Abstract
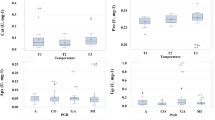
Variations of predawn and midday leaf water potential and relative growth rates were studied in mature carob trees (Ceratonia siliqua L. cv “Mulata”) submitted to a fertigation experiment. Three levels of irrigation were tested: 0%, 50% and 100%, based on daily standard evaporation values. For each irrigation level two nitrogen amounts were applied −21 and 63 kg N ha-1 year-1 as ammonium nitrate. The experiment was run between July 91 and August 1993. Measurements of leaf water potential and absolute branch length increments were made at monthly intervals, during the entire experimental period or during seasonal growth, respectively. Leaf water potential was related to soil volumetric water content, maximum and minimum air temperature and daily evaporation. Predawn leaf water potentials were always higher than −1.1 MPa. Midday leaf water potential values presented very large seasonal variations and very low values independent of treatments. The low leaf water potentials observed for the fertigated trees during summer, suggest that this parameter may be related not only to the evaporative demand but also to growth investment. The amount of fertigation was positively correlated with vegetative growth increment and fruit production. Practical implications for irrigation schedules of leaf water potential patterns together with drought adaptation mechanisms of carob tree are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acherar M and Rambal S 1992 Comparative water relations of four Mediterranean oak species. Vegetatio 99–100, 177–184.
Correia O and Catarino FM 1994 Seasonal changes in soil-to-leaf resistance in Cistus sp. and Pistacia lentiscus. Acta Oecol. 15 (3) 289–300.
Correia P and Martins-Loução M A 1990 Effect of different water quantities on the vegetative growth of young carob-trees (Ceratonia siliqua L.). Acta Hortic. 6, 412–417.
Correia P and Martins-Loução M A 1992 Effect of N-nutrition and irrigation water on carob-tree (Ceratonia siliqua L.). Growth responses. Suelo y Planta 2, 773–785.
Correia P and Martins-Loução M A 1993a Effect of N-nutrition and irrigation on fruit production of carob (Ceratonia siliqua L.). Physiol. Plant. 89, 669–672.
Correia P and Martins-Loução M A 1993b Water-use efficiency in carob (Ceratonia siliqua L.). A fertigation experiment using mature trees. 1 st Simposium Hispano-Português sobre Relações Hidricas en las Plantas. pp 131–134.
Diamantoglou S and Mitrakos K 1981 Leaf longevity in Mediterranean evergreen sclerophylls. In Components of Productivity of Mediterranean Climate Regions. Basic and Applied Aspects. Eds. N S Margaris and H A Mooney. pp 17–19. Junk Publishers, ISBN 90–6193–944–5.
Doorenbos J 1976 Agro-meteorological field stations. In Irrigation and Drainage Paper, 27. FAO Rome.
Esbenshade H and Wilson G 1986 Growing carobs in Australia. Capitol Press Pty Ltd., Australia. 136 p.
Fernandez J F, Moreno F, Cabrera F, Arrue J L and Martin-Aranda J 1992 Drip irrigation, soil characteristics and the root distribution and root activity of olive trees. Plant and Soil 133, 239–252.
Gower S T, Vogt K A and Grier C C 1992 Carbon dynamics of rocky mountain Douglas-firt influence of water and nutrient availability. Ecol Monogr. 62, 43–65.
Herwitz S R, Yair A and Shachak M 1988 Water use patterns of introduced carob trees (Ceratonia siliqua L.) on rocky hillslopes in the Negev desert. J. Arid Environ. 14, 83–92.
Leidi O E and Lips S H 1990 Effect of NaCl ion salinity on photosynthesis, 14C translocation and yield of wheat plants irrigated with ammonium or nitrate solutions. Irrig. Sci. 11, 155–161.
Lloveras J and Marti J T 1992 Response of carob tree to nitrogen fertilization. HortSci. 27, 849.
Lo Gullo M A and Salleo S 1988 Different strategies of drought resistance in three Mediterranean sclerophyllous trees growing in the same environmental conditions. New Phytol. 108, 267–276.
Marti J T and Caravaca I B 1990 El Algarrobo. Ediciones Mundi-Prensa, Madrid.
Martins-Loução M A and Brito de Carvalho J H 1989 A cultura da alfarrobeira. Direcção Geral Planeamento e Agricultura. Série de Divulgação no 1.
Merwin M L 1980 The culture of carob (C. siliqua L.) for food, fodder and fuel in semi-arid environments. In Tree Crops for Energy Coproduction on Farms. US Department of Energy. Solar Energy Res. Inst., USA, pp 79–95.
Nel A A and Berliner P R 1990 Quantifying leaf water potential for scheduling irrigation of wheat under specific soil-climate conditions. S. Afr. Tydskr. Plant Grond. 7, 68–71.
Nunes M A, Catarino F M and Pinto E 1989 Seasonal drought acclimation strategies in Ceratonia siliqua leaves. Physiol. Plant. 77, 150–156.
Nunes M A, Ramalho J D C and Rijo P S 1992 Seasonal changes in some photosynthetic properties of Ceratonia siliqua (carob-tree) leaves under natural conditions. Physiol. Plant. 86, 381–387.
Oliveira G, Correia O A, Martins-Loução M A and Catarino F M 1992 Water relations of cork-oak (Quercus suber L.) under natural conditions. Vegetatio 99–100, 199–208.
Peñuelas J, Savé R, Marfá O and Serrano L 1992 Remotely measured canopy temperature of greenhouse strawberries as indicator of water status and yield under mild and very mild water stress conditions. Agric. For. Meteorol. 58, 63–77.
Rambal S 1992 Quercus ilex facing water stress: a functional equilibrium hypothesis. Vegetatio 99–100, 147–153.
Rambal S 1993 The differential role of mechanisms for drought resistance in a Mediterranean evergreen shrub: a simulation approach. Plant Cell Environ. 16 (1), 35–44.
Rhizopoulou S and Davies W J 1991 Influence of soil drying on root development, water relations and leaf growth of Ceratonia siliqua L. Oecologia 88, 41–47.
Salleo S and Lo Gullo M A 1989 Different aspects of cavitation resistance in Ceratonia siliqua, a drought-avoiding Mediterranean tree. Ann. Bot. 64, 325–336.
Torrecillas A, Ruiz-Sanchez M C, Leon A and DelAmor F 1989 The response of young almond trees to different drip-irrigated conditions. Development and Yield. J. Hort. Sci. 64, 1–7.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Correia, P.J., Martins-Loucão, M.A. Seasonal variations of leaf water potential and growth in fertigated carob-trees (Ceratonia siliqua L.). Plant Soil 172, 199–206 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011322
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011322