver. Limnol. 9: 1–38.
Wynne, D., 1977. Alternations in activity of phosphatases during the Peridinium bloom in Lake Kinneret. Physiol. Plant. 40: 219–224.
Wynne, D., N. J. Patni, S. Aaronson & T. Berman, 1982. The relationship between nutrient status and chemical composition of Peridinium cinctum during the bloom in Lake Kinneret. J. Plankton. Res. 4: 125–136.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pollingher, U., Berman, T., Kaplan, B. et al. Lake Kinneret phytoplankton: Response to N and P enrichments in experiments and in nature. Hydrobiologia 166, 65–75 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00017484
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00017484