Abstract
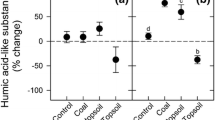
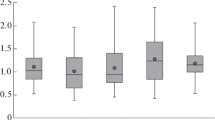
Coal-derived sodium humate was found to stimulate primary root growth of seedlings of cantaloupe (Cucumis melo L.) at 1000 mg L−1, lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) and onion (Allium cepa L.) at 500 and 1000 mg L−1, as well as hypocotyl growth of cantaloupe at 1000 mg L−1. Growth enhancement was not due to release of nutrient elements by the product, and, in the case of lettuce and onion, was not due to increased availability or uptake of mineral elements. Growth stimulation of cantaloupe, however, was dependent on the provision of nutrient solution. Growth stimulation of onion roots under axenic conditions indicated an effect of the humate per se rather than a response mediated via microbial breakdown products.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chizhevsky M G and Dikusar M M 1955 [The role of humus and micro-organisms in the root nutrition of the higher plants in water and sand cultures.] Izvestiya timiryazevskoi sel skokhozyaistvennoi akademii 2, 173–192.
Dekker J, Cronje I J, Louwrens H B and Swart H 1990 Non-catalytic oxidation of water-slurried coal with oxygen: A promising new route to oxihumic and oxifulvic acids. Proceedings of the Seventh Annual International Coal Conference, University of Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh, PA. pp 703–708.
Fialova S 1969 Influence of sodium humate and nutritive conditions on the content of nucleic acids, particularly on the ribosomal ribonucleic acid in wheat roots. Biol. Plant. 11, 8–22.
Hewitt E J 1966 Sand and Water Culture Methods used in the Study of Plant Nutrition. CMI Bureau, Bucks.
Lee Y S and Bartlett R J 1976 Stimulation of plant growth by humic substances. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 40, 876–879.
Malik K A and Azam F 1985 Effect of humic acid on wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) seedling growth. Environ. Exp. Bot. 25, 245–252.
Mortensen J L 1963 Complexing of metals by soil organic matter. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 27, 179–186.
Mylonas V A and McCants C B 1980 Effects of humic and fulvic acids on growth of tobacco I. Root initiation and elongation. Plant and Soil 54, 485–490.
Rauthan B S and Schnitzer M 1981 Effects of a soil fulvic acid on the growth and nutrient content of cucumber (Cucumis sativus) plants. Plant and Soil 63, 491–495.
Sladky Z 1959 The effect of extracted humus substances on growth of tomato plants. Biol. Plant. 1, 142–150.
Sladky Z and Tichy V 1959 Application of humus substances to overground organs of plants. Biol. Plant. 1, 9–15.
Sweet H C and Bolton W E 1979 The surface decontamination of seeds to produce axenic seedlings. Am. J. Bot. 66, 692–698.
Tan K H and Nopamornbodi V 1979 Effect of different levels of humic acids on nutrient content and growth of corn (Zea mays L.). Plant and Soil 51, 283–287.
Varshney T N and Gaur A C 1974 Effect of spraying sodium humate and hydroquinone on Glycine max var. Bragg and Solanum lycopersicum var. Heiz 1370. Curr. Sci. 43, 95–96.
Vaughan D 1974 A possible mechanism for humic acid action on cell elongation in root segments of Pisum sativum under aseptic conditions. Soil Biol. Biochem. 6, 241–247.
Vaughan D and Linehan D J 1976 The growth of wheat plants in humic acid solutions under axenic conditions. Plant and Soil 44, 445–449.
Vaughan D and Malcolm R E 1985 Influence of humic substances on growth and physiological processes. In Soil Organic Matter and Biological Activity. Eds. D Vaughan and R E Malcolm. pp 37–76. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands.
Vaughan D, Malcolm R E and Ord B G 1985 Influence of humic substances on biochemical processes in plants. In Soil Organic Matter and Biological Activity. Eds. D Vaughan and R E Malcolm. pp 77–108. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van de Venter, H.A., Furter, M., Dekker, J. et al. Stimulation of seedling root growth by coal-derived sodium humate. Plant Soil 138, 17–21 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011803
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011803