Abstract
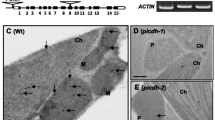
The cDNA encoding castor bean endosperm isocitrate lyase (ICL) was expressed under the control of the promoter of the small subunit of pea ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase in transformed tobacco. ICL protein was detected using anti-ICL antibodies on immunoblots of total leaf protein extracts. Nycodenz density gradient separation of the extracts from the transgenic tobacco leaves showed ICL co-fractionated with hydroxypyruvate reductase, a peroxisomal matrix marker protein, and away from lactate dehydrogenase, a cytosolic marker protein. Immunoelectron microscopy of ultrathin leaf sections demonstrated the location of ICL within the matrix of the leaf peroxisomes of the transgenic plants. In vitro transcribed and translated ICL was also imported into leaf peroxisomes isolated from germinating sunflower seeds. The in vivo and in vitro import of this protein into leaf peroxisomes provides strong support for the notion that the import machinery of glyoxysomes and peroxisomes is very similar.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnon DI: Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts. Polyphenoloxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24: 1–15 (1949).
Anderson CW, Straus JW, Dudock BS: Preparation of a cell-free protein-synthesizing system from wheat germ. Meth Enzymol 101: 635–644 (1983).
Bevan M: Binary Agrobacterium vectors for plant transformations. Nucl Acids Res 12: 8711–8721 (1984).
Behari R, Baker A: The carboxy-terminus of isocitrate lyase is not essential for import into glyoxysomes in an in vitro system. J Biol Chem, in press.
Beeching JR, Northcote DH: Nucleic acid (cDNA) and amino acid sequences of isocitrate lyase from castor bean. Plant Mol Biol 8: 471–475 (1987).
Beevers H: Microbodies in higher plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 30: 159–193 (1979).
Beevers H: The role of the glyoxylate cycle. In Stumpf PK (ed). The Biochemistry of Plants: A Comprehensive Treatise, vol. 4, pp. 117–130. Academic Press, New York (1980).
Bolivar F, Backman K: Plasmids of Escherichia coli as cloning vectors. Meth Enzymol 68: 245–267 (1979).
Boyer HW, Roulland-Dussoix D: A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol 41: 459–472 (1969).
Dahlin C, Cline K: Developmental regulation of the plastid protein import apparatus. Plant Cell 3: 1131–1140 (1991).
deBellis L, Picciarelli P, Pistelli L, Alpi A: Localization of glyoxylate cycle marker enzymes in peroxisomes of senescent leaves and green cotyledons. Planta 180: 435–439 (1990).
deBoer D, Cremer F, Teertstra R, Smits L, Hille J, Smeekens S, Weisbeek P: In vivo import of plastocyanin and a fusion protein into developmentally different plastids of transgenic plants. EMBO J 7: 2631–2635 (1989).
DeDuve C, Beaufay H, Jacques P, Rahman-Li Y, Sellinger OZ, Wattiaux R, DeConinck S: Intracellular localization of catalase and some oxidases in rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta 40: 186–187 (1960).
Draper J, Scott R, Armitage P, Walden R: Plant Genetic Transformation and Gene Expression: A Laboratory Manual. Blackwell, Oxford (1988).
Gerhardt B: Basic metabolic function of the higher plant peroxisome. Physiol Vég 24: 397–410 (1986).
Gibson TJ: Studies on the Epstein-Barr virus genome. Ph.D. thesis, Cambridge University (1984).
Gould SJ, Keller GA, Hosken N, Wilkinson J, Subramani S: A conserved tripetide sorts proteins to peroxisomes. J Cell Biol 108: 1657–1664 (1989).
Graham IA, Leaver CJ, Smith SM: Induction of malate synthase gene expression in senescent and detached organs of cucumber. Plant Cell 4: 349–357 (1992).
Harlow E, Lane D: Antibodies: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY (1988).
Heinemann P, Just WW: Peroxisomal protein import, in vivo evidence for novel translocation competent compartment. FEBS Lett 300: 179–182 (1992).
Hock B, Beevers H: Development and decline of the glyoxylate cycle enzymes in watermelon seedlings (Cirullus vulgaris). Effects of dactinomycin and cycloheximide. Z Pfl Physiol 55: 405–414 (1966).
