Summary
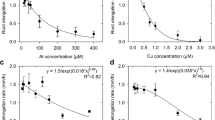
Root uptake rate and root uptake coefficient for Cl ions were determined in corn at two transpiration rates and three solution concentrations. Transpiration rate had pronounced effect on root uptake rate and root uptake coefficient especially at low solution concentration. Root uptake rate increased as the concentration of Cl ions in the solution increased. The root uptake coefficient decreased as Cl concentration in the solution increased from 20 meq/l to 40 meq/l but it did not change when the concentration was raised to 80 meq/l.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barber S. A., A diffusion and massflow concept of soil nutrients availability Soil Sci. 93, 39–49 (1962).
BrewsterJ. L. and TinkerP. B. H., Nutrient flow rates into roots. Soils and Fert. 35, 355–359 (1972).
BouldinD. R., Mathematical description of diffusion process in soil plant system. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 25, 476–480 (1961).
Geering, H. R., A mathematical description of the transport of nutrients from soil to the plant root by diffusion and massflow. M. S. Thesis, Cornell Univ. (1967).
ChapmanH. D. and PrattP. F., Methods of analysis for soils. Plants and Waters. University of California, Division of Agricultural Science, California, U.S.A. (1961).
OlsenS. R. and KemperW. D., Movement of nutrient to plant roots. Adv. Agron. 20, 91–151 (1968).
PassiouraJ. B., A mathematical model for the uptake of ions from the soil solution. Plant and Soil 18, 225–238 (1963).
RussellR. S. and ShorrocksV. M., The relationship between transpiration and the absorption of inorganic ions by intact plants. J. Exptl. Botany 10, 301–316 (1959).
SinhaB. K. and SinghN. T., Effect of transpiration rate on salt accumulation around corn roots in a saline soil. Agron. J. 66, 557–560 (1974).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Soil Physicist, Department of Soil & Water Engineering and Professor of Soils, Department of Soils, Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana, Punjab, India, respectively.
Soil Physicist, Department of Soil & Water Engineering and Professor of Soils, Department of Soils, Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana, Punjab, India, respectively.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sinha, B.K., Singh, N.T. Root uptake coefficient for Cl ions in corn as affected by transpiration rates and solution concentration. Plant Soil 44, 521–525 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011372
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011372