Abstract
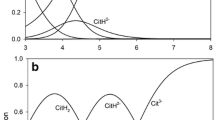
CaSO3 is a by-product formed by several of the processes used for scrubbing SO2 from flue gas produced by coal-burning power generators. Using CaSO3 to improve the calcium status of acid soils would be a beneficial alternative to disposal in landfills. CaSO3 has biocidal properties and is used as a disinfectant and food and drink preservative. It is important to evaluate under what conditions application to soils would not harm plant growth. Laboratory experiments confirmed that two transformations of CaSO3 occurred in soil systems: (1) decomposition to produce SO2 gas, and (2) oxidation to calcium sulfate. Conversion to SO2 occurred in solution and soil at low pH, and acid soils treated with CaSO3 were initially toxic to seedling root growth. The degree of toxicity was time-dependent, with reduction in toxicity occurring as CaSO3 oxidized to calcium sulfate. Soil reaction also influenced toxicity, and at soil pH levels above 6, little seedling toxicity was evident.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alpkem Corp. 1991 Sulfate, Method #A303-S031–04. Alpkem Corp. Clackamas, OR 97015.
Clark R B, Ritchey K D and Baligar V C 1993 Dry matter yields of maize grown with coal combustion by-products. Proceedings Tenth International Ash Use Symposium Volume 1: High-Volume Uses/Concrete Application. EPRI TR-101774. pp 15–1 to 15–11.
Garsed S G and Rutter A J 1982 Relative performance of conifer populations in various tests for sensitivity to SO2, and the implications for selecting trees for planting in polluted areas. New Phytol. 92, 349–367.
Inglis F and Hill D J 1974 The effect of sulphite and fluoride on carbon dioxide uptake by mosses in the light. New Phytol. 73, 1207–1213.
Olszyk D M, Bytnerowicz A, Kats G, Dawson P J, Wolf J and Thompson C R 1986 Effects of sulfur dioxide and ambient ozone on winter wheat and lettuce. J. Environ. Qual., 15, 363–369.
Pasiuk-Bronikowska W, Bronikowski T and Uiejczyk M 1992 Mechanism and kinetics of autoxidation of calcium sulfite slurries. Environ. Sci. Technol. 26, 1976–1981.
Peiser G and Shang Fa Yang 1985 Biochemical and physiological effects of SO2 on nonphotosynthetic processes in plants. In Sulfur Dioxide and Vegetation. Eds. W E Winner, H A Mooney and R A Goldstein. Stanford University Press, Stanford, CA.
Shainberg I, Sumner M E, Miller W P, Farina M P W, Pavan M A and Fey M V 1989 Use of gypsum on soils: a review. Adv. Soil Sci. 9, 1–111.
Thomas G W 1982 Exchangeable cations. In Methods of Soil Analysis. Part 2, 2nd Ed. Agronomy 9. Eds. A L Page, R H Miller and D R Keeney. pp 159–165. Am. Soc. Agron., Madison, WI.
US Environmental Protection Agency 1984 Methods for chemical analysis of water and wastes, EPA-600/4–79–020. Environmental Monitoring and Support Laboratory, Office of Support and Development, US EPA, Cincinnati, OH 45268.
Vogel A I 1961 A Textbook of Quantitative Inorganic Analysis Including Elementary Instrumental Analysis. 3rd ed. John Wiley and Sons, Inc., New York.
Weast R C (Ed) 1978 CRC Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. pp B-105. CRC Press, Inc., West Palm Beach, FL.
Wedzicha B L 1984 Chemistry of Sulfur Dioxide in Foods. Elsevier Applied Science Publications, Amsterdam. 381p.
Windholz M (Ed.) 1976 The Merck Index, 9th edition. Merck and Co., Inc. Rahway, NJ. p216.
Yuan T L 1959 Determination of exchangeable hydrogen in soils by a titration method. Soil Sci. 88, 164–167.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ritchey, K.D., Kinraide, T.B. & Wendell, R.R. Interactions of calcium sulfite with soils and plants. Plant Soil 173, 329–335 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011471
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011471