Hoekema A, Hirsch PR, Hooykaas PJJ, Schilperoort RA: A binary plant vector strategy based on separation of vir- and T-region of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti-plasmid. Nature 303: 179–180 (1983).
Hofte H, Faye L, Dickinson C, Herman EM, Chrispeels MJ: The protein-body proteins phytohaemagglutinin and tonoplast intrinsic protein are targeted to vacuoles in leaves of transgenic plants. Planta 184: 431–437 (1991).
Hruban Z, RechciglJr M: Microbodies and related particles: morphology, biochemistry and physiology. Int Rev Cytol Suppl 1: 1–251 (1969).
Huang AHC, Beevers H: Microbody enzymes and carboxylases in sequential extracts from C4 and C3 plants. Plant Physiol 50: 242–248 (1972).
Huang AHC, Trelease RN, Moore TS: Plant Peroxisomes. Academic Press, New York (1983).
Kindl H: β oxidation of fatty acids by specific organelles. In: Stumpf PK (ed) The Biochemistry of plants, vol 9: Lipids: Structure and Function, pp. 31–52. Academic Press, New York (1987).
Kindl H, Lazarow PB (eds) Peroxisomes and Glyoxysomes. The New York Academy of Sciences (1982).
Kohn LD, Warren WA: The kinetic properties of spinach leaf glyoxylic acid reductase. J Mol Chem 245: 3831–3839 (1970).
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook J: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY (1989).
Maeshima M, Beevers H: Purification and properties of glyoxysomal lipase from castor bean. Plant Physiol 79: 489–493 (1985).
Martin C: Plant cell differentiation during seed germination. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK (1981).
Mori H, Nishimura M: Glyoxysomal malate synthase is specifically degraded in microbodies during greening of pumpkin cotyledons. FEBS Lett 244: 163–166 (1989).
Murashige T, Skoog F: A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15: 473–479 (1962).
Nabeshima S, Tanaka A, Fukui S: Effect of carbon sources on the level of glyoxylate cycle enzymes in alkaneutilizing yeast. Agric Biol Chem 41: 275–279 (1972).
Reynolds ES: The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol 17: 208–212 (1963).
Rodriguez D, Ginger S, Baker A, Northcote DH: Nucleotide sequence of a cDNA clone encoding malate synthase of castor bean (Ricinus communis) reveals homology to DAL7, a gene involved in allantoin degradation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Plant Mol Biol 15: 501–504 (1990).
Sautter C: Microbody transition in greening watermelon cotyledons. Double immunocytochemical labelling of isocitrate lyase and hydroxypyruvate reductase. Planta 167: 491–503 (1986).
Schubert KR: Products of biological nitrogen fixation in higher plants: synthesis, transport and metabolism. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 37: 539–574 (1986).
Swinkels BW, Gould SJ, Bodnar AG, Rachubinski RA, Subramani S: A novel, cleavable peroxisomal targeting signal at the amino-terminus of the rat 3-keto-acyl-CoA thiolase. EMBO J 10: 3255–3262 (1991).
Titus DE, Becker WM: Investigation of the glyoxysome-peroxisome transition in germinating cucumber cotyledons using double-label immunoelectron microscopy. J Cell Biol 101: 1288–1299 (1985).
Tolbert NE: Microbodies-peroxisomes and glyoxysomes. In: Tolbert NE (ed) The Biochemistry of Plants, vol 1, pp. 359–388. Academic Press, New York (1980).
Tolbert NE: Photorespiration. In Davies DD (ed), The Biochemistry of plants, vol 2, pp. 487–523 (1980).
Tolbert NE: Metabolic pathways in peroxisomes and glyoxysomes. Annu Rev Biochem 50: 133–157 (1981).
Tolbert NE, Essener E: Micobodies: Peroxisomes and glyoxysomes. J Cell Biol 91: 271–283 (1981).
VanDijken JP, Veehuis M, Vermeulen CA, Harder W: Cytochemical localization of catalase activity in methanol-grown Hansenula polymorpha. Arch Microbiol 105: 261–267 (1975).
Vigil EL: Plant microbodies. J Hist Cytochem 21: 958–962 (1973).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Onyeocha, I., Behari, R., Hill, D. et al. Targeting of castor bean glyoxysomal isocitrate lyase to tobacco leaf peroxisomes. Plant Mol Biol 22, 385–396 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00015970
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00015970