Abstract
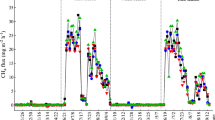
The relationship between the amount of CH4 emission to the atmosphere from submerged paddy soils with rice plants and the application level (0–8 g kg-1) of rice straw (RS) in soil was investigated in a pot experiment. Amounts of CH4 emitted from pots with respective RS levels differed between a clayey yellow soil and a silty gray lowland soil. However, the increase in cumulative amounts of CH4 emission with the increase in the application level of RS was similar in pattern between the two soils, and the increase (Y) was formulated with a logistic curve: x, application level of RS; k, a coefficient for relative CH4 emission.
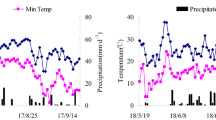
Since the seasonal variations in coefficients a, b, and c in the logistic equation were also formulated as the function of the sum of effective temperature (E, Σ(T−15); T, daily average temperature), the increase in cumulative amounts of CH4 emission from any paddy soil by any level of RS application was known to be estimated by the following equation:
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asami T and Kumada K 1959 A new method for determining free iron in paddy soils. Soil Plant Food 5, 141–146.
Cicerone R J, Delwiche C C, Tyler S C and Zimmerman P R 1992 Methane emissions from California rice paddies with varied treatments. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 6, 233–248.
Delwiche C C and Cicerone R J 1993 Factors affecting methane production under rice. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 7, 143–155.
Jermsawatdipong P, Murase J, Prabuddham P, Hasathon Y, Khomthong N, Naklang K, Watanabe A, Haraguchi H and Kimura M 1994 Methane emission from plots with differences in fertilizer application in Thai paddy fields. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 40 63–71.
Kimura M, Miura Y, Watanabe A, Katoh T and Haraguchi H 1991 Methane emission from paddy field (Part 1). Effect of fertilization, growth stage and midsummer drainage: Pot experiment. Environ. Sci. 4, 265–271.
Lindau C W and Bollich P K 1993 Methane emissions from Louisiana first and ratoon crop rice. Soil Sci. 156, 42–47.
Murase J, Kimura M and Kuwatsuka S 1993 Methane production and its fate in paddy fields. III. Effects of percolation on methane flux distribution to the atmosphere and the subsoil. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 39, 63–70.
Sass R L, Fisher F M, Harcombe P A and Turner F T 1991 Mitigation of methane emissions from rice fields: Possible adverse effects of incorporated rice straw. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 5, 275–287.
Schütz H, Holzapfel-Pschorn A, Conrad R, Rennenberg H and Seiler W 1989 A 3-year continuous record on the influence of daytime, season, and fertilizer treatment on methane emission rates from an Italian rice paddy. J. Geophys. Res. 94, 16405–16416.
Sherman G D, Mc Hargue J S and Hodgkiss W S 1942 Determination of active manganese in soil. Soil Sci. 54, 253–257.
Watanabe A, Katoh K and Kimura M 1993a Effect of rice straw application on CH4 emission from paddy fields. I. Effect of weathering of rice straw in the field during off-crop season. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 39, 701–706.
Watanabe A, Katoh K and Kimura M 1993b Effect of rice straw application on CH4 emission from paddy fields. II. Contribution of organic constituents in rice straw. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 39, 707–712.
Watanabe A, Katoh K and Kimura M 1994 Effect of rice straw application of CH4 emission from paddy fields. III. Effect of incorporation site of rice straw on CH4 emission rates and their variation among shoots of a rice plant. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 40, 497–504.
Yagi K and Minami K 1990 Effect of organic matter application on methane emission from some Japanese paddy fields. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 36, 599–610.
Yoshino T and Dei Y 1977 Prediction of nitrogen release in paddy soils by means of the concept effective temperature. J. Cent. Agric. Exp. Stn. 25, 1–62 (In Japanese).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Watanabe, A., Satoh, Y. & Kimura, M. Estimation of the increase in CH4 emission from paddy soils by rice straw application. Plant Soil 173, 225–231 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011459
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011459