Abstract
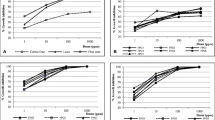
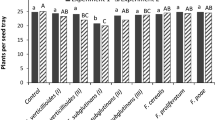
To test the effect of seed treatment with fungicides on the development of mycorrhizal fungi, bean seeds were treated with fungicide dry or vehicled in the organic solvents, ethanol or dichloromethane and then planted in soil inoculated with the mycorrhizal fungus Glomus macrocarpum and/or the plant pathogenic fungus Fusarium solani. Measurements were made at 4 day intervals, to assess the presence of mycorrhizae or disease in the roots as well as top dry weight, root fresh weight and root length. Fungicidal seed treatment did not affect the initial occurrence of mycorrhizae, number of spores of G. macrocarpum in the soil or root length. Fresh weights of roots and dry weights of tops were greater in the presence of the mycorrhizal fungus. The onslaught of symptoms by F. solani was significantly retarded by treatment with fungicides plus mycorrhizal fungi or fungicides plus organic solvents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey J E and Safir G R 1978 Effect of benomyl on soybean endomycorrhizae. Phytopathology 68, 1810–1812.
Burke D W and Miller D E 1983 Control of Fusarium root rot with resistant beans and cultural management. Plant Disease 67, 1312–1317.
Daniels B A and Skipper H D 1982 Methods for the recovery and quantitative estimation of propagules from soil. In Methods and Principles of Mycorrhizal Research. Ed. N CSchenck pp 29–35. APS, St. Paul, MN.
Dhingra O D and Muchovej J J 1980 Dichloromethane, trichloromethane and carbontetrachloride as solvents for bean seed treatment with systemic fungicides. Seed Sci. Technol. 8, 77–83.
Dhingra O D and Muchovej J J 1982 Organic solvent seed treater. Seed Sci. Technol. 10, 105–108.
Fitter A H and Nichols R 1988 The use of benomyl to control infection by vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi. New Phytol. 110, 201–206.
Harley J L 1989 The significance of mycorrhiza. Mycol. Res. 92, 129–139.
Hayman D S 1983 The physiology of vesicular-arbuscular endomycorrhizal symbiosis. Can. J. Bot. 61, 944–963.
Mosse B, Stribley D P and LeTacon F 1981 Ecology of mycorrhizae and mycorrhizal fungi. Adv. Microb. Ecol. 5, 137–210.
Muchovej J J 1987 Automotive ethanol for treatment of soybean seeds with fungicides. Seed Sci. Technol. 15, 265–269.
Muchovej J J and Dhingra O D 1980 Acetone, benzene and ethanol for treating Phaseolus seed in the dry state with systemic fungicides. Seed Sci. Technol. 8, 351–356.
Muchovej J J, Muchovej R M C and Gonçalves E J 1991 Effect of kind and method of fungicidal treatment of bean seed on infections by the VA-mycorrhizal fungus Glomus macrocarpum and by the pathogenic fungus Fusarium solani. II. Temporal-spatial relationships. Plant and Soil 132, 47–51.
Nesheim O N and Linn M B 1959 Deleterious effects of certain fungitoxicants on the formation of mycorrhizae on corn by Endogone fasciculata and on corn root development. Phytopathology 59, 297–300.
Phillips J M and Hayman D S 1970 Improved procedures for clearing roots and staining parasitic infection. Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 55, 158–161.
Rhodes L H and Larsen P O 1981 Effects of fungicides on mycorrhizal development of creeping bentgrass. Plant Disease 65, 145–147.
Sutton J C and Sheppard B R 1976 Aggregation of sand-dune soil by endomycorrhizal fungi. Can. J. Bot. 54, 326–333.
Trappe J M, Molina R and Castellano M 1984 Reactions of mycorrhizal fungi and mycorrhiza formation to pesticides. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 22, 331–359.
Tuite J 1969 Plant Pathological Methods, Fungi and Bacteria, Burgess, MN.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gonçalves, E.J., Muchovej, J.J. & Muchovej, R.M.C. Effect of kind and method of fungicidal treatment of bean seed on infections by the VA-mycorrhizal fungus Glomus macrocarpum and by the pathogenic fungus Fusarium solani . Plant Soil 132, 41–46 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011010
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011010