Summary
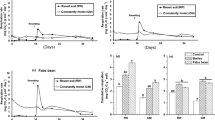
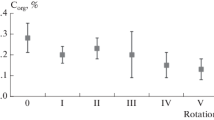
Laboratory studies were conducted to compare the effect of the nature of organic matter and aerated and saturated conditions in the reclamation of sodic soils. Removal of exchangeable Na from the soil increased under saturated conditions. These effects were more pronounced where Sesbania aculeata was added as a source of organic matter as compared with barley straw which has a wider C:N ratio than the former. The results indicate that the production of CO2 and organic acids under saturated conditions may be very helpful in removing exchangeable sodium from both calcareous and non-calcareous sodic soils. Incubation under saturated conditions brought about greater improvement in the physical status of the silty clay soil than in the fine sandy loam. re]19730220
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coutinet, S., Methodes d'analysis utilizables pour les soles, calcaires et gypseux L'Agron. Trop. 12, 1242–53 (1965).
Goertzen, J. O., and Bower, C. A., Carbondioxide from plant roots as a factor in the replacement of adsorbed sodium in calcareous soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 22, 36–37 (1958).
Jackson, M. L., Soil Chemical analysis-advanced course, University of Wisconsin, Madison, Wisc. U.S.A. (1956).
Janitzky, P., and Whittig, L. D., Natural leaching processes in some salt-affected soils of California. Symp. Sodic Soils Proc. Budapest, Hungary, p. 251–260 (1965).
McNeal, B. L., Pearson, G. S., Hatcher, J. T., and Bower, C. A., Effect of rice culture on the reclamation of sodic soils. Agron. J. 58, 238–40 (1966).
Overstreet, R., Martin, J. C., Schulz, R. K., and McCutcheon, O. D., Reclamation of an alkali soil of the Hacienda series. Hilgardia 24, 53–58 (1955).
Richards, L. A., Modulus of rupture as an index of crusting of soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 17, 321–23 (1953).
Whittig L. D., and Janitzky P., Mechanisms of formation of sodium carbonate in soils. J. Soil Sci. 14, 322–333.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, N.T. Physico-chemical changes in sodic soils incubated at saturation. Plant Soil 40, 303–311 (1974). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011512
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011512