Abstract
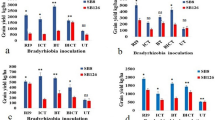
Soybean [Glycine max (L.) Merr.] forms a symbiosis with serogroups of Bradyrhizobium japonicum that differ in their dinitrogen fixing abilities. The objectives of this study were to identify soybean genotypes that would restrict nodulation by relatively inefficient serogroups indigenous to a large portion of the southeastern USA, and then characterize the nodulation responses of selected genotypes with specific bradyrhizobial strains under controlled conditions. From field screening trials followed by controlled single and competitive inoculations of serogroups USDA 31, 76 and 110, twelve soybean genotypes out of 382 tested were identified with varying levels of exclusion abilities. Soybean nodule occupancies and nodulation characteristics were influenced by plant genotype, environment (i.e. field or greenhouse), bradyrhizobial serogroup, and location of nodules (i.e. tap or lateral root). The cultivar Centennial sustains high seed yields even though it nodulates to a high degree with the inefficient serogroup USDA 31. In contrast, data from the released cultivars Braxton, Centennial and Coker 368 indicate that they may have been selected to exclude the inefficient serogroup USDA 76 from their tap root nodules, possibly contributing to high seed yield.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Caldwell B E and Hartwig E E 1970 Serological distribution of soybean root nodule bacteria in soils of southeastern USA. Agron. J. 62, 621–622.
Caldwell B E and Vest G 1968 Nodulation interactions between soybean genotypes and serogroups of Rhizobium japonicum. Crop Sci. 8, 680–682.
Caldwell B E and Vest G 1970 Effects of Rhizobium japonicum strains on soybean yields. Crop Sci. 10, 19–21.
Chew V 1977 Comparisons among treatment means in an analysis of variance. U.S. Department of Agriculture, ARS/H/6, 64 p.
Coale F J, Meisinger J J and Wiebold W J 1985 Effects of plant breeding and selection on yields and nitrogen fixation in soybeans under two soil nitrogen regimes. Plant and Soil 84, 357–367.
Cregan P B and Keyser H H 1986 Host restriction of nodulation by Bradyrhizobium japonicum strain USDA 123 in soybean. Crop Sci. 26, 911–916.
Date R A 1970 Microbiological problems in the inoculation and nodulation of legumes. Plant and Soil 32, 703–725.
Devine T E 1985 Host range and compatibility of soybean with rhizobial microsymbionts, In World Soybean Res. Conf. III: Proc. Ed. R Shibles. pp 484–492. Westview Press, Boulder, CO, USA.
Devine T E and Breithaupt B H 1981 Frequencies of nodulation response alleles, Rj2 and Rj4 in soybean plant introductions and breeding lines. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Technical Bulletin Nol. 1628, 42 p.
Franco A A and Vincent J M 1976 Competition amongst rhizobial strains for the colonization and nodulation of two tropical legumes. Plant and Soil 45, 27–48.
Fuhrmann J and WollumII A G 1985 Simplified enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for routine identification of Rhizobium japonicum antigens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 49, 1010–1013.
Fuhrmann J and Wollum II A G 1988 Nodulation competition among Bradyrhizobium japonicum strains as influenced by rhizosphere bacteria and iron availability. Biol. Ferti. Soils 7. (Accepted.)
Halverson L J and Stacey G 1984 Host recognition in the Rhizobium-soybean symbiosis. Plant Physiol. 74, 84–89.
Howle P K W, Shipe E R and Skipper H D 1987 Soybean specificity for Bradyrhizobium japonicum strain 110. Agron. J. 79, 595–598.
Hunt P G, Matheny T A and WollumII A G 1985 Rhizobium japonicum nodular occupancy, nitrogen accumulation, and yield for determinate soybean under conservation and conventional tillage. Agron. J. 77, 579–584.
Israel D W 1981 Cultivar and Rhizobium strain effects on nitrogen fixation and remobilization by soybeans. Agron. J. 73, 509–516.
Keyser H H and Cregan P B 1987 Nodulation and competition for nodulation of selected soybean genotypes among Bradyrhizobium japonicum serogroup 123 isolates. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 53, 2631–2635.
Kosslak R M, Bohlool B B, Dowdle S and Sadowsky M J 1983 Competition of Rhizobium japonicum strains in early stages of soybean nodulation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 46, 870–873.
Kosslak R M and Bohlool B B 1985 Influence of environmental factors on interstrain competition in Rhizobium japonicum. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 49, 1128–1133.
Mahler R L and WollumII A G 1981 The influence of irrigation and Rhizobium japonicum strains on yields of soybeans grown in a Lakeland sand. Agron. J. 73, 647–651.
Means U M, Johnson H W and Date R A 1964 Quick serological method of classifying strains of Rhizobium japonicum in nodules. J. Bacteriol. 87, 547–553.
Peterson M A and Barnes D K 1981 Inheritance of ineffective nodulation and non-nodulation in alfalfa. Crop Sci. 21, 611–616.
Sadowsky M J, Tully R E, Cregan P B and Keyser H H 1987 Genetic diversity in Bradyrhizobium japonicum serogroup 123 and its relation to genotype-specific nodulation of soybean. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 53, 2624–2630.
Singleton P W and Stockinger K R 1983 Compensation against ineffective nodulation in soybean. Crop Sci. 23, 69–72.
Snedecor G W 1946 Statistical methods. Collegiate Press, Inc., Ames, IA, USA.
Weiser G C, Grafton K F and Berryhill D L 1985 Nodulation of dry beans by commerical and indigenous strains of Rhizobium phaseoli. Agron. J. 77, 856–859.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weiser, G.C., Skipper, H.D. & Wollum, A.G. Exclusion of inefficient Bradyrhizobium japonicum serogroups by soybean genotypes. Plant Soil 121, 99–105 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00013102
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00013102