Summary
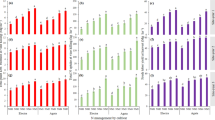
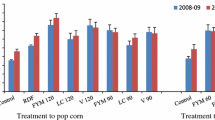
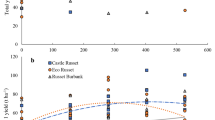
‘Recently matured’ leaf samples were collected, at 45, 60 and 75 days after planting, from potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) plants of cultivar ‘Kufri sindhuri’ grown with varying levels of nitrogen (0, 60, 120, 180 and 240 kg N/ha) and phosphorus (0, 60, 120 and 180 kg P2O5/ha) on loam soil at Pantnagar. They were separated into petiole, midrib and leaf-lets and analysed for NO3-N content. Petiole samples were also analysed for PO4-P content. Nitrogen application increased the NO3-N content of all the leaf components. P application increased the PO4-P content in petiole. NO3-N content and PO4-P content in leaf tissues were positively correlated with final tuber yield. The association of NO3-N content of petiole with the final tuber yield was very consistant. Hence this proved to be the best indicator tissue for reflecting the nitrogen status of the plant, particularly at 45 days after planting. NO3-N content of midrib, at this stage, was also a good indication of nitrogen nutrition status of the plant. PO4-P content of petiole at 45 days after planting was a good indication of nutritional status of plant with respect to phosphorus. The critical concentration of NO3-N in petioles of 45 days old plants was in the range of 9100–9600 ppm. The corresponding range for midrib was 3000 to 3900 ppm. The critical concentration of PO4-P for petioles of 45 days old plants was 2250 ppm.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fullmer F. S., Leaf and soil analysis survey in two California potato growing areas. Proc. Am. Soc. Hort. Sci. 70, 385 (1957).
Gupta A. and SaxenaM. C., Response of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) to nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization. Indian J. Agron. 20, 265 (1975).
Hylton Jr.L. O., WilliamsD. E., UlrichA. and CorneliusD. R., Critical nitrate levels for growth of Italian Rye grass. Crop. Sci. 4, 16 (1964).
Johnson C. M. and UlrichA., Analytical methods for use in plant analysis. California Agr. Expt. Sta. Bull. 766, 25 (1959).
Tyler K. B., LorenzO. A. and FullmerF. S., Plant and soil analysis as guides in potato nutrition. California Agr. Expt. Sta. Bull. 781, 1 (1961).
Ulrich A., HillsF. J., RirieD., GeorgeA. G. and MorseM. D., Plant analysis a guide for sugarbeet fertilization. California Agr. Expt. Sta. Bull. 766, 1 (1959).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Publication No 796 under journal series of the G.B. Pant University of Agriculture and Technology, Experiment Station, Pantnagar.
Junior Agronomist, Indian Institute of Horticultural Research, Bangalore-6, India.
Junior Agronomist, Indian Institute of Horticultural Research, Bangalore-6, India.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, A., Saxena, M.C. Evaluation of leaf analysis as a guide to nitrogen and phosphorus fertilization of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Plant Soil 44, 597–605 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011379
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011